Raleigh County, West Virginia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Raleigh County
|
||
|---|---|---|

The Raleigh County Courthouse in Beckley
|
||
|
||
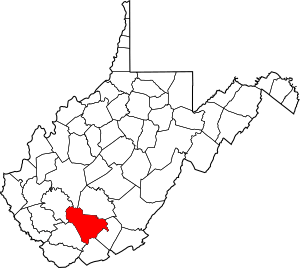
Location within the U.S. state of West Virginia
|
||
 West Virginia's location within the U.S. |
||
| Country | ||
| State | ||
| Founded | January 23, 1850 | |
| Named for | Sir Walter Raleigh | |
| Seat | Beckley | |
| Largest city | Beckley | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 609 sq mi (1,580 km2) | |
| • Land | 605 sq mi (1,570 km2) | |
| • Water | 4.0 sq mi (10 km2) 0.7% | |
| Population
(2020)
|
||
| • Total | 74,591 | |
| • Estimate
(2021)
|
73,771 |
|
| • Density | 122.48/sq mi (47.29/km2) | |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | |
| Congressional district | 1st | |
Raleigh County is a county located in the state of West Virginia in the United States. In 2020, about 74,591 people lived there. The main town and county seat is Beckley.
Raleigh County was created in 1850. It was named after Sir Walter Raleigh, a famous English explorer. The county is part of the Beckley, West Virginia, area.
Contents
Discovering Raleigh County's Past
Raleigh County and the land around it have been home to many Native American groups for a very long time. Early explorers wrote that the Moneton people lived here. They spoke a language called Catawban and were friends with the Monacan people. The Moneton people called this area "okahok amai."
Later, other tribes like the Tutelo also lived here. When European settlers arrived, some Native American tribes moved to West Virginia. They were known as Mingo, which means "distant relatives of the Iroquois Confederacy."
How Raleigh County Was Formed
Raleigh County was officially formed on January 23, 1850. It was created from parts of Fayette County, which was then part of Virginia. Alfred Beckley, who helped found the county, chose the name to honor Sir Walter Raleigh. Raleigh was known for supporting early efforts to start colonies in Virginia.
West Virginia became a state on June 20, 1863. Raleigh was one of the fifty counties that joined the new state. At first, counties were divided into "townships" to help with local government. But this didn't work well in rural areas. So, in 1872, townships became "magisterial districts."
Raleigh County started with six townships: Clear Fork, Marsh Fork, Richman, Shady Spring, Town, and Trap Hill. A seventh district, Slab Fork, was added later from land that used to be part of Wyoming County. These districts stayed mostly the same for about 100 years. In the 1970s, they were combined into three new districts: District 1, District 2, and District 3.
Coal Mining and Important Events
Raleigh County has a long history with coal mining. This industry has seen many serious accidents. One of the worst was the Eccles Mine Disaster in 1914, where many miners lost their lives. More recently, the 2010 Upper Big Branch Mine disaster also happened in Raleigh County, taking the lives of twenty-nine miners.
Miners in Raleigh County also worked hard to improve their working conditions. Sometimes, these efforts led to conflicts. For example, during the 1902-1903 New River coal strike, there was a difficult event known as the Battle of Stanaford. People like Mother Jones supported the miners and shared their stories. These events were important steps in the history of workers' rights in West Virginia.
A famous person from Raleigh County was Senator Robert C. Byrd, who lived in the town of Sophia.
Exploring Raleigh County's Landscape
The New River flows along the eastern edge of Raleigh County. The county's land is made up of wooded hills with many streams and valleys. The land generally slopes down towards the north and west. The highest point in the county is about 3,524 feet (1,074 meters) above sea level, near its southern corner.
Raleigh County covers a total area of 609 square miles (1,577 square kilometers). Most of this is land (605 square miles or 1,567 square kilometers), with a small part being water (4.0 square miles or 10 square kilometers).
Main Roads and Routes
Neighboring Counties
- Kanawha County (north)
- Fayette County (northeast)
- Summers County (east)
- Mercer County (southeast)
- Wyoming County (southwest)
- Boone County (northwest)
Parks and Natural Areas
- Little Beaver State Park
- New River Gorge National Park and Preserve (part of it is in Raleigh County)
Lakes in Raleigh County
- Flat Top Lake
- Glade Creek Reservoir
- Little Beaver Lake
- Stephens Lake
People and Population
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1850 | 1,765 | — | |
| 1860 | 3,367 | 90.8% | |
| 1870 | 3,673 | 9.1% | |
| 1880 | 7,367 | 100.6% | |
| 1890 | 9,597 | 30.3% | |
| 1900 | 12,436 | 29.6% | |
| 1910 | 25,633 | 106.1% | |
| 1920 | 42,482 | 65.7% | |
| 1930 | 68,072 | 60.2% | |
| 1940 | 86,687 | 27.3% | |
| 1950 | 96,273 | 11.1% | |
| 1960 | 77,826 | −19.2% | |
| 1970 | 70,080 | −10.0% | |
| 1980 | 86,821 | 23.9% | |
| 1990 | 76,819 | −11.5% | |
| 2000 | 79,220 | 3.1% | |
| 2010 | 78,859 | −0.5% | |
| 2020 | 74,591 | −5.4% | |
| 2021 (est.) | 73,771 | −6.5% | |
| US Decennial Census 1790–1960 1900–1990 1990–2000 2010–2020 |
|||

Population Facts from 2010
In 2010, there were 78,859 people living in Raleigh County. There were 31,831 households, which are groups of people living together. The average number of people in a household was 2.36. The average age of people in the county was 41.1 years old.
Most people in the county were white (88.5%). About 8.2% were black or African American, and 0.9% were Asian. A small number of people were American Indian (0.2%) or from other backgrounds. About 1.3% of the population was of Hispanic or Latino origin.
The average income for a household in the county was $38,036. For families, the average income was $49,837. About 17.5% of all people in the county lived below the poverty line. This included 26.1% of those under 18 years old.
Towns and Communities
Cities
- Beckley (This is the county seat, meaning it's the main administrative town.)
Towns
Magisterial Districts
Current Districts
- District 1
- District 2
- District 3
Historic Districts
- Clear Fork
- Marsh Fork
- Richmond
- Shady Spring
- Slab Fork
- Town
- Trap Hill
Census-Designated Places (CDPs)
These are areas that are like towns but are not officially incorporated as cities or towns.
Unincorporated Communities
These are smaller communities that don't have their own local government.
- Abney
- Abraham
- Affinity
- Amigo
- Arnett
- Artie
- Beaver
- Besoco
- Big Stick
- Blue Jay
- Blue Jay 6
- Cedar
- Cool Ridge
- Crow
- Dorothy
- Eastgulf
- Egeria
- Fireco
- Flat Top
- Glen Daniel
- Glen Morgan
- Grandview
- Hollywood
- Hot Coal
- Hotchkiss
- Jonben
- Josephine
- Killarney
- Lego
- Lillybrook
- McAlpin
- McVey
- Montcoal
- Naoma
- New
- Odd
- Pemberton
- Pickshin
- Pinepoca
- Pluto
- Price Hill
- Princewick
- Raleigh
- Redbird
- Rhodell
- Shiloh
- Slab Fork
- Soak Creek
- Stotesbury
- Sullivan
- Sylvia
- Tams
- Ury
- Whitby
- White Oak
- Willibet
- Winding Gulf
- Woodpeck
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Raleigh para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Raleigh para niños


