Subdivisions of Egypt facts for kids
Egypt is a country in Africa that is organized into different levels for its public administration. This helps the government manage things across the country. Egypt has a very centralized system, meaning most decisions come from the main government. This system is officially called "local administration" and is part of the country's executive branch.
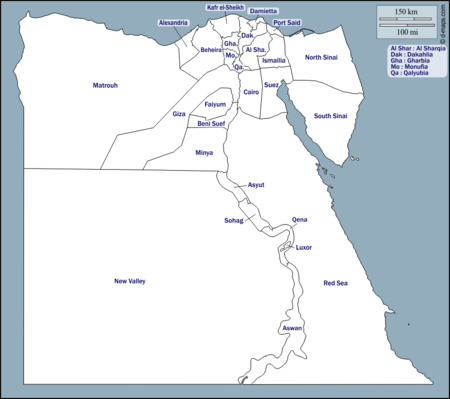
At the very top, Egypt is divided into 27 areas called governorates. Think of them like states or provinces. Each governorate has a leader called a governor. The President of Egypt chooses these governors, and they report directly to the Prime Minister of Egypt. The Minister of Local Development helps coordinate all the governors and their budgets.
Below the governorates, there are smaller areas called marakiz (counties) or aqsam (sections). Even smaller than those are districts and villages. Each of these levels has its own way of being managed. Sometimes, districts are even split into smaller sub-districts.
Besides these administrative divisions, Egypt also has seven special economic regions. These are used for planning how the country will grow and develop, but they don't have their own administrative duties.
Contents
How Egypt is Organized
Egypt's local administration generally has three main levels, each with a leader. There's also an economic level that doesn't manage daily tasks:
- Economic regions: These are groups of governorates used for planning, not for daily management.
- Governorates: These are the largest divisions. Some are like "city-governorates" where the governor is also the head of the main city.
- Marakiz (counties) and cities: A markaz is like a county, and its head often leads the main city within it. Some large cities, like Giza, are independent.
- Districts (ahyaa) and main villages: Districts are parts of cities, and main villages are parts of marakiz.
- For police and census records, districts are sometimes divided into smaller police wards called qism.
- Shiakha are even smaller urban areas used for counting people, but they aren't administrative. Main villages can also have smaller connected villages or hamlets.
There are also New Urban Communities, which are like new cities built by a national authority. These new cities are meant to be transferred to the regular local administration later, but so far, none have been. New villages built by the Ministry of Agriculture in desert areas are also initially managed by them before being transferred.
Some governorates, like Cairo, Port Said, and Suez, are entirely urban. This means the governor is also the head of the city, and all the smaller units within them are urban areas. Alexandria is similar, but it has one rural county. The other 23 governorates are made up of counties (marakiz), with one city acting as the capital for the county and overseeing smaller towns and rural villages.
In 2008, two new governorates, Helwan and 6th of October, were created. However, in 2011, they were merged back into Giza and Cairo governorates. Luxor was created in 2009, bringing the total number of governorates to 27.
A Look Back at Egypt's Administration
Before the 1952 Egyptian revolution, powerful local leaders had a lot of say in rural areas. After the revolution, the government worked to reduce their power and connect directly with farmers through cooperatives. This helped bring services and development to villages. Local branches of the ruling party also helped involve villagers and keep local leaders connected to the government.
Over time, the government continued to have a strong presence in the countryside. While efforts to involve villagers and provide services changed, administrative control remained. Local families and village leaders regained some influence, but they were still part of the government's system.
Until 1979, local governments in Egypt had limited power because the country was very centralized. Governors were chosen by the president, and they appointed their own staff. Later, in 1979, a new law gave governors more authority and reduced some of the central government's control over the provinces. Local councils, which were elected, gained the right to approve or reject local budgets. They were also encouraged to raise local taxes to reduce their reliance on the central government.
Under President Hosni Mubarak (1981-2011), some believed that local areas gained more control, allowing policies to fit local needs. However, others felt that local governance was still weak, and elected local councils often had a more ceremonial role compared to appointed councils that managed departments. Elections for these local councils were also sometimes seen as unfair.
After the January 2011 uprising that removed Mubarak, parliament and local councils were dissolved. Later constitutions in 2012 and 2014 aimed to give more power to local areas. However, as of late 2022, this hasn't fully happened, and many local council seats have been empty for over ten years.
Egypt's Governorates
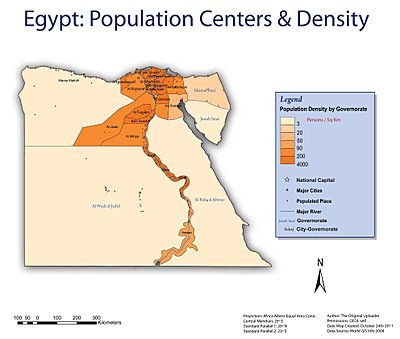
Egypt is divided into 27 governorates. Each governorate has a capital city and at least one other city. The governor, appointed by the President, leads each governorate. Most governorates have a high population density, meaning many people live in a small area. However, the three largest governorates have very few people per square kilometer.
