Arctic coastal tundra facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Arctic coastal tundra |
|
|---|---|

Tundra vegetation on Yukon's coastal plain
at the Firth River delta |
|
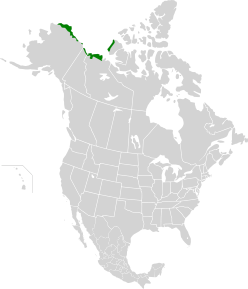
109. Arctic Coastal Tundra
|
|
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Nearctic |
| Biome | Tundra |
| Borders | Arctic foothills tundra, Low Arctic tundra, Middle Arctic tundra and Northwest Territories taiga |
| Animals | caribou, bear, wolf, muskox, snow goose, brant goose, polar bear, fox, lemming, ermine, seal, fish |
| Bird species | 74 |
| Mammal species | 31 |
| Geography | |
| Area | 98,200 km2 (37,900 sq mi) |
| Countries | United States and Canada |
| States | Alaska, Northwest Territories and Yukon |
| Elevation | 0–150 metres (0–492 ft) |
| Geology | coastal plain |
| Rivers | the Mackenzie River delta |
| Climate type | Tundra (ET) |
| Conservation | |
| Conservation status | Relatively Stable/Intact |
| Global 200 | Yes |
| Habitat loss | 0% |
| Protected | 49.8% |
The Arctic coastal tundra is a special natural area in the far northern parts of North America. It's like a huge nursery for many different kinds of wildlife. This amazing place is where many animals come to have their babies and find food.
Contents
What is the Arctic Coastal Tundra?
The Arctic coastal tundra is a unique ecoregion. An ecoregion is a large area of land or water that has its own special climate, plants, and animals. This particular ecoregion is known for its cold weather and flat, open landscapes near the ocean.
Where is this amazing place?
You can find this ecoregion along the northern coast of Alaska in the United States. It also stretches into Canada, covering parts of the Northwest Territories and Yukon. Key areas include the east coast plain of Banks Island and the coastal plains near the Anderson River and Horton River. The Tuktoyaktuk coast is also part of this vast region.
The Land of Ice and Thaw
This area is mostly low, flat, and often wet, like a boggy plain right next to the sea. The ground beneath your feet holds a secret: a thick layer of permanently frozen soil called permafrost. In the short summer months, usually late June, July, and August, the very top layer of this frozen ground melts. This melting creates many small "thaw lakes" or ponds, which are sometimes called thermokarst lakes.
You might also see interesting ice features here. Some are called ice wedges, which are cracks in the ground filled with ice. Others are pingos, which are mounds of earth pushed up by a core of ice. Even in summer, the weather can be chilly, and frosts can happen. This coastal tundra is generally wetter than other Arctic tundra regions further west.
Plants of the Cold North
Despite the cold, many plants thrive here. This ecoregion is perfect for wetland plants. You'll find lots of sedges and grasses. These plants love damp soil.
Tiny Survivors: Plant Life Cycle
Mosses and lichens also cover the ground, especially in the peat bogs right along the coast. These small plants are tough survivors. They have adapted to grow and complete their life cycle during the short, cool summer. In slightly warmer spots, like the Mackenzie River delta and the Yukon coast, you might even see small trees. These include dwarf birch, different kinds of willows, northern Labrador tea (a plant called Dryas), and alders. These plants provide food and shelter for many animals.
Animals of the Arctic Coast
This ecoregion is a vital home for many animals. It's especially important for caribou.
Caribou: Long Journeys and Reproduction
Four large groups of caribou come here to have their calves. These are the Western Arctic, Teshekpuk, Central Arctic, and Porcupine caribou herds. This area provides safe places for the mothers to give birth and for the young calves to grow strong. The reproduction of these herds depends on the healthy habitats found here.
Other Amazing Arctic Creatures
Another important animal is the muskox. You can find them on Banks Island and along the coast of the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge. Many other mammals also live here. These include tiny lemmings, powerful polar bears, and large walruses. You might also spot beluga whales in the coastal waters. Smaller animals like snowshoe hares, Arctic hares, red foxes, and grey wolfs also call this place home. Look for Arctic ground squirrels and different types of seals too.
The coast is a busy place for many waterbirds that come to breed. These include the beautiful snow goose, and several types of eider ducks like the spectacled eider, Steller's eider, and king eider. You can also see different loons, such as the red-throated loon, pacific loon, and yellow-billed loon. Important bird areas include the Colville River delta, Teshekpuk Lake, and Kasegaluk Lagoon, which is a breeding spot for the brant goose. Snowy owls are also here, hunting for waterbirds and lemmings. In the cold waters, you can find fish like the Arctic char.
Protecting this Special Place
Most of the natural habitat in the Arctic coastal tundra is still untouched, about 90% of it. This is great news for the plants and animals that live here. However, some areas have changed due to human activities.
Balancing Nature and Resources
Near places like Utqiaġvik, Alaska and the energy resource areas of Prudhoe Bay, Alaska and Kuparuk, there have been developments. These areas are important for providing energy that people use. It's a challenge to find a balance between using these natural resources and protecting the delicate Arctic environment.
The Arctic National Wildlife Refuge is a very important protected area along this coast. It helps keep a large part of this special ecoregion safe for wildlife. Other areas, like those around the Dalton Highway and the Trans-Alaska Pipeline, also have some human activity. Scientists and conservationists work hard to make sure that these activities do not harm the unique plants and animals of the Arctic coastal tundra.
See also
 In Spanish: Tundra costera del Ártico para niños
In Spanish: Tundra costera del Ártico para niños
- List of ecoregions in Canada (WWF)
- List of ecoregions in the United States (WWF)

