Lamborghini facts for kids
 |
|

Headquarters in Sant'Agata Bolognese, Italy
|
|
| Subsidiary | |
| Industry | Automotive |
| Founded | 1963 |
| Founder | Ferruccio Lamborghini |
| Headquarters |
Sant'Agata Bolognese, Emilia-Romagna
,
Italy
|
|
Number of locations
|
135 dealerships |
|
Area served
|
Worldwide |
|
Key people
|
Stephan Winkelmann (CEO) |
|
Production output
|
|
| Revenue | |
|
Operating income
|
|
| Total equity | |
|
Number of employees
|
1,779 (December 2020) |
| Parent | Audi AG |
| Subsidiaries | Ducati Motor Holding S.p.A. Italdesign Giugiaro |
Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A. (often called Lamborghini or Lambo) is an Italian company. It makes very fancy sports cars and SUVs. The company is based in Sant'Agata Bolognese, Italy. It is owned by the Volkswagen Group through its company Audi.
Ferruccio Lamborghini (1916–1993) was an Italian businessman. He started Automobili Ferruccio Lamborghini S.p.A. in 1963. He wanted to build cars that could compete with Ferrari's cars. Lamborghini cars became known for having their engine in the middle-back and power going to the back wheels.
Lamborghini grew quickly in its first ten years. But sales dropped a lot after the 1973 worldwide money problems and the oil crisis. The company changed owners three times after 1973. It even went bankrupt in 1978.
American company Chrysler Corporation took over Lamborghini in 1987. They sold it to a Malaysian and an Indonesian group in 1994. In 1998, these groups sold Lamborghini to the Volkswagen Group. Volkswagen put Lamborghini under the control of its Audi division.
New cars and models were created, and the company became more productive. In the late 2000s, during a big economic downturn, Lamborghini's sales dropped by almost half.
As of 2025, Lamborghini makes the Temerario plug-in hybrid sports car. It also produces the Urus SUV and the Revuelto hybrid supercar. The company also builds powerful V12 engines for offshore powerboat racing boats.
There is also a company called Lamborghini Trattori. It was started in 1948 by Ferruccio Lamborghini. This company makes tractors and is based in Pieve di Cento, Italy. Since 1973, Lamborghini Trattori has been a separate company from the car division.
Contents
The Story of Lamborghini Cars
Ferruccio Lamborghini was a successful businessman. He started the car company in 1963. His goal was to make fancy touring cars that could compete with brands like Ferrari.
The company's first cars, like the 350 GT, came out in the mid-1960s. Lamborghini became famous for the 1966 Miura sports car. This car had its engine placed in the middle-back, which was very special.
Ferruccio Lamborghini founded Lamborghini Automobili on May 7, 1963. He was already a successful maker of tractors, boilers, and air conditioners.
The company's main office was built in Sant'Agata Bolognese. Ferruccio hired very talented engineers. Giotto Bizzarrini designed the engine. Gian Paolo Dallara and Paolo Stanzani worked on the car's frame. Franco Scaglione designed the car's look.
The first model, the 350 GTV, was a unique prototype. It had a very futuristic style. The design was then given to Touring, a company in Milan. They created a more classic design. This new car was called the 350 GT. It was a fast and elegant two-seater car. It was the first Lamborghini car made in large numbers. It sold pretty well and was followed by the 400 GT and 400 GT 2+2 in 1966.
Lamborghini grew fast for its first ten years. But sales dropped because of money problems and an oil crisis in 1973. Ferruccio Lamborghini sold the company to Georges-Henri Rossetti and René Leimer. He then retired in 1974.
The company went bankrupt in 1978. Brothers Jean-Claude and Patrick Mimran took over in 1980. The Mimrans bought the company in 1984 and invested a lot of money. Under their leadership, Lamborghini added more models. These included the Jalpa sports car and the LM002 off-road vehicle.
The Mimrans sold Lamborghini to the Chrysler Corporation in 1987. Chrysler replaced the Countach with the Diablo. They also stopped making the Jalpa and LM002. Chrysler then sold Lamborghini to a Malaysian and an Indonesian group in 1994. In 1998, these groups sold Lamborghini to the Volkswagen Group. It was then put under the control of Volkswagen's Audi division.
New cars and models were created, which made Lamborghini more productive. In the late 2000s, during a big economic downturn, Lamborghini's sales dropped by almost half.
