Germanic peoples facts for kids
The Germanic peoples were groups of people who lived in Northern Europe. They are known for speaking Germanic languages, which include languages like English, German, Dutch, and the Scandinavian languages. Over time, these groups moved across Europe. They mixed with local people like the Celts and Romans. This mixing helped form many of the nations we know today, which share similar languages and histories.
The word Germani was first used by Julius Caesar, a famous Roman leader. However, the Germanic tribes themselves did not have one single name for all Germanic-speaking people. In English, the word German first appeared in the 1500s.
Contents
Who Were the Germanic Tribes?
By the 1st century A.D., Roman writers like Caesar and Tacitus described different groups of Germanic-speaking peoples. These groups lived in specific areas:
- Near the Oder and Vistula rivers in what is now Poland. These were the East Germanic tribes.
- Along the lower Rhine river. These were called the Istvaeones.
- Near the Elbe river. These were known as the Irminones.
- In Jutland (part of Denmark) and the Danish islands. These were the Ingvaeones.
The Istvaeones, Irminones, and Ingvaeones are often called the West Germanic tribes. Other Germanic people who stayed in Scandinavia are known as North Germanic tribes. Each of these groups developed their own ways of speaking. This led to the different Germanic languages we hear today. It's important to know that these divisions (West, East, and North Germanic) are modern ways that language experts classify these groups.
How Were They Organized?
The Germanic tribes were independent. Each tribe had its own leader, often a king who inherited their position. These kings often claimed they were related to mythical founders of their tribes. Some of these mythical founders include:
- Angul for the Angles
- Burgundus for the Burgundians
- Dan for the Danes
- Gothus for the Goths
- Longobardus for the Lombards
- Saxneat for the Saxons
- Suiones for the Swedes
History of the Germanic Peoples
Where Did They Come From?
The early Germanic tribes spoke similar dialects, meaning they could mostly understand each other. They also shared a common culture and mythology. We know this from old stories like Beowulf and the Volsunga saga.
Unlike the Romans, who built a large empire and united many peoples, the Germanic tribes mostly remained independent. They were led by their own chosen or hereditary leaders.
Images for kids
-
Roman bronze statuette representing a Germanic man with his hair in a Suebian knot
-
The Roman province of Germania, in existence from 7 BCE to 9 CE. The dotted line represents the Limes Germanicus, the fortified border constructed following the final withdrawal of Roman forces from Germania.
-
A bog body, the Osterby Man, displaying the Suebian knot, a hairstyle which, according to Tacitus, was common among Germanic warriors.
-
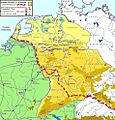
Germanic kingdoms and peoples after the end of the Western Roman Empire in 476 CE
-
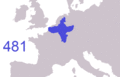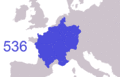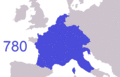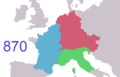
Frankish expansion from the early kingdom of Clovis I (481) to the divisions of Charlemagne's Empire (843/870)
-
The Sutton Hoo helmet from c. 625 in the British Museum.
-
Roughly carved wooden idols from Oberdorla moor, modern Thuringia. The idols were found in context with animal bones and other evidence of sacrificial rites.
-
Page from the Codex Argenteus containing the Gothic Bible translated by Wulfila.
-
The Istaby Stone (DR359) is a runestone that features a Proto-Norse Elder Futhark inscription describing three generations of men. Their names share the common element of 'wolf' (wulfaz) and alliterate.
-
Image of Romans fighting the Marcomanni on the Column of Marcus Aurelius (193 CE).
-
A 5th-century CE gold collar from Ålleberg, Sweden. It displays Germanic filigree work.
-
The Minerva Bowl, part of the Hildesheim Treasure, likely a Roman diplomatic gift. The treasure may date from the reign of Nero (37–68 CE) or the early Flavian dynasty (69–96 CE).
See also
 In Spanish: Pueblos germánicos para niños
In Spanish: Pueblos germánicos para niños