Opisthokont facts for kids
Quick facts for kids OpisthokontTemporal range: 1010–0Ma
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
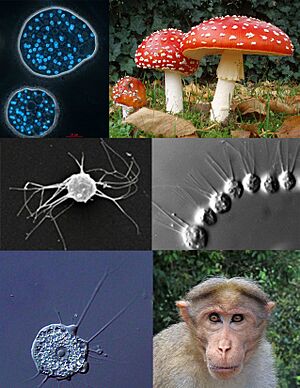
| Clockwise, from top left: Abeoforma whisleri (Mesomycetozoea); Amanita muscaria (Fungi); Desmarella moniliformis (Choanoflagellatea); bonnet macaque (Metazoa); Nuclearia thermophila (Nucleariida); Ministeria vibrans (Filasterea) | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| (unranked): | Unikonta |
| (unranked): | Obazoa |
| (unranked): | Opisthokonta Copeland 1956, emend. Cavalier-Smith 1987, emend. Adl et al., 2005 |
| Subgroups | |
|
|
The opisthokonts are a huge group of eukaryotes. This means they are living things whose cells have a nucleus. This amazing group includes both the animal and fungus kingdoms. So, if you're an animal, you're an opisthokont!
Think of all life on Earth as a giant family tree. Opisthokonta is one of the main branches on this tree. It connects millions of different species, from tiny yeast to giant whales. Scientists are always learning new things about this diverse group. They discover new species and understand how all these life forms are related. It truly shows how much amazing life there is on our planet!
Contents
What Makes an Opisthokont Special?
The name "Opisthokonta" sounds a bit tricky, but it has a cool meaning. It comes from Greek words: "opisthos" means "behind," and "kontos" means "flagellum." A flagellum is like a tiny tail that some single-celled organisms use to swim.
So, what's special about it for opisthokonts? In most opisthokont cells that have a flagellum, this tiny tail is found at the back of the cell. This "tail at the back" is a key feature that helps scientists group these organisms together. It's like a secret family code that connects them all!
Animals and Fungi: Close Relatives
Opisthokonta is mainly split into two huge branches: Animalia (animals) and Fungi (fungi). You might think these two groups are very different. But they are actually closely related! They share a common ancestor that had that special "tail at the back." Let's explore each branch.
The Animal Kingdom (Animalia)
This branch is full of all kinds of animals. They range from tiny creatures you can barely see to enormous whales! Here are some of the main groups:
- Sponges: These are simple animals that live in water. They filter food from the water around them. Sponges have been around for a very long time. We have fossil evidence of them from over 500 million years ago!
- Cnidarians: This group includes jellyfish, corals, and sea anemones. They have special stinging cells called nematocysts to catch their food. Coral reefs, built by coral animals, are amazing places. They are home to thousands of different species. The Great Barrier Reef in Australia is over 2,300 kilometers long!
- Worms: This is a very large group. It includes earthworms, flatworms, and segmented worms. Earthworms are super important for healthy soil. They help to loosen and enrich the soil. A single earthworm can move up to 10 kilograms of soil in a year!
- Mollusks: This group includes snails, slugs, clams, oysters, and squid. Mollusks have soft bodies. Many of them have shells to protect themselves. Did you know that giant clams can weigh over 200 kilograms?
- Arthropods: This is the largest group of animals on Earth! It includes insects, spiders, crustaceans, and centipedes. Scientists think there are over a million different kinds of insects that we know about. There are probably many millions more still waiting to be discovered!
- Echinoderms: This group includes starfish, sea urchins, and sea cucumbers. They have spiny skins and usually live in the ocean.
- Vertebrates: This group includes all animals with backbones. This means fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Yes, that includes you! There are over 65,000 known vertebrate species. Vertebrates have changed and adapted over hundreds of millions of years. They now live in almost every habitat on Earth.
The Fungi Kingdom (Fungi)
Fungi are also incredibly diverse. They play very important roles in ecosystems all over the world. This group includes:
- Yeast: These are single-celled fungi. They are used in baking bread and brewing drinks. Yeast reproduce by a process called budding. A new cell grows out from an existing cell.
- Mushrooms: What we call a mushroom is just the part you see above ground. The main part of the organism, called the mycelium, is a network of thread-like structures underground. Some mushrooms are safe to eat, but others are poisonous. Never eat a mushroom unless an adult who knows about them tells you it's safe! The largest known living organism is a honey fungus in Oregon. It covers over 2,385 acres!
- Molds: These fungi grow on decaying organic matter. They help to break it down. Some molds produce antibiotics, like penicillin. Penicillin is used to fight bacterial infections. It was discovered in 1928 by Alexander Fleming.
- Mycorrhizae: These are fungi that form special relationships with the roots of plants. This is called a symbiotic relationship, meaning they live together and help each other. The fungi help the plants get nutrients from the soil. In return, the plants give the fungi sugars. Mycorrhizae are super important for the health of many ecosystems.
Deep Connections: Why Animals and Fungi are Family
Even though animals and fungi look very different, they share some surprising things. At a tiny level, inside their cells, they have similar structures. They also use similar ways to store energy. And remember that shared ancestor with the "tail at the back"? That's a very strong sign of how closely related they are in the big family tree of life!
Images for kids
-
Chytrid (flagellated fungus)
-
Salpingoeca (Choanoflagellatea)
-
Desmarella sp. colony (Choanoflagellatea)
See also
 In Spanish: Opisthokonta para niños
In Spanish: Opisthokonta para niños