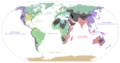
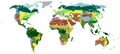
Global 200 facts for kids
The Global 200 is a special list of places on Earth that are super important to protect. It was created by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), which is a group that works to save nature.
These special places are called ecoregions. An ecoregion is like a big area of land or water where plants and animals live together. They share similar weather, types of land, and natural conditions. The WWF chose these 200 ecoregions because they are home to many different kinds of plants and animals, and they are very important for the health of our planet.
The WWF also gives each ecoregion a "conservation status." This tells us how much danger the ecoregion is in. The statuses are:
- Critical or endangered: These places are in big trouble and need urgent help.
- Vulnerable: These places are at risk and could become endangered if we don't protect them.
- Relatively stable or intact: These places are still mostly healthy, but we still need to watch over them.
Sadly, more than half of the Global 200 ecoregions are already endangered! This means they are in serious danger of losing their unique plants and animals.
Contents
- Global 200: Land Ecoregions
- Tropical and Subtropical Moist Broadleaf Forests
- Tropical and Subtropical Dry Broadleaf Forests
- Tropical and Subtropical Coniferous Forests
- Temperate Broadleaf and Mixed Forests
- Temperate Coniferous Forests
- Boreal Forests/Taiga
- Tropical and Subtropical Grasslands, Savannas, and Shrublands
- Temperate Grasslands, Savannas, and Shrublands
- Flooded Grasslands and Savannas
- Montane Grasslands and Shrublands
- Tundra
- Mediterranean Forests, Woodlands, and Shrub
- Deserts and Xeric Shrublands
- Mangroves
- Global 200: Freshwater Ecoregions
- Global 200: Marine Ecoregions
- Related pages
- Images for kids
- See also
Global 200: Land Ecoregions
These are important land areas.
Tropical and Subtropical Moist Broadleaf Forests
These forests are warm and wet all year round. They have many tall trees with wide leaves. They are often called rainforests.
Africa
- Guinean moist forests
- Congolian coastal forests
- Albertine Rift montane forests
- Madagascar lowlands and subhumid forests
Australia and Pacific Islands
- Sulawesi moist forests
- New Guinea montane forests
- Queensland tropical rain forests
- New Caledonia moist forests
Asia
- South Western Ghats montane rain forests (India)
- Sri Lanka moist forests
- Sumatran Islands lowland and montane forests
- Philippines moist forests
- Borneo lowland and montane forests
South and Central America
- Greater Antillean moist forests (Caribbean islands)
- Choco-Darien moist forests (Colombia, Panama)
- Northern Andean montane forests
- Guianan moist forests
- Atlantic forests (Brazil)
Oceania
- South Pacific Islands forests
- Hawaii moist forests
Tropical and Subtropical Dry Broadleaf Forests
These forests are also warm, but they have a dry season. Trees here often lose their leaves during the dry period.
Africa
- Madagascar dry deciduous forests
Australia and Pacific Islands
- Nusa Tenggara dry forests
Asia
- Indochina dry forests
South and Central America
- Mexican dry forests
- Chiquitano dry forests
Tropical and Subtropical Coniferous Forests
These forests are warm and have many cone-bearing trees like pines.
North America
- Sierra Madre Oriental and Occidental pine-oak forests (Mexico)
South and Central America
- Greater Antillean pine forests
- Mesoamerican pine-oak forests
Temperate Broadleaf and Mixed Forests
These forests are found in areas with four seasons. Trees here often change color in autumn.
Australia and Pacific Islands
- Eastern Australian temperate forests
- New Zealand temperate forests
Asia
- Eastern Himalayan broadleaf and conifer forests
North America
- Appalachian and mixed mesophytic forests
Europe and Northern Asia
- Southwest China temperate forests
- Russian Far East temperate forests
Temperate Coniferous Forests
These forests have many evergreen trees that bear cones, like firs and spruces. They are found in cooler, often mountainous areas.
