Star of India (flag) facts for kids
 |
|
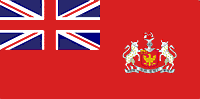
| Name | Flag of the Viceroy and Governor-General of India |
|---|---|
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Adopted | 1885–1947 |
| Design | Union Jack with the Order of the Star of India in the centre, surmounted by the Tudor Crown. |

Variant flag of India
|
|
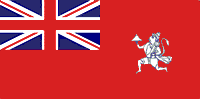
| Use | Civil ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Adopted | 1880–1947 |
| Design | Red Ensign with the Union Jack occupying one quarter of the field placed in the canton and defaced with the Order of the Star of India. |

Variant flag of India
|
|
| Use | State and naval ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Adopted | 1879–1947 |
| Design | Blue Ensign with the Union Jack occupying one quarter of the field placed in the canton and defaced with the Order of the Star of India. |
The Star of India refers to a group of flags used when India was under British rule, known as the British Raj. During this time, India had many different flags for various purposes.
Local rulers in India, called Princely States, had their own flags. These flags were flown next to the British flag. This showed that the British had power over them. The main official flag for land use was the Union Flag of the United Kingdom. This was the flag taken down when India became independent in 1947.
The flag of the governor-general of India (the top British official) had the Star of India symbol on it. Ships also used flags with the Star of India emblem. Merchant ships used the Red Ensign, and naval ships used the Blue Ensign.
Contents
History of India's Flags
When the British first thought about a flag for India, they wanted it to show their empire's power. This was not about Indian nationalism. After the Indian Rebellion of 1857 and the start of the British Raj, a new symbol was needed.
In 1863, several designs were suggested for the first Star of India flag. These designs were similar to flags used in other British colonies like Canada and Australia. They combined British symbols like the Union Jack and the Tudor Crown with symbols special to India.
Early Company Flags
In 1600, Queen Elizabeth I allowed the English East India Company to trade in the Indian Ocean. The company then adopted a flag with thirteen red and white stripes. It had the flag of England in the corner.
Over time, the flag in the corner changed. First, it became the flag of Great Britain in 1707. Then, it changed to the Union Jack in 1801. These flags were also used during the Company rule in India.
After the Indian Rebellion of 1857, the British government took over India. The East India Company's striped flag was replaced by the Union Jack.
Flags of British India
-
Photograph of the Blue Ensign, used as the naval jack of the Royal Indian Navy
In 1876, Queen Victoria became the Empress of India. A year later, a naval flag with the symbol of the Order of the Star of India was approved. This flag was used on ships of the Indian Marine (later the Royal Indian Navy). It was also used for other military and naval purposes.
In 1928, its use changed. The Royal Indian Navy started using the White Ensign as its main naval flag. The Blue Ensign then became the naval jack, a smaller flag flown at the front of a ship.
Red Ensign: Civil Flag
-
Civil ensign of British India, which was also sometimes used to represent India internationally.
-
The Red Ensign used to represent India as a member of the Allies in World War II, showing the original United Nations in 1942
The Blue Ensign was for military ships. The Red Ensign was used for merchant ships and other civilian purposes. It sometimes represented India at international events. For example, it was used when India joined the Allies during World War II. Merchant ships registered in British Indian ports used a plain red ensign.
Flag of the Viceroy and Governor-General
-
Flag of the Viceroy and Governor-General of India.
-
Indian hockey players arrive in the Netherlands for the 1928 Summer Olympics
-
Flag of the Viceroy of India being used to represent India at the 1936 Summer Olympics
Around 1885, the viceroy of India was allowed to fly a special Union Flag. It had the 'Star of India' symbol in the middle, topped with a crown. This flag was often used to represent India at international events. It was like an "unofficial national flag."
This flag was not just for the viceroy. Other British officials in India, like governors, also used it. When at sea, only the viceroy flew the flag from the main mast. Other officials flew it from the front mast.
Flags After Independence
-
Flag of the Governor-General of the Dominion of India (1947-1950).
-
Flag of the Governor-General of the Dominion of Pakistan (1947-1953) depicted with Tudor Crown.
-
Flag of the Governor-General of the Dominion of Pakistan (1953-1956) depicted with St. Edward's Crown.
The Star of India flags stopped being used in 1947. This was when India and Pakistan became independent countries, called Dominions. The new governors-general of India and Pakistan used a dark blue flag. It had the royal crest (a lion on a crown) and the words 'INDIA' or 'PAKISTAN' in gold letters.
These flags were also stopped when India and Pakistan became constitutional republics. India became a republic in 1950, and Pakistan in 1956.
British Indian Army Flag
The British Indian Army used a red flag with the Star of India symbol. It also had two crossed swords and the Tudor Crown. They also used a blue flag with the Union Flag in the corner. This blue flag had the Star of India and two crossed swords in the main part.