In 2021, Lamborghini's CEO said that by 2024, all its models would be hybrid cars.
| Years | Owner |
|---|---|
| 1963–1972 | Ferruccio Lamborghini |
| 1972–1977 | Georges-Henri Rossetti and René Leimer |
| 1977–1984 | Receivership (company managed by others) |
| 1984–1987 | Patrick Mimran |
| 1987–1994 | Chrysler Corporation |
| 1994–1995 | MegaTech |
| 1995–1998 | V'Power and Mycom Sedtco |
| 1998–present | Audi AG |
Lamborghini Products
Automobiles
As of 2018, Lamborghini makes three types of cars. Two are mid-engine two-seat sports cars. The third is a front-engine, all-wheel-drive SUV.
Current Models
- Revuelto
The new Revuelto started being made in mid-2023. It was delivered in late 2023 as a 2024 model. It has a 6.5-liter V12 engine and three electric motors. Together, they make 1,001 horsepower. The Revuelto took the place of the Aventador.
- Temerario
The Temerario is a mid-engine plug-in hybrid sports car. It was officially shown on August 16, 2024.
- Urus
Lamborghini wanted to double its sales by 2019. So, they added an SUV called the Urus to their lineup. It has a V8 engine and is an all-wheel-drive vehicle.
Marine Engines
Motori Marini Lamborghini makes large V12 marine engines. These are used in World Offshore Series Class 1 powerboats. A Lamborghini marine engine is about 8.17 liters in size. It produces around 940 horsepower.
Lamborghini Motorcycle
In the mid-1980s, Lamborghini made a small number of 1,000 cc sports motorcycles. Only 24 of these were made. They had a special Lamborghini alloy frame. The engine was from a Kawasaki GPz1000RX. These motorcycles were designed by Lamborghini stylists. They were built by a French company called Boxer Bikes.
Branded Merchandise
Lamborghini lets other companies use its brand name. These companies make many Lamborghini-branded items. These include small model cars, clothes, bags, and laptop computers.
Motorsport Activities
|
Trade name
|
Squadra Corse |
|---|---|
| Subsidiary | |
| Industry |
|
| Headquarters |
Sant'Agata Bolognese
,
Italy
|
|
Area served
|
Worldwide |
|
Key people
|
|
| Owner | Automobili Lamborghini |
| Parent | Audi AG |
Cars for Racing
Lamborghini's Motorsport Division, called Squadra Corse, builds GT3 cars. They also make cars for their Super Trofeo races. These cars are based on the Gallardo and Huracán models. Squadra Corse also builds special cars for customers who ask for them.
GT3 and Super Trofeo Cars
- Gallardo LP 570-4 Super Trofeo
- Gallardo LP 560-4 Super Trofeo
- Huracán LP 620-2 Super Trofeo EVO
- Huracán LP 620-2 Super Trofeo EVO2
- Huracán Super Trofeo GT2
- Huracán GT3
- Huracán GT3 Evo
- Huracán GT3 Evo 2
Special Cars
These cars were built by Squadra Corse for specific customers.
- Essenza SCV12
- SC18 Alston
- SC20
Racing Events
Lamborghini Super Trofeo
The Super Trofeo is a series of races organized by Squadra Corse. They use their Super Trofeo cars, which are racing versions of road cars. Currently, they use the Huracán Super Trofeo EVO.
These events are held in three different series: America, Asia, and Europe. Many private racing teams take part in these races.
Each series has six rounds. Each round includes practice, qualifying, and two 50-minute races. There are four driver categories: Pro, Pro-Am, Am, and Lamborghini Cup. The season ends with the Lamborghini Super Trofeo World Final.
Lamborghini GT3
The Lamborghini GT3 is another series of races. Squadra Corse uses Huracán GT3 cars for these events. These cars follow the rules set by the FIA GT3. Any customer with a Huracán GT3 car can join these races.
Lamborghini currently uses Huracán GT3 Evo cars for these events. More than 60 private racing teams participate.