North America
- Pacific temperate rainforests (USA, Canada)
- Sierra Nevada forests (USA)
South America
- Valdivian temperate forests (Chile)
Europe and Northern Asia
- Caucasus-Anatolian-Hycanian temperate forests
- Altai-Sayan montane forests
Boreal Forests/Taiga
These are cold, northern forests with lots of evergreen trees. They are found in places like Canada and Russia.
North America
Europe and Northern Asia
- Ural Mountains taiga
- East Siberian taiga
Tropical and Subtropical Grasslands, Savannas, and Shrublands
These are large areas of grass with scattered trees, often found in warm climates.
Africa
- Horn of Africa acacia savannas
- East African acacia savannas
Australia
- Northern Australia and Trans-Fly savannas
Asia
- Terai-Duar savannas and grasslands (India, Nepal)
South America
- Llanos savannas (Colombia, Venezuela)
- Cerrado woodlands and savannas (Brazil)
Temperate Grasslands, Savannas, and Shrublands
These are grassy areas in cooler climates, like prairies.
North America
- Northern prairie (USA, Canada)
South America
- Patagonian steppe (Argentina, Chile)
Europe and Northern Asia
- Daurian steppe (Mongolia, Russia, China)
Flooded Grasslands and Savannas
These are grassy areas that are often underwater for part of the year.
Africa
- Sudd-Sahelian flooded grasslands and savannas
South America
- Everglades flooded grasslands (USA)
- Pantanal flooded savannas (Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay)
Montane Grasslands and Shrublands
These are grassy or shrubby areas found high up in mountains.
Africa
- Ethiopian Highlands
- Drakenberg montane shrublands and woodlands (South Africa)
South America
Europe and Northern Asia
- Tibetan Plateau steppe
Tundra
Tundra is a very cold, treeless area where the ground is often frozen.
North America
- Alaskan North Slope coastal tundra
Europe and Northern Asia
- Fenno-Scandia alpine tundra and taiga
- Taimyr and Russian coastal tundra
Mediterranean Forests, Woodlands, and Shrub
These areas have hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. Plants here are often adapted to drought.
Africa
- Fynbos (South Africa)
Australia
- Southwestern Australia forests and scrub
North America
South America
Europe
Deserts and Xeric Shrublands
These are very dry areas with little rainfall. Plants and animals here are specially adapted to survive with little water.
Africa
- Namib-Karoo-kaokoveld deserts
- Madagascar spiny thicket
North America
- Sonoran-Baja deserts
- Chihuahuan-Tehuacan deserts
South America
- Galapagos Islands scrub
- Atacama-Sechura deserts
Europe and Asia
- Central Asian deserts
Mangroves
Mangroves are special trees and shrubs that grow in salty coastal waters, often where rivers meet the sea. They are important nurseries for many sea creatures.
Africa
- Gulf of Guinea mangroves
- East African mangroves
Asia
- Sundarbans mangroves (India, Bangladesh)
- Greater Sundas mangroves (Indonesia, Malaysia)
South and Central America
- Guianan-Amazon mangroves
- Panama Bight mangroves
Global 200: Freshwater Ecoregions
These are important rivers, lakes, and wetlands.
Large Rivers
These are huge rivers that flow across continents.
Africa
- Congo River (Democratic Republic of Congo)
Asia
- Mekong River (China, Vietnam, Thailand, etc.)
- Yangtze River (China)
North America
- Colorado River (USA, Mexico)
- Lower Mississippi River (USA)
South America
- Amazon River (Brazil, Peru, Colombia)
- Orinoco River (Venezuela, Colombia)
Large River Headwaters
These are the areas where large rivers begin, often in mountains or highlands.
Africa
- Congo basin piedmont rivers and streams
North America
- Mississippi piedmont rivers and streams
South America
Large River Deltas
These are flat, low-lying areas where a river splits into many channels before flowing into the sea. They are very rich in wildlife.
