History of spaceflight facts for kids
Spaceflight started in the 1900s thanks to big ideas from scientists like Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, Robert H. Goddard, and Hermann Oberth. They all wrote about using rockets to travel to space. The first successful large rocket programs were started in Nazi Germany by Wernher von Braun.
After World War II, the Soviet Union led the way in the Space Race. They launched the first satellite, the first animal, the first human, and the first woman into orbit. The United States made history by landing the first people on the Moon in 1969. Later in the 20th century, countries like France, the United Kingdom, Japan, and China also began working on their own space projects.
After the Space Race ended, countries started working together more in space. It became cheaper to reach low Earth orbit, and more private companies got involved. Space probes have visited every planet in our Solar System. Humans have also lived in space for long periods on space stations like Mir and the ISS. More recently, China became the third country to send its own astronauts into space. Private companies have also developed rockets that can be reused and spacecraft launched from planes. In 2020, SpaceX became the first private company to successfully send astronauts to the International Space Station with their Crew Dragon Demo-2 mission.
Contents
- Early Ideas and First Steps
- The Space Race Begins
- Spaceflight Diversifies
- New Competition in Space
- Space Programs by Country
- Images for kids
- See also
Early Ideas and First Steps
At the start of the 1900s, many scientists became interested in space travel. They were inspired by exciting stories from writers like Jules Verne (who wrote From the Earth to the Moon) and H.G. Wells (who wrote The War of the Worlds).
The first real plan for spaceflight was written by Konstantin Tsiolkovsky in 1903. His book was called The Exploration of Cosmic Space by Means of Reaction Devices.
Space travel became possible for engineers thanks to Robert H. Goddard's work in 1919. He showed how to use a special nozzle with liquid fuel rockets to create enough power for space travel. His ideas greatly influenced Hermann Oberth and Wernher von Braun, who later became very important in spaceflight.
In 1929, a Slovene officer named Hermann Noordung was the first to imagine a complete space station in his book The Problem of Space Travel.
The first rocket to reach space was the German V-2 rocket in June 1944. After World War II, the British launched a few more V-2 rockets to study them.
In 1947, the US sent the first animals in space, which were fruit flies, using a V-2 rocket. On June 14, 1949, the US launched the first mammal into space, a monkey named Albert II. Sadly, Albert II did not survive the landing. On July 22, 1951, the Soviets launched two dogs, Dezik and Tsygan, who were the first dogs in space to return safely.
The Space Race Begins
The Space Race was a competition between the United States and the Soviet Union to achieve milestones in space exploration.
First Satellites in Orbit

The race officially began in 1957. Both the US and the USSR announced plans to launch artificial satellites. On October 4, 1957, the Soviet Union launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite to orbit Earth.
On November 3, 1957, the Soviet Union launched Sputnik 2, which carried the first living animal into orbit, a dog named Laika. Sputnik 3 was launched in May 1958 and carried many instruments to study Earth's upper atmosphere.
After some failed attempts, the US launched its first satellite, Explorer 1, on February 1, 1958. This satellite discovered the Van Allen radiation belt. The launch of Sputnik 1 shocked the US public, leading to the creation of NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) in 1958. NASA then started Project Mercury to send single astronauts into Earth orbit.
First Human in Space
On April 12, 1961, the USSR made history by sending the first cosmonaut (Russian word for space traveler), Yuri Gagarin, into space. Gagarin's flight, part of the Soviet Vostok program, lasted 108 minutes and completed one orbit around Earth.
On August 7, 1961, Gherman Titov, another Soviet cosmonaut, became the second person to orbit Earth during his Vostok 2 mission. He orbited Earth 17 times in over 25 hours. By June 1963, the USSR had launched six Vostok cosmonauts into space.
On May 5, 1961, the US launched its first astronaut, Alan Shepard, on a suborbital flight in the Freedom 7 capsule.
First Woman in Space
The first woman in space was Valentina Tereshkova, a former parachutist. She orbited Earth on June 16, 1963, aboard the Soviet mission Vostok 6.
Space Race Heats Up
The Soviet Union tried to quickly achieve more space firsts. They modified the Vostok capsule to fit two or three people, calling it Voskhod. Only two of these missions were launched. Voskhod 1 was the first spacecraft with a crew of three. On March 8, 1965, Alexei Leonov performed the first spacewalk from Voskhod 2. He had trouble getting back into the spacecraft because his suit inflated.
The US Gemini missions, launched in 1965 and 1966, helped the US catch up. They achieved important goals like space rendezvous (meeting another spacecraft in orbit) and docking (connecting two spacecraft). They also showed that astronauts could do useful work outside a spacecraft during extra-vehicular activity (EVA).