Racecars Over the Years
| Year | Car | Image | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1986 | Lamborghini Countach QVX |  |
Group C1 |
| 1988 | Lamborghini Countach 5000QV | Group B | |
| 1991 | Lambo 291 |  |
Formula 1 |
| 1998 | Lamborghini Diablo 132 GT1 |  |
Group GT1 |
| 2004 | Lamborghini Murciélago R-GT |  |
Group GT |
| 2005 | Lamborghini Murciélago RG-1 |  |
GT500 GT300 |
| 2006 | Lamborghini Gallardo LP520 GT3 |  |
Group GT3 |
| 2007 | Lamborghini Gallardo |  |
GT300 |
| 2009 | Lamborghini Gallardo LP 560 GT2 |  |
LM GTE |
| 2010 | Lamborghini Gallardo LP600+ GT3 |  |
Group GT3 |
| Lamborghini Murciélago LP 670 R-SV |  |
Group GT1 | |
| 2014 | Lamborghini Huracán LP 620-2 Super Trofeo | Lamborghini Super Trofeo | |
| 2015 | Lamborghini Huracán GT3 | Group GT3 | |
| 2019 | Lamborghini Huracán GT3 Evo |  |
Group GT3 |
| Lamborghini Huracán LP 620-2 Super Trofeo EVO | Lamborghini Super Trofeo | ||
| 2020 | Lamborghini Huracán Super Trofeo GT2 |  |
SRO GT2 |
| 2022 | Lamborghini Huracán GT3 Evo 2 |  |
Group GT3 |
| Lamborghini Huracán LP 620-2 Super Trofeo EVO2 |  |
Lamborghini Super Trofeo | |
| 2024 | Lamborghini SC63 |  |
LMDh |
Lamborghini in Formula One
| Notable staff | Mauro Forghieri |
|---|---|
| Formula One World Championship career | |
| First entry | 1989 Brazilian Grand Prix |
| Last entry | 1993 Australian Grand Prix |
| Races entered | 80 |
| Chassis | Lola, Lotus, Lambo, Ligier, Minardi, Venturi, Larrousse |
| Constructors' Championships | 0 |
| Drivers' Championships |
0 |
| Race victories | 0 |
| Podiums | 1 |
| Points | 20 |
| Pole positions | 0 |
| Fastest laps | 0 |
Unlike his rival Enzo Ferrari, Ferruccio Lamborghini decided early on not to have factory racing teams. He thought racing was too expensive and used too many company resources. This was unusual because many sports car makers showed off their speed and technology through racing.
Ferruccio's decision caused some tension with his engineers. Many of them loved racing and had worked at Ferrari before. When engineers started working on the P400 prototype in their free time, they designed it for both racing and road use. Ferruccio found out but let them continue. He saw it as a way to promote the company, but he insisted it would not be raced. The P400 later became the famous Miura.
The closest Lamborghini came to building a real race car under Ferruccio was a few modified prototypes. These included cars built by test driver Bob Wallace.
In the mid-1970s, Lamborghini agreed to help BMW build 400 cars for racing. Lamborghini had financial problems and fell behind schedule. BMW took over the project and finished the car themselves. BMW named the car the M1.
In 1985, Lamborghini's British importer developed the Countach QVX for the 1986 Group C championship. Only one car was built. It raced only once in South Africa. But without enough money from sponsors, the project was stopped.
Lamborghini supplied engines for Formula One races from 1989 to 1993. They provided engines to teams like Larrousse, Lotus, Ligier, and Minardi. They also supplied engines to the Modena team in 1991. Lamborghini saw itself as an engine supplier, not a racing team owner.
The 1992 Larrousse-Lamborghini car was not very competitive. It was known for spraying oil from its exhaust. Lamborghini's best result was in 1990. Aguri Suzuki finished third at the Japanese Grand Prix with a Larrousse car.
In 1991, a Lamborghini Formula One engine was used in a sports car called the Konrad KM-011. But the project was soon canceled. The same engine, rebranded as a Chrysler engine, was tested by McLaren in late 1993. McLaren considered using it for the 1994 season. Driver Ayrton Senna liked the engine's power. But McLaren chose a Peugeot engine instead, and Chrysler ended the project.

Two racing versions of the Diablo were made for the Diablo Supertrophy. This was a special racing series held from 1996 to 1999. Lamborghini also developed the Murciélago R-GT. This was a racing car for the FIA GT Championship and other races in 2004. In 2006, a Murciélago R-GT won its first race in Japan. A GT3 version of the Gallardo was also developed. In 2007, a Murciélago R-GT won a major international race in China. This was Lamborghini's first big international win.
Lamborghini Brand and Names
Brand Identity
The world of bullfighting is a very important part of Lamborghini's identity. In 1962, Ferruccio Lamborghini visited a ranch in Spain. It belonged to Don Eduardo Miura, a famous breeder of Spanish fighting bulls. Ferruccio was so impressed by these strong bulls. He decided to use a charging bull as the symbol for his new car company.