Here is a list of Egypt's governorates:
| Name | Area | Population (November 2023 estimate) |
Density (November 2023) |
Capital | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | sq mi | per km2 | per sq mi | |||
| 2,300 | 890 | 5,703,824 | 2,480 | 6,400 | Alexandria | |
| 62,726 | 24,219 | 1,698,201 | 27 | 70 | Aswan | |
| 25,926 | 10,010 | 5,071,485 | 196 | 510 | Asyut | |
| 9,826 | 3,794 | 6,940,234 | 706 | 1,830 | Damanhur | |
| 10,954 | 4,229 | 3,618,395 | 330 | 850 | Beni Suef | |
| 3,085 | 1,191 | 10,456,284 | 3,389 | 8,780 | Cairo | |
| 3,538 | 1,366 | 7,058,212 | 1,995 | 5,170 | Mansoura | |
| 910 | 350 | 2,023,380 | 2,223 | 5,760 | Damietta | |
| 6,068 | 2,343 | 4,141,222 | 682 | 1,770 | Faiyum | |
| 1,942 | 750 | 5,483,000 | 2,823 | 7,310 | Tanta | |
| 13,184 | 5,090 | 9,534,283 | 723 | 1,870 | Giza | |
| 5,067 | 1,956 | 1,482,999 | 293 | 760 | Ismailia | |
| 3,467 | 1,339 | 3,731,540 | 1,076 | 2,790 | Kafr El Sheikh | |
| 460 | 180 | 1,429,385 | 3,107 | 8,050 | Luxor | |
| 166,563 | 64,310 | 580,304 | 3 | 7.8 | Marsa Matruh | |
| 32,279 | 12,463 | 6,332,918 | 196 | 510 | Minya | |
| 2,499 | 965 | 4,743,341 | 1,898 | 4,920 | Shibin El Kom | |
| 440,098 | 169,923 | 324,600 | 0.7 | 1.8 | Kharga | |
| 28,992 | 11,194 | 544,494 | 19 | 49 | Arish | |
| 1,345 | 519 | 835,193 | 621 | 1,610 | Port Said | |
| 1,124 | 434 | 6,137,896 | 5,461 | 14,140 | Banha | |
| 10,798 | 4,169 | 3,651,215 | 338 | 880 | Qena | |
| 119,099 | 45,984 | 409,394 | 3 | 7.8 | Hurghada | |
| 4,911 | 1,896 | 8,032,683 | 1,636 | 4,240 | Zagazig | |
| 11,022 | 4,256 | 5,714,903 | 518 | 1,340 | Sohag | |
| 31,272 | 12,074 | 145,934 | 5 | 13 | El Tor | |
| 9,002 | 3,476 | 843,385 | 94 | 240 | Suez | |
| Total | 1,010,407 | 390,120 | 106,668,704 | 106 | 270 | Cairo |
Municipal Divisions
At the municipal level, Egypt has different types of areas: markaz (counties), kism (sections), police-managed areas, and new cities. Generally, rural areas are divided into markaz, while urban areas are divided into kism. As of 2013, there were 351 such subdivisions. Some areas are also "unorganized," meaning they don't fit neatly into these categories.
- k means kism (an urban section)
- m means markaz (a county, usually rural)
- n means new city
- p means police-administered area
Sub-Municipal Divisions
The smallest local unit in rural areas is the village. In cities, the equivalent is a district. The leaders of villages or districts are chosen by the governors. Sometimes, districts are further divided into smaller neighborhoods called sheyakha in rural areas, or residential districts in urban areas.
Population Details
This section provides information about how many people live in urban (city) versus rural (countryside) areas in each governorate.