Both nations faced tragedies in early 1967. On January 27, the entire crew of Apollo 1 (Gus Grissom, Ed White, and Roger Chaffee) died in a fire during a ground test. On April 24, the pilot of Soyuz 1, Vladimir Komarov, died when his landing parachutes failed. Both accidents were caused by design flaws, which were fixed before more crewed flights.
Exploring Venus
On February 12, 1961, the Soviet spacecraft Venera 1 was the first probe launched to another planet (Venus), but it lost contact. Venera 3 was the first human-made object to touch another planet when it crashed into Venus in 1966. Later Venera probes successfully entered Venus's atmosphere and even landed.
In 1970, Venera 7 was the first spacecraft to send back data after landing on another planet. Venera 9 sent back the first photos from the surface of Venus in 1975. In 1981, Venera 13 drilled into Venus's surface and took a sample. It also recorded sounds from Venus, a first.
The first successful flyby of Venus was by the American Mariner 2 spacecraft in 1962. It found that Venus has almost no magnetic field and a very hot atmosphere (around 500°C).
Human Missions to the Moon
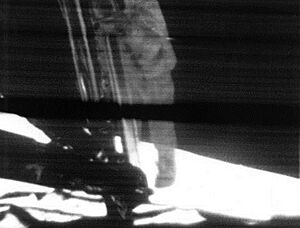
The US sent the first crewed mission to orbit the Moon with Apollo 8 on December 21, 1968. Then, on July 20, 1969, Apollo 11 achieved President Kennedy's goal of landing humans on the Moon. Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin were the first people to walk on the Moon. Six successful Moon landings happened through 1972, with one mission, Apollo 13, having a major problem but returning safely.
The later Apollo missions (Apollo 15, 16, and 17) used a special lunar rover. This allowed astronauts to explore much farther and collect more Moon rocks. More Moon landings were planned, but public interest decreased after Apollo 11, and NASA's budget was cut.
The Soviet Union also tried to reach the Moon with their large N1 rocket, but it failed four times. They officially stopped their human lunar program in 1974.
Moving Towards Cooperation
After the Moon race, both nations launched smaller, temporary space laboratories: the Soviet Salyut stations and the US Skylab. They used their Soyuz and Apollo spacecraft to ferry crews. The US launched one Skylab, while the USSR launched seven Salyut stations.
The Space Race officially ended on July 17, 1975, with the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The two spacecraft docked in orbit, and their crews visited each other. This showed a new era of cooperation.
Spaceflight Diversifies

From the very beginning, private companies and other countries besides the US and Soviet Union were involved in spaceflight. The first commercial satellite was launched in 1962. By 1965, a third country achieved orbital spaceflight. The launch of Sputnik itself was part of an international scientific year. Soon, countries started creating international laws for outer space.
In the 1970s, the Soviet Union invited other countries to send their people into space through its Intercosmos program. The United States also started including women and people of color in its astronaut program.
The US and Soviet Union slowly began sharing more information and working together. This led to the Apollo-Soyuz mission, which paved the way for the Shuttle-Mir program and eventually the International Space Station programme. This international cooperation grew as more countries gained spaceflight abilities and private companies became more involved. By the 1990s, space exploration seemed more common to the public.
New Competition in Space
Starting in the 2010s, the space sector became more competitive again. Some call this a New Space Race, especially with China's fast progress and other Asian countries advancing their spaceflight achievements.
Even with new competition, international cooperation and private spaceflight are still important. For example, Axiom Space works with different countries for private human spaceflight, often using the International Space Station. Private companies like Space-X with its Starlink satellites have also become important in international politics.
Many new lunar spaceflight programs are being planned, often as international projects. These include the Artemis program (led by the US), China and Russia's plans for a lunar base, and the European Space Agency's planned Moon Village. This mix of competition and international commercial development is often called New Space.
Space Programs by Country
| Orbital human spaceflight (beyond Kármán line) | |||
| Program | Years | Flights | First Crewed Flight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vostok | 1961–1963 | 6 | Vostok 1 |
| Mercury | 1962–1963 | 4 | Mercury-Atlas 6 |
| Voskhod | 1964–1965 | 2 | Voskhod 1 |
| Gemini | 1965–1966 | 10 | Gemini 3 |
| Soyuz | 1967–present | 141 | Soyuz 1 |
| Apollo | 1968–1972 | 11 | Apollo 7 |
| Skylab | 1973–1974 | 3 | Skylab 2 |
| Apollo-Soyuz | 1975 | 1 | Apollo-Soyuz |
| Space Shuttle | 1981–2011 | 135 | STS-1 |
| Shenzhou | 2003–present | 6 | Shenzhou 5 |
| Crew Dragon | 2020–present | 11 | Demo-2 |
| Suborbital human spaceflight | |||
| Program | Year | Flights | |
| Mercury | 1961 | 2 | Mercury 3 |
| X-15 | 1963 | 2 | Flight 90 |
| Soyuz 18a | 1975 | 1 | Soyuz 18a |
| SpaceShipOne | 2004 | 3 | Flight 15P |
| SpaceShipTwo | 2018–present | 3 | VP03 |
United States Space Programs
Until the 2000s, space programs in the United States were run only by government agencies. In the 21st century, several private aerospace companies began to develop their own space industries, with SpaceX being one of the most successful.