Car Names
After making two cars with numbers and letters, Lamborghini looked to the bull breeder again for ideas. Don Eduardo was very proud when Ferruccio named a car after his family and their bulls. The fourth Miura car made was shown to him at his ranch.
The car company continued to use bullfighting names for many years. The Islero was named after the bull that killed the famous bullfighter Manolete in 1947. Espada is the Spanish word for sword, sometimes used for the bullfighter. The Jarama's name had two meanings. It referred to a historic bullfighting area in Spain. Ferruccio also worried about confusion with the Jarama motor racing track.
After naming the Urraco after a bull breed, Lamborghini changed tradition in 1974. They named the Countach not after a bull, but after a word from the Piedmontese language. It's said that Nuccio Bertone said the word in surprise when he first saw the Countach prototype. The LM002 SUV and the Silhouette were other exceptions to the bullfighting names.
The Jalpa (1982) was named after a bull breed. Diablo was named after a fierce bull famous for a battle in 1869. Murciélago was a legendary bull whose life was saved in 1879. Gallardo was named after one of the oldest types of Spanish fighting bulls. Reventón was the bull that defeated a young Mexican bullfighter in 1943. The Estoque concept car (2008) was named after the sword used by bullfighters.
Concept Cars
Throughout its history, Lamborghini has shown many concept cars. These are special cars made to show new ideas. The first was the 350GTV prototype in 1963. Other famous ones include the 1967 Marzal and the 1974 Bravo.
A retro-style Lamborghini Miura concept car was shown in 2006. The company's CEO said it was a way to celebrate their history. But he said Lamborghini is about the future, so they would not make a new Miura.
At the 2008 Paris Motor Show, Lamborghini showed the Estoque. This was a four-door sedan concept. Lamborghini has not decided if they will produce this car.

At the 2010 Paris Motor Show, Lamborghini showed the Sesto Elemento. This concept car is made almost entirely of carbon fiber. This makes it very light, weighing only 999 kg. The Sesto Elemento has the same V10 engine as the Lamborghini Gallardo. Lamborghini hopes this car shows a new direction for the company. They want to make more agile, track-focused cars, not just cars focused on top speed. This concept car can go from 0 to 100 km/h in 2.5 seconds. It can reach a top speed of over 290 km/h.
At the 2012 Geneva Motor Show, Lamborghini showed the Aventador J. This was a version of the Lamborghini Aventador without a roof or windows. It used the same powerful engine as the standard Aventador.
At the 2012 Beijing Motor Show, Lamborghini showed the Urus SUV. This was the first SUV built by Lamborghini since the LM002.
To celebrate 50 years of Lamborghini, the company created the Egoista. The Egoista is designed for only one person to drive. Only one Egoista was made.
At the 2014 Paris Motor Show, Lamborghini showed the Asterion LPI910-4 hybrid concept car. It was named after a creature from Greek stories that was half-man, half-bull. This was the first hybrid Lamborghini ever. It combined the Huracán's V10 engine with three electric motors. Together, they produced 907 horsepower. The car could go from 0 to 100 km/h in just over 3 seconds. Its top speed was about 298 km/h.
How Lamborghini Works
Company Structure
As of 2011, Lamborghini is a company fully owned by Audi AG. Its full name is Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A.
Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A. controls five main smaller companies. These include Ducati Motor Holding S.p.A., which makes motorcycles. It also controls Italdesign Giugiaro S.p.A., a design company. MML S.p.A. makes marine engines. Volkswagen Group Italia S.p.A. sells Audi and other Volkswagen Group cars in Italy.
The main Lamborghini office and factory are in Sant'Agata Bolognese, Italy. When they started making the Urus SUV, the factory size doubled. It grew from 80,000 square meters to 160,000 square meters.
On November 13, 2020, Stephan Winkelmann became the new CEO of Lamborghini. He was also the President of Bugatti. He started his new job on December 1, 2020.
