Tenby facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tenby
|
|
|---|---|
 The harbour and old town |
|
| Population | 4,696 (2011 census) |
| OS grid reference | SN129007 |
| Principal area | |
| Ceremonial county | |
| Country | Wales |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | TENBY |
| Postcode district | SA70 |
| Dialling code | 01834 |
| Police | Dyfed-Powys |
| Fire | Mid and West Wales |
| Ambulance | Welsh |
| EU Parliament | Wales |
| UK Parliament |
|
| Welsh Assembly |
|
| Website | www.aroundtenby.co.uk |
Tenby (which means "fortlet of the fish" in Welsh) is a lovely seaside town in Pembrokeshire, Wales. It sits right on Carmarthen Bay.
This historic town is famous for its beautiful sandy beaches, which stretch for about 3 miles. You can also explore the Pembrokeshire Coast Path here. Tenby has amazing old buildings like its 13th-century medieval town walls with the Five Arches gatehouse. Don't miss the Tenby Museum and Art Gallery, the grand 15th-century St. Mary's Church, and the National Trust's Tudor Merchant's House.
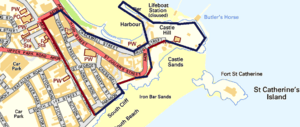
From Tenby's harbour, you can take a boat trip to Caldey Island, where monks live. St Catherine's Island is another island you can reach when the tide is out. It has an old fort from the 1800s. The town also has its own train station.
Contents
Tenby's Past: A Journey Through Time
Tenby was a great place for people to settle because of its perfect location. It's on the far west coast of the British Isles and has a natural harbour. This harbour is safe from the strong waves of both the Atlantic Ocean and the Irish Sea.
Early Days and Norman Times
The first mention of Tenby is in an old poem from the 800s. Back then, it was probably a hill fort, a strong place on a hill. Later, it became a trading town, possibly influenced by Vikings from Ireland.
When the Normans came to West Wales in the early 1100s, they took over Tenby. The town's first stone fort was built on Castle Hill. Tenby grew into an important seaport for the Normans.
However, Welsh forces attacked and damaged the town and castle several times. After a big attack in 1260, William de Valence, 1st Earl of Pembroke ordered new, stronger walls to be built. These stone walls, with towers and gates, protected a large part of the town. Once the new walls were finished, Tenby Castle was no longer needed and was left empty.
Protecting the Town
In 1457, Jasper Tudor, who was the uncle of Henry Tudor, helped pay to make Tenby's defences even better. This was because the town was very important for trade in Wales. They made the walls taller and added more places for archers to shoot from. They also added towers at the ends of the walls and made the ditch outside the walls wider.
Because of its strong defences, Tenby received money from the king to keep its walls and harbour in good shape. Traders from Tenby sailed to places like Bristol, Ireland, France, Spain, and Portugal. They exported things like wool, animal skins, and coal. In 1566, Portuguese sailors even brought the first oranges to Wales! Tenby was so busy and important back then that it was considered a national port.
During the Wars of the Roses, Henry Tudor, who later became King Henry VII, hid in Tenby before sailing away in 1471. In the mid-1500s, the large D-shaped tower called "Five Arches" was built because people were worried about another attack from Spain.
A Time of Decline
Tenby's importance quickly dropped because of two main events. First, during the English Civil War, Tenby supported the Parliament. After being attacked twice, it was finally captured in 1648. The town was left in ruins.
Second, a terrible plague hit Tenby in 1650, killing half of the people who were left. With fewer people and damaged buildings, the town's economy suffered. Most of the merchants and business people left, and Tenby became run down. By the late 1700s, a visitor named John Wesley wrote that "Two-thirds of the old town is in ruins or has entirely vanished."
Tenby's Comeback
Surprisingly, another war helped Tenby recover. After 1798, the French leader Napoleon Bonaparte was conquering Europe. This made it hard for rich British people to travel to European spa towns. So, they started looking for places to visit in Britain.
In 1802, a local businessman and politician named Sir William Paxton bought property in Tenby. He invested a lot of money to make the town a popular place for visitors.
People believed that bathing in saltwater was good for their health. So, Paxton hired engineers and architects to build a "fashionable bathing establishment" for the rich. His sea-bathing baths opened in 1806. He also turned an inn into a fancy place for visitors to stay.
In 1814, Paxton paid to build a road on arches overlooking the harbour. He also arranged for fresh water to be piped into the town. Paxton's efforts worked, and Tenby became a popular Victorian holiday spot.
During the Georgian and Victorian eras, Tenby was known as a health resort. Many walkways were built to make it easy for people to stroll by the sea. This is why many of Tenby's beaches still have good access today.

In 1852, a lifeboat was stationed in Tenby to help fishermen and sailors in trouble. The Royal National Lifeboat Institution took over in 1854. This led to the building of the first lifeboat station with a slipway in 1905, which was replaced in 2008.
The Tenby railway station opened in 1863, making it easier for visitors to reach the town. In 1867, work began on the Palmerston Fort on St Catherine's Island. This fort was built to protect the coast from possible attacks.
How Tenby is Governed
Tenby has two levels of local government. There's the Tenby Town Council, which looks after local town matters. Then there's the Pembrokeshire County Council, which handles bigger county-wide issues. The town council is based at the De Valence Pavilion.
Tenby has been an old borough for a very long time, receiving its first special charter in 1290. This meant it had certain rights and freedoms. Over the years, the way the town was governed changed, but it has always had its own local council.
