Weather facts for kids
Weather is what the air around us is like from day to day, or even hour to hour. It includes things like wind, lightning, storms, hurricanes, tornadoes, rain, hail, and snow. The Energy from the Sun plays a huge part in making our weather.
Climate is different from weather. Climate tells us what kind of weather an area usually has over a long time, like what to expect in summer or winter. Weather changes can affect how we feel and what we do. For example, we wear different clothes and choose different foods depending on the season and weather.
Weather stations all over the world help us understand weather. They measure things like wind speed, wind direction, temperature, and humidity (how much water is in the air). Scientists called meteorologists use these measurements to make weather forecasts. They use powerful computers and complex mathematical models to predict what the weather will be like in the future.
What is Severe Weather?
Sometimes, weather can be very strong and even dangerous. This is called severe weather. It can cause harm to people and their homes, or just make life difficult.
Some examples of severe weather are:
- Tropical cyclones (like hurricanes)
- Heavy rainstorms
- Drought (when there's not enough rain for a long time)
- Heat waves (when it's super hot for many days)
- Tornadoes (spinning columns of air)
- Blizzards (heavy snowstorms with strong winds)
Why Does Weather Happen?
Weather happens because different parts of the Earth get different amounts of heat from the Sun. This creates different climates around the world. Places near the tropics (the middle of the Earth) get the most heat because the Sun shines directly on them. The poles (top and bottom of the Earth) get the least heat because the Sun's rays hit them at a low angle.
Warmer air is lighter than cooler air. This means warm air tends to rise high into the sky, a process called convection.
The air always has some water mixed into it, which is called humidity. When this warm, moist air rises and cools down, the water can change from a gas (vapor) into tiny liquid droplets. This process is called condensation. These droplets form clouds, and if there are enough of them, the water can fall back to Earth as rain or snow. After the air rises and loses its water, it gets colder and starts to sink back towards the ground. Because it lost its water, this sinking air is usually very dry.
When two large areas of air with different temperatures meet, they form what we call a warm front or a cold front. These fronts often bring changes in weather. The way air moves all around the Earth is known as atmospheric circulation.
Images for kids
-
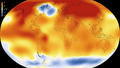
2015 – Warmest Global Year on Record (since 1880) – Colors show how much warmer or colder it was than average (NASA/NOAA; 20 January 2016).
-
Thunderstorm near Garajau, Madeira.
-
A Cumulus mediocris cloud surrounded by stratocumulus clouds.
-
New Orleans, Louisiana, after being struck by Hurricane Katrina. Katrina was a Category 3 hurricane when it hit, but had been a Category 5 in the Gulf of Mexico.
-
Early morning sunshine over Bratislava, Slovakia. February 2008.
-
Jupiter's Great Red Spot in February 1979, photographed by the unmanned Voyager 1 NASA space probe.
-
Aurora Borealis (Northern Lights).
See also
 In Spanish: Tiempo atmosférico para niños
In Spanish: Tiempo atmosférico para niños