Sales Numbers
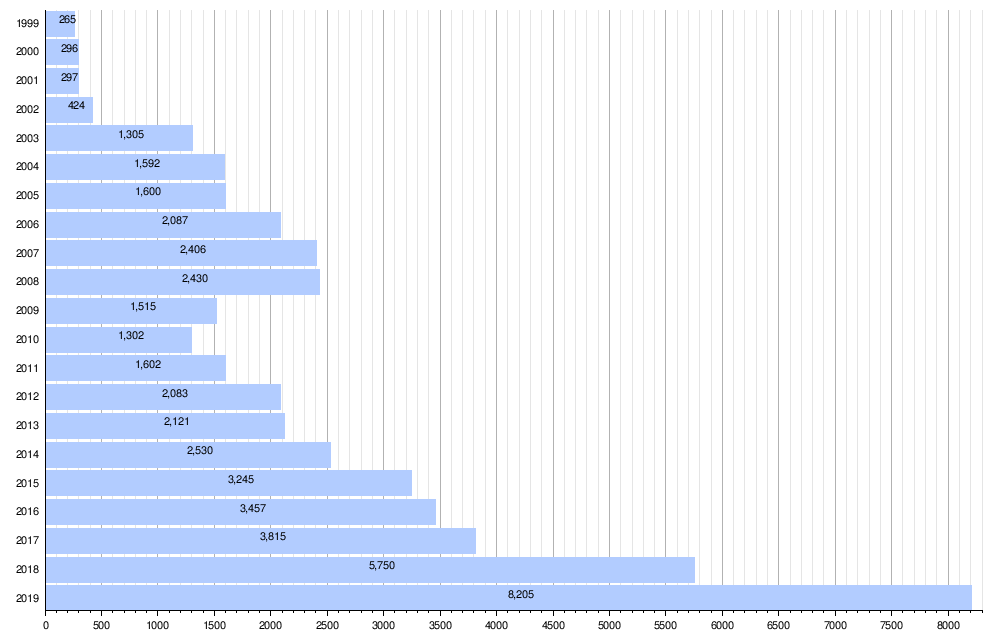
In 2004, the most important markets for Lamborghini sports cars were the U.S. (41%), Germany (13%), Great Britain (9%), and Japan (8%). Before the Gallardo car came out in 2003, Lamborghini made about 400 cars each year. In 2011, Lamborghini made 1,711 cars.
- Annual Lamborghini New Car Sales
| Year | Sales |
|---|---|
| 1968 | 353 |
| Data missing | |
| 1991 | 673 |
| 1992 | 166 |
| 1993 | 215 |
| Data missing | |
| 1996 | 211 |
| 1997 | 209 |
| Data missing | |
| 1999 | 265 |
| Year | Sales |
|---|---|
| 2000 | 296 |
| 2001 | 297 |
| 2002 | 424 |
| 2003 | 1,305 |
| 2004 | 1,592 |
| 2005 | 1,600 |
| 2006 | 2,087 |
| 2007 | 2,406 |
| 2008 | 2,430 |
| 2009 | 1,515 |
| Year | Sales |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 1,302 |
| 2011 | 1,602 |
| 2012 | 2,083 |
| 2013 | 2,121 |
| 2014 | 2,530 |
| 2015 | 3,245 |
| 2016 | 3,457 |
| 2017 | 3,815 |
| 2018 | 5,750 |
| 2019 | 8,205 |
 |
Licensing and Other Ventures
Lamborghini in Latin America
Automóviles Lamborghini Latinoamérica S.A. de C.V. is a company that sells and makes Lamborghini-branded cars and products in Latin America and South America.
In 1995, MegaTech, which owned Lamborghini at the time, made a deal with a Mexican businessman. This deal gave Automóviles Lamborghini Latinoamérica the only right to sell Lamborghini cars and products in Latin America. It also allowed them to make Lamborghini cars and sell them worldwide.
Automóviles Lamborghini has made two special versions of the Diablo car. These were called the Eros and the Coatl. The company has also announced plans to make a speedboat called the Lamborghini Glamour.
Lamborghini Museums
There are two museums in Bologna, Italy, that are all about the Lamborghini brand.
Museo Lamborghini
This museum has two floors and is next to the main Lamborghini office. It shows the history of Lamborghini cars and SUVs. You can see many modern and old models. The museum uses cars, engines, and photos to tell the story of Lamborghini's important moments.
Museo Ferruccio Lamborghini
This museum is about Ferruccio Lamborghini himself. It is 9,000 square feet in size. It has several cars, industrial prototypes, drawings, personal items, and family photos from Ferruccio's early life.
See also
 In Spanish: Lamborghini para niños
In Spanish: Lamborghini para niños
- Automotive industry in Italy
- List of automobile manufacturers of Italy
- List of companies of Italy
