Africa
- Niger River delta (Nigeria)
Asia
- Indus River Delta (India, Pakistan)
- Mesopotamian delta and marshes (Iran, Iraq)
Europe
- Volga River Delta (Russia)
- Danube River delta (Romania, Ukraine, etc.)
Small Rivers
These are smaller rivers and streams that are still very important for their unique wildlife.
Africa
- Madagascar freshwater
- Cape rivers and streams (South Africa)
Australia and Pacific Islands
- New Guinea rivers and streams
- New Caledonia rivers and streams
- Kimberley rivers and streams (Australia)
Asia
- Western Ghats Rivers and Streams (India)
- Sundaland rivers and swamps (Malaysia, Indonesia)
North America
- Southeastern rivers and streams (USA)
- Pacific Northwest coastal rivers and streams (USA)
South America
- Guianan freshwater
- Greater Antillean freshwater (Cuba, Dominican Republic)
Large Lakes
These are very big lakes that are home to many unique species.
Africa
- Rift Valley lakes (Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, etc.)
South America
- High Andean lakes (Peru, Bolivia)
Europe and Asia
- Lake Baikal (Russia)
- Lake Biwa (Japan)
Small Lakes
Even smaller lakes can be very important for nature.
Africa
- Cameroon crater lakes
Australia and Pacific Islands
- Lakes Kutubu and Sentani (Papua New Guinea)
Asia
- Inle Lake (Myanmar)
- Yunnan lakes and streams (China)
North America
- Mexican highland lakes
Xeric Basins
These are dry areas where rivers and streams don't flow to the ocean, but instead dry up or flow into inland lakes.
Australia
- Central Australian freshwater
North America
- Chihuahuan freshwater (Mexico, USA)
Global 200: Marine Ecoregions
These are important ocean areas.
Polar Seas
These are the very cold waters near the North and South Poles.
Antarctic Ocean
- Antarctic Peninsula & Weddell Sea
Arctic Ocean
- Bering Sea (USA, Russia)
- Barents-Kara Sea (Norway, Russia)
Temperate Shelves and Seas
These are cooler ocean areas over continental shelves, where the water is not too deep.
Mediterranean Sea
- Mediterranean Sea (many countries around it)
North Temperate Atlantic
- Northeast Atlantic Shelf Marine (Europe)
- Grand Banks (Canada, USA)
North Temperate Indo-Pacific
- Yellow Sea (China, Korea)
- Sea of Okhotsk (Japan, Russia)
Southern Ocean
- Patagonian Southwest Atlantic (Argentina, Brazil)
- New Zealand Marine
Temperate Upwelling Areas
Upwelling is when cold, nutrient-rich water from the deep ocean rises to the surface. This brings lots of food for marine life.
North Temperate Indo-Pacific
- California Current (USA, Mexico)
South Temperate Atlantic
- Benguela Current (Namibia, South Africa)
South Temperate Indo-Pacific
- Humboldt Current (Chile, Peru)
Tropical Upwelling Areas
These are warm ocean areas where upwelling also brings nutrients to the surface.
Eastern Indo-Pacific
- Gulf of California (Mexico)
- Galápagos Marine (Ecuador)
Tropical Coral Reefs
Coral reefs are like underwater cities built by tiny animals called corals. They are home to an amazing variety of fish and other sea creatures.
Central Indo-Pacific
- Sulu-Sulawesi Seas (Indonesia, Philippines)
- Great Barrier Reef (Australia)
- Palau Marine
Eastern Indo-Pacific
- Hawaiian Marine
- Fiji Barrier Reef
Western Indo-Pacific
- Maldives, Chagos, and Lakshadweep atolls
- Red Sea (Egypt, Saudi Arabia, etc.)
- East African Marine
Western Tropical Atlantic
- Mesoamerican Reef (Belize, Mexico)
- Greater Antillean Marine (Cuba, Jamaica, etc.)
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Global 200 para niños
In Spanish: Global 200 para niños