Learning in Tenby
Tenby has four schools: three primary schools and one secondary school. The primary schools are Ysgol Hafan-y-Mor, Tenby Church in Wales Primary School, and St. Teilo's RC School. The secondary school is Ysgol Greenhill Secondary.
Most students from St. Teilo's and Tenby Church in Wales schools automatically go to Greenhill School. Ysgol Hafan y Môr is a Welsh-speaking school, and most of its students go on to a Welsh-speaking secondary school called Ysgol y Preseli.
Fun Things to Do in Tenby
Tenby is a popular place for tourists. You can enjoy its two beautiful, sheltered sandy beaches. You can also take boat trips to Caldey Island. St Catherine's Island is another cool spot with its 19th-century fort, which you can sometimes visit when the tide is low.
Tenby has lots of shops, pubs, and restaurants for visitors. In 2019, The Sunday Times newspaper even named Tenby's Castle Beach the best beach in the UK!
Getting Around Tenby
The Tenby railway station connects the town to other places. Trains run towards Pembroke and also east to places like Whitland, Carmarthen, and Swansea. During busy times, you can even find direct trains from London to Tenby on Saturdays. The closest airport is Cardiff International.
Sports and Events
Tenby has a rugby union club called Tenby United RFC, which started in 1876.
A fun event in Tenby is the Boxing Day Swim, which began in 1970. It's a big Christmas attraction where about 600 swimmers, many in fancy dress, jump into the sea! Thousands of people come to watch. Each swimmer who raises money for charity gets a medal.
Tenby also hosts the Welsh Ironman Triathlon every September, which is a very tough race. There's also the Tenby Aces Cycling Club and an 18-hole Tenby Golf Course right by the coast.
Famous People from Tenby


Many interesting people have connections to Tenby:
- Robert Recorde (around 1512–1558), a doctor and mathematician.
- Sir William Paxton (1744−1824), a businessman who helped Tenby become a seaside resort.
- Charles Norris (1779–1858), an artist and writer who moved to Tenby.
- Fanny Price-Gwynne (1819–1901), a writer, artist, and composer born in Tenby.
- Gwen John (1876–1939), a Welsh artist.
- Augustus John (1878–1961), a famous Welsh painter, born in Tenby.
- Nina Hamnett (1890–1956), a Welsh artist and writer, also born in Tenby.
- Kenneth Griffith (1921–2006), a Welsh actor and filmmaker, born in Tenby.
- Rosie Swale-Pope (born 1946), an author and adventurer who lives in Tenby.
- Michael Bonacini (born 1960), a Welsh-Canadian chef, born and raised in Tenby.
- Kate Lamb (born 1988), an actress who grew up in Tenby.
Wally the Walrus
In March 2021, an Arctic walrus named Wally was seen on the rocks near Tenby! He had traveled all the way from Ireland. Wally often rested on the new RNLI Lifeboat slipway in Tenby. People were worried when he disappeared for a few days, but he soon returned.
Many people think Wally traveled from the Arctic on a piece of ice. The RSPCA (a animal welfare charity) believes this was the furthest south a walrus has ever been seen.
Wally was mostly resting and looking for food, but he did cause a little mischief. He was reported to have tipped over a small boat and damaged a fishing boat while trying to climb onto them.
Freedom of the Town
Some special people and military groups have been given the "Freedom of the Town" of Tenby. This is a special honour.
Individuals
- David Lloyd George
- Augustus John: 30 October 1959.
- Wilfred Harrison MBE: 1969.
- Mrs Sue Lane: 10 May 2023.
- Cllr Trevor Hallett: 10 May 2023.
Military Units
- HMS Tenby, RN: 1970.
Tenby's Weather
Like the rest of Wales and the UK, Tenby has a maritime climate. This means it has cool summers and mild winters, often with strong winds. Because it's on the southwest coast, Tenby is one of the sunnier places in Wales.
| Climate data for Tenby 5m asl, 1971-2000 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 8.5 (47.3) |
8.0 (46.4) |
9.7 (49.5) |
11.7 (53.1) |
14.8 (58.6) |
17.3 (63.1) |
19.5 (67.1) |
19.3 (66.7) |
17.1 (62.8) |
14.2 (57.6) |
11.2 (52.2) |
9.5 (49.1) |
13.4 (56.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 3.1 (37.6) |
2.8 (37.0) |
3.8 (38.8) |
4.7 (40.5) |
7.4 (45.3) |
9.9 (49.8) |
12.0 (53.6) |
11.8 (53.2) |
10.3 (50.5) |
8.3 (46.9) |
5.3 (41.5) |
4.0 (39.2) |
7.0 (44.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 115.4 (4.54) |
90.1 (3.55) |
87.2 (3.43) |
61.3 (2.41) |
51.5 (2.03) |
66.6 (2.62) |
52.7 (2.07) |
92.7 (3.65) |
101.6 (4.00) |
131.3 (5.17) |
129.9 (5.11) |
126.4 (4.98) |
1,106.5 (43.56) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 58.0 | 75.4 | 115.6 | 184.8 | 218.2 | 205.8 | 218.9 | 200.6 | 149.1 | 106.0 | 71.7 | 49.9 | 1,654 |
| Source: Met Office | |||||||||||||
See also
 In Spanish: Tenby para niños
In Spanish: Tenby para niños