Royal Indian Air Force Flag
The Royal Indian Air Force used a round symbol similar to the Royal Air Force. It had a star in the center. Their flag was light blue with the UK flag in the corner. It also had the Royal Indian Air Force's round symbol in the main part.
Proposed Flags for New Nations
In 1947, Lord Mountbatten, the last British leader in India, suggested flags for India and Pakistan. His idea for India's flag was the Indian National Congress flag with a Union Jack in the corner. But Nehru, a key Indian leader, said no. He thought it would upset some people who wanted full independence from Britain.
Mountbatten's idea for Pakistan's flag was the Muslim League flag with a Union Jack. But Jinnah, Pakistan's founder, also said no. He felt a flag with a Christian cross (from the Union Jack) next to an Islamic crescent would not be acceptable to Muslims.
The Star of India Emblem
| Star of India | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Armiger | Emperor/Empress of India Viceroy of India |
| Adopted | 1861 |
| Motto | "Heaven's Light Our Guide" |
| Order(s) | Order of the Star of India |
| Use | Emblem of the Indian Empire, alongside the Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom |
The Star of India was the symbol of the Order of the Star of India. This was a special group of knighthood honors. The emblem was a silver five-pointed star with rays. It was decorated with diamonds. Around it was a sunburst with many rays.
In the center of the sunburst was a light blue ribbon. It had the motto of the Order: "Heaven's Light Our Guide". This motto was chosen to be fair to people of different religions in India. "Heaven" also referred to the stars, which sailors used to find their way to India. Unlike most British symbols, the Star did not have Christian meanings. This was because Indian rulers might not have accepted them.
Legacy of the Star of India
After India gained independence on August 15, 1947, the Star of India flags were replaced. India adopted the Tiraṅgā (Indian Tricolour). Pakistan adopted the Parc̱am-e Sitārah o-Hilāl (Flag of the Star and Crescent). Pakistan's first Coat of Arms also used the star as a main part.
The Star of India emblem was used for many symbols during British rule. It is still used in modern India today. You can see it in the logos of many organizations. These include The Oriental Insurance Company, Board of Control for Cricket in India, Indian Olympic Association, and Mumbai Police.
-
Insignia of Khatau Mills, Bombay.
Other Flags from British India
Home Rule Flag
The Indian Home Rule movement used a flag with five red and four green stripes. In the top left corner was the Union Flag. This showed that the movement wanted India to be a Dominion, like Canada or Australia. A white crescent moon and a seven-pointed star were in the top right. Seven white stars were arranged like the Saptarishi constellation (Ursa Major), which is sacred to Hindus.
Coronation Standard
The Coronation Standard of British Raj had a Saint George's Cross. In its center was the 'Star of India' topped with a Crown.
Bengal Presidency Flag
The flag of Bengal Presidency was blue. It had the badge of Bengal on it. The badge showed a tiger walking, with a sailing ship below it.
Calcutta Port Commissioners Flag
From 1896, the Commissioners of the Port of Calcutta used a Red Ensign. It had their special badge on it.
Bombay Port Conservator Flag
In 1880, a special flag was approved for the Conservator of the Port of Bombay. It was a red St George's Cross on a white background. It had three thin red stripes in each quarter. A large round badge was in the center.
The badge had two oval shields with a crown on top. A red ring around them said "Conservator of the Port of Bombay." One shield showed parts of the Trustees' flag. The other shield showed the arms of the City of Bombay from 1877. This included a red lion and ostrich feathers. It also showed three dhows (ships).
Bombay Port Trustees Flag
The Trustees of the Port of Bombay also had a special flag. It was a blue St George's cross. Each quarter showed a different maritime scene. These included a lighthouse, a steamer, a dhow, and a signal station.
Merchant Flags of Princely States
-
Flag of Travancore State Merchant
-
Flag of Junagadh State Merchant
-
Flag of Cochin State Merchant
List of Flags Used in British India
| Flag | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
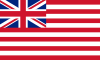 |
1733–1858 | Flag of the East India Company. |
 |
1858–1947 | The official flag of the British Empire. |
 |
1885–1947 | Flag of the Viceroy and Governor-General of India. |
 |
1880–1947 | Civil ensign for British India. |
 |
1879–1947 | Naval flag for the Indian Marine (later Royal Indian Navy). |
 |
1884–1928 | Naval jack of the Royal Indian Marine. |
 |
1928–1950 | Ensign of the Royal Indian Marine (later Royal Indian Navy). Same as the White Ensign of the Royal Navy. |
 |
1942–1947 | Ensign of the British Indian Army. |
 |
1945-1947 | Ensign of the Royal Indian Air Force. |