Proterozoic facts for kids
The Proterozoic Eon was a very long time in Earth's history. It happened before the Phanerozoic Eon, which is when lots of complex life forms started to appear. The word "Proterozoic" means "earlier life" in Greek. This eon lasted from about 2.5 billion years ago (2500 million years ago) until 541 million years ago. It's the most recent part of what scientists used to call the Precambrian time.
During the Proterozoic, Earth changed a lot. Continents formed, oxygen filled the air, and the first complex living things began to evolve.
Contents
Time Periods of the Proterozoic
The Proterozoic Eon is divided into three main time periods, from the oldest to the youngest:
- Palaeoproterozoic: This period was from 2500 to 1600 million years ago.
- Mesoproterozoic: This period was from 1600 to 1000 million years ago.
- Neoproterozoic: This period was from 1000 to 542 million years ago.
Big Events in the Proterozoic
Many important things happened during the Proterozoic Eon that shaped our planet and the life on it.
Earth's Changing Surface
- Ice Ages: Earth experienced several huge ice ages. One of the most famous was the Snowball Earth event during the Cryogenian period in the late Neoproterozoic. During this time, much of the planet was covered in ice.
- Continent Building: Pieces of Earth's outer layer, called the crust, came together to form large landmasses called continents.
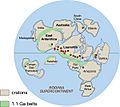
- Supercontinents: Two giant landmasses, known as supercontinents, formed. These were Laurentia in the Palaeoproterozoic and Rodinia in the Neoproterozoic. Imagine all the continents today squished together!
- Plate Tectonics: The slow movement of Earth's large plates, called plate tectonics, started to work much like it does today. This movement causes earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain ranges.
- Mountain Building: As continents crashed into each other, huge mountain ranges were pushed up.
Life and Atmosphere Changes
- Oxygen in the Air: One of the biggest changes was the rise of oxygen in Earth's atmosphere. This event is called the Great Oxygenation Event. Before this, there was very little oxygen in the air.
- First Complex Life: The first eukaryote fossils appeared about 2.1 billion years ago. Eukaryotes are cells that have a nucleus and other complex parts, like the cells that make up plants, animals, and fungi.
- Ediacaran Period: The very end of the Proterozoic, called the Ediacaran period (from 635 to 542 million years ago), is special. During this time, many soft-bodied, multicellular organisms evolved. These were some of the earliest large, complex living things on Earth.
Scientists study rocks from this eon to learn about these amazing changes. They see how continents grew quickly and how supercontinents formed and broke apart.
Related pages
| Precambrian (4.567 gya – 541 mya) | |
|---|---|
| In the left column are Eons, bold are Eras, not bold are Periods. gya = billion years ago, mya = million years ago | |
| Hadean (4.567 gya – 4 gya) | Chaotian Zirconian |
| Archaean (4 gya – 2.5 gya) | Eoarchaean (4 gya – 3.6 gya)
Palaeoarchaean (3.6 gya – 3.2 gya) |
| Proterozoic (2.5 gya – 541 mya) | Palaeoproterozoic (2.5 gya – 1.6 gya) Siderian (2.5 gya – 2.3 gya) Rhyacian (2.3 gya – 2.05 gya) Orosirian (2.05 gya – 1.8 gya) Statherian (1.8 gya – 1.6 gya)
Mesoproterozoic (1.6 gya – 1 gya) Calymmian (1.6 gya – 1.4 gya) Ectasian (1.4 gya – 1.2 gya) Stenian (1.2 gya – 1 gya) Neoproterozoic (1 gya - 541 mya) Tonian (1 gya – 720 mya) Cryogenian (720 mya – 635 mya) Ediacaran (635 mya – 541 mya) |
Images for kids
-
Rodinia, a supercontinent about 750 million years ago.
See also
 In Spanish: Eón proterozoico para niños
In Spanish: Eón proterozoico para niños