NASA's Early Missions
NASA is the main US government agency for space exploration.
Project Mercury: First Americans in Orbit
Project Mercury was the first US program to send humans into space, from 1958 to 1963. Its goal was to put an American into Earth orbit and bring them back safely, ideally before the Soviet Union. John Glenn became the first American to orbit Earth on February 20, 1962.
Project Gemini: Learning to Maneuver in Space
Project Gemini was NASA's second human spaceflight program, from 1961 to 1966. This program taught astronauts how to perform orbital maneuvers and how to meet and connect spacecraft in orbit. Ed White became the first American to do a "spacewalk" (EVA) in 1965. Gemini missions also achieved the first space rendezvous and docking of two spacecraft.
Apollo Program: Landing on the Moon
The Apollo program was NASA's third human spaceflight program. Its main goal was to land crewed vehicles on the Moon. The program ran from 1969 to 1972. Apollo 8 was the first human spaceflight to leave Earth orbit and go around the Moon in 1968. Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first people to walk on the Moon during the Apollo 11 mission in 1969.
Skylab: America's First Space Station
Skylab was NASA's first space station. It was launched in 1973. Many experiments were done on board, including studies of the Sun. The longest mission on Skylab lasted 84 days. Skylab eventually fell from orbit in 1979.
Space Shuttle: Reusable Spacecraft
Space exploration continued after the Space Race. The United States launched the first reusable spacecraft, the Space Shuttle, on April 12, 1981. The Soviet Union also launched its own reusable shuttle, Buran, in 1988, but it only flew once.
Sally Ride became the first American woman in space in 1983. Eileen Collins was the first female Shuttle pilot and the first woman to command a US spacecraft in 1999. The US continued missions to the ISS with the Space Shuttle until it was retired in 2011.
Soviet Union Space Programs
The Soviet space program was the space exploration program of the former Soviet Union.
Sputnik: First Earth Satellite
Sputnik 1 became the first artificial Earth satellite on October 4, 1957. It sent a radio signal back to Earth, allowing scientists to study the upper atmosphere. Sputnik 1 broadcast for 21 days before its batteries ran out.
Luna Program: Exploring the Moon
The Luna program was a series of uncrewed robotic missions to study the Moon, from 1959 to 1976. It achieved many firsts and collected data on the Moon's chemistry, gravity, temperature, and radiation. Luna 2 was the first human-made object to reach the Moon's surface in 1959. Luna 3 sent back the first photos of the far side of the Moon in 1959.
Vostok Program: First Humans in Space
The Vostok Program was the first Soviet project to send people into low Earth orbit and bring them back safely. It carried out six crewed flights between 1961 and 1963. Yuri Gagarin became the first man in space on April 12, 1961, aboard Vostok 1. Gherman Titov was the first person to stay in orbit for a full day. Valentina Tereshkova became the first woman in space on June 16, 1963.
Voskhod Program: Multi-Person Crews and Spacewalks
The Voskhod program began in 1964 and had two crewed flights. Voskhod 1 was the first crewed spaceflight with more than one person. Alexei Leonov performed the first spacewalk from Voskhod 2 in 1965.
Salyut Program: First Space Stations
The Salyut program was the Soviet Union's first space station program, from 1971 to 1986. Its goal was to study how people live in space for long periods and to do scientific experiments. Salyut 1 became the world's first crewed space station.
Soyuz Program: Long-Lasting Spacecraft
The Soyuz program started in the 1960s and is still active today, run by Roscosmos (Russia's space agency). It has completed over 140 flights. Since the US Space Shuttle retired, Soyuz has been the only spacecraft to transport humans to the International Space Station.
Mir: A Long-Term Space Station
Mir was a Soviet (and later Russian) space station that operated from 1986 to 2001. It was the first modular space station, meaning it was built piece by piece in orbit. Mir was used for many scientific experiments and hosted astronauts and cosmonauts from many different countries.
International Space Station (ISS)
Recent space exploration has involved a lot of worldwide cooperation, especially with the building and operation of the International Space Station (ISS). The ISS is a huge orbiting laboratory where astronauts from many countries live and work together.