Urban and Rural Populations
Here's a look at the urban and rural populations in Egypt's governorates, based on data from CAPMAS (Egypt's statistics agency) in 2016:
| Governorate | % Urban | Population (2016) | Rural | Urban |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alexandria | 98.8 | 4,812,186 | 56,698 | 4,755,488 |
| Aswan | 42.3 | 1,431,488 | 826,543 | 604,945 |
| Asyut | 26.5 | 4,245,215 | 3,119,112 | 1,126,103 |
| Beheira | 19.5 | 5,804,262 | 4,674,346 | 1,129,916 |
| Beni Suef | 23.2 | 2,856,812 | 2,193,871 | 662,941 |
| Cairo | 100.0 | 9,278,441 | 0 | 9,278,441 |
| Dakahlia | 28.2 | 5,949,001 | 4,271,428 | 1,677,573 |
| Damietta | 38.7 | 1,330,843 | 815,244 | 515,599 |
| Faiyum | 22.5 | 3,170,150 | 2,456,368 | 713,782 |
| Gharbia | 30.0 | 4,751,865 | 3,324,630 | 1,427,235 |
| Giza | 58.6 | 7,585,115 | 3,138,310 | 4,446,805 |
| Ismailia | 45.4 | 1,178,641 | 643,778 | 534,863 |
| Kafr El Sheikh | 23.1 | 3,172,753 | 2,441,246 | 731,507 |
| Luxor | 37.8 | 1,147,058 | 713,422 | 433,636 |
| Matruh | 70.6 | 447,846 | 131,841 | 316,005 |
| Minya | 18.9 | 5,156,702 | 4,183,284 | 973,418 |
| Monufia | 20.6 | 3,941,293 | 3,128,460 | 812,833 |
| New Valley | 48.0 | 225,416 | 117,180 | 108,236 |
| North Sinai | 60.2 | 434,781 | 173,095 | 261,686 |
| Port Said | 100.0 | 666,599 | 0 | 666,599 |
| Qalyubia | 44.7 | 5,105,972 | 2,825,045 | 2,280,927 |
| Qena | 19.7 | 3,045,504 | 2,445,051 | 600,453 |
| Red Sea | 95.1 | 345,775 | 17,062 | 328,713 |
| Sharqia | 23.1 | 6,485,412 | 4,987,707 | 1,497,705 |
| Sohag | 21.4 | 4,603,861 | 3,618,543 | 985,318 |
| South Sinai | 51.1 | 167,426 | 81,924 | 85,502 |
| Suez | 100.0 | 622,859 | 0 | 622,859 |
| Total | 42.7 | 87,963,276 | 50,384,188 | 37,579,088 |
Population Density
Population density tells us how many people live in each square kilometer. This table shows the population density for each governorate in 2014, based on both the total area and just the inhabited (lived-in) area.
| Governorate | Population in thousands (2014-07-01) | Pop. Density (Inhabited Area) | Pop. Density (Total Area) | % Inhabited to Total | Inhabited Area | Total Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alexandria | 4,761 | 2,841.5 | 2,070.0 | 72.8 | 1,675.50 | 2,300.00 |
| Aswan | 1,412 | 13,477.1 | 22.5 | 0.2 | 104.77 | 62,726.00 |
| Asyut | 4,181 | 2,656.3 | 161.3 | 6.1 | 1,574.00 | 25,926.00 |
| Beheira | 5,720 | 806.3 | 582.1 | 72.2 | 7,093.84 | 9,826.00 |
| Beni Suef | 2,812 | 2,053.4 | 256.7 | 12.5 | 1,369.41 | 10,954.00 |
| Cairo | 9,184 | 48,235.3 | 2,976.8 | 6.2 | 190.40 | 3,085.12 |
| Dakahlia | 5,881 | 1,662.1 | 1,662.1 | 100.0 | 3,538.23 | 3,538.23 |
| Damietta | 1,316 | 1,968.7 | 1,445.7 | 73.4 | 668.47 | 910.26 |
| Faiyum | 3,118 | 1,680.0 | 513.8 | 30.6 | 1,856.00 | 6,068.00 |
| Gharbia | 4,698 | 2,418.7 | 2,418.7 | 100.0 | 1,942.34 | 1,942.34 |
| Giza | 7,487 | 6,286.3 | 567.9 | 9.0 | 1,191.00 | 13,184.00 |
| Ismailia | 1,162 | 229.3 | 229.3 | 100.0 | 5,066.97 | 5,066.97 |
| Kafr El Sheikh | 3,132 | 903.5 | 903.5 | 100.0 | 3,466.69 | 3,466.69 |
| Luxor | 1,132 | 4,992.7 | 469.8 | 9.4 | 226.73 | 2,409.68 |
| Matruh | 437 | 111.4 | 2.6 | 2.4 | 3,921.40 | 166,563.00 |
| Minya | 5,076 | 2,104.8 | 157.3 | 7.5 | 2,411.65 | 32,279.00 |
| Monufia | 3,890 | 1,596.9 | 1,556.6 | 97.5 | 2,435.93 | 2,499.00 |
| New Valley | 222 | 205.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 1,082.24 | 440,098.00 |
| North Sinai | 428 | 203.7 | 14.8 | 7.2 | 2,100.84 | 28,992.00 |
| Port Said | 660 | 499.7 | 490.7 | 98.2 | 1,320.68 | 1,344.96 |
| Qalyubia | 5,044 | 4,702.1 | 4,486.4 | 95.4 | 1,072.72 | 1,124.28 |
| Qena | 3,001 | 1,724.1 | 277.9 | 16.1 | 1,740.63 | 10,798.00 |
| Red Sea | 341 | 4,794.0 | 2.9 | 0.1 | 71.13 | 119,099.13 |
| Sharqia | 6,402 | 1,343.7 | 1,303.6 | 97.0 | 4,764.28 | 4,911.00 |
| Sohag | 4,536 | 2,845.8 | 411.5 | 14.5 | 1,593.92 | 11,022.00 |
| South Sinai | 166 | 9.9 | 5.3 | 53.7 | 16,791.00 | 31,272.00 |
| Suez | 615 | 68.3 | 68.3 | 100.0 | 9,002.21 | 9,002.21 |
| Total | 86,814 | 1109.1 | 85.9 | 7.8 | 78272.98 | 1010407.87 |