The United States continues to be a major partner in the ISS. Russia, as a successor to the Soviet Union, also has a significant space program. They provide commercial launch services and support the ISS with their own modules and spacecraft.
European Space Agency (ESA)
The European Space Agency (ESA) has been a leader in commercial uncrewed launches. ESA has launched many satellites, used the Spacelab module on US shuttles, and sent probes to comets and Mars. It also participates in the ISS with its own module and cargo spacecraft. ESA is working on future plans, including a program to develop its own crewed spacecraft.
China's Space Program
China has had a space program since 1956. They launched their first satellite, "Dong Fang Hong I", in 1970. China has made great progress in space activities, especially since the early 2000s. They have developed a large family of Long March rockets, including the powerful Long March 5. China launched over 140 spaceflights between 2015 and 2020. They operate many satellite systems for communication, Earth imaging, weather forecasting, and navigation (like their BeiDou Navigation Satellite System).
China's Human Spaceflight Program
The China Manned Space Program began in 1992. After Shenzhou 5, their first successful crewed spaceflight in 2003, China became the third country with its own human spaceflight capability. They have developed important skills like spacewalks and docking spacecraft. China's modular orbital station, the Tiangong space station, became fully operational in November 2022 and has been continuously crewed since then. It has three main modules: Tianhe core module, Wentian module, and Mengtian module. The station conducts scientific experiments and supports China's goals for a lunar research base.
China's Lunar Exploration Program
The Chinese Lunar Exploration Program started in 2004. It launched two lunar orbiters, Chang'e 1 and Chang'e 2. On December 14, 2013, China successfully landed its Chang'e 3 Moon lander and its rover Yutu on the Moon, becoming the first Asian country to do so. This was followed by Chang'e 4, the first landing on the far side of the Moon, in 2019. In 2020, Chang'e 5 brought back samples from the Moon, a first for an Asian country. China plans to build a permanent International Lunar Research Station on the Moon.
China's Planetary Exploration
China's first attempt at interplanetary exploration was in 2011 with Yinghuo-1, a Mars orbiter, but it failed. In July 2020, China launched Tianwen-1, which included an orbiter, a lander, and a rover, to Mars. Tianwen-1 successfully entered Mars orbit in February 2021 and landed the Zhurong rover on Mars in May 2021. This made China the second country to successfully land a fully working spacecraft on Mars.
Japan's Space Program
Japan's space agency, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), is a major player in Asia. Japan has a module on the ISS and operates an uncrewed cargo spacecraft. JAXA's Hayabusa probe was the first to bring samples back from an asteroid. IKAROS was the first working solar sail. Japan plans to launch a new crewed spacecraft by 2025 and establish a Moon base by 2030.
India's Space Program
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), India's national space agency, has an active space program. It operates a commercial launch service and launched a successful uncrewed lunar mission, Chandrayaan-1, in 2007. India successfully launched an interplanetary mission, the Mars Orbiter Mission, in 2013, reaching Mars in 2014. This made India the first country to succeed in a Mars mission on its first try. In 2019, India sent Chandrayaan-2 to the Moon.
Other Nations in Space
Astronauts and cosmonauts from many other nations have flown in space. The first was Vladimir Remek from the Czech Republic in 1978. As of 2013, over 536 people from 38 countries have traveled into space.
Private Space Companies
Private companies are playing a growing role in spaceflight.
SpaceX (USA)
SpaceX is a private company that has developed fully reusable rockets like Starship. Starship consists of a first stage called Super Heavy and a second stage also named Starship.
Blue Origin
Blue Origin made the first reusable suborbital rocket booster, New Shepard. They are also leading a team to design a lunar lander.
Bigelow Aerospace
Bigelow Aerospace made the first commercial inflatable module in space (BEAM). They also designed and built the first inflatable habitats in space.
Northrop Grumman
Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems makes commercial supply runs to the ISS with their Cygnus spacecraft. They also helped develop spacecraft during the Space Race.
United Launch Alliance
United Launch Alliance is a joint venture between Boeing and Lockheed Martin that provides launch services for the US government.
Arianespace
Arianespace is a European company that provides launch services for satellites.
Rocket Lab
Rocket Lab is a company that develops and launches small rockets for small satellites.
Images for kids
-
The number of spacewalks required to construct the International Space Station dwarfed the then existing experience base for this activity, a hurdle called the "Wall of EVA."
-
Description of a space station in Hermann Noordung's The Problem of Space Travel (1929).
See also
 In Spanish: Historia de los vuelos espaciales para niños
In Spanish: Historia de los vuelos espaciales para niños