This page is about
WWF classifications. For an alternate classification system, see Ecozones of Canada.
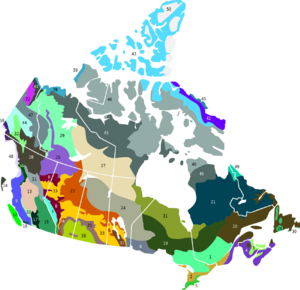
Terrestrial ecoregions of Canada
Imagine Canada as a giant puzzle! This article lists the different "puzzle pieces" called ecoregions in Canada. An ecoregion is a large area of land or water. It has its own special mix of plants, animals, and ecosystems. These areas are identified by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF). They help us understand and protect nature.
Land Ecoregions: Canada's Natural Zones
Canada has many different land ecoregions. They are all part of a bigger area called the Nearctic realm. This realm covers most of North America. The Nearctic realm, along with the Palearctic realm in Europe and Asia, forms the Holarctic realm. This huge area covers the northern half of the world.
British Columbia is Canada's most diverse province. It has 18 different ecoregions! These regions spread across four main types of natural areas, called biomes. On the other hand, Prince Edward Island is much smaller. It has only one ecoregion. This single ecoregion, called the Gulf of St. Lawrence lowland forests, covers the whole island.
What are Biomes?
A biome is a very large natural area. It has a specific climate, plants, and animals. Think of it as a major type of habitat. Canada has several biomes, from cold tundras to vast forests.
Canada's Terrestrial Ecoregions by Biome
Here's a look at the different land ecoregions you can find in Canada. They are grouped by their main biome type.
| Biome |
Ecoregion |
Province/Territory |
| Boreal forests/taiga |
Central Canadian Shield forests |
Ontario, Quebec |
| Boreal forests/taiga |
Eastern Canadian forests |
New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Quebec |
| Boreal forests/taiga |
Eastern Canadian Shield taiga |
Newfoundland and Labrador, Quebec |
| Boreal forests/taiga |
Interior Alaska–Yukon lowland taiga |
Yukon |
| Boreal forests/taiga |
Mid-Continental Canadian forests |
Alberta, Manitoba, Northwest Territories, Saskatchewan |
| Boreal forests/taiga |
Midwestern Canadian Shield forests |
Alberta, Manitoba, Ontario, Saskatchewan |
| Boreal forests/taiga |
Muskwa–Slave Lake forests |
Alberta, British Columbia, Northwest Territories |
| Boreal forests/taiga |
Newfoundland Highland forests |
Newfoundland and Labrador |
| Boreal forests/taiga |
Northern Canadian Shield taiga |
Alberta, Manitoba, Northwest Territories, Nunavut, Saskatchewan |
| Boreal forests/taiga |
Northern Cordillera forests |
British Columbia, Northwest Territories, Yukon |
| Boreal forests/taiga |
Northwest Territories taiga |
Northwest Territories, Yukon |
| Boreal forests/taiga |
South Avalon–Burin oceanic barrens |
Newfoundland and Labrador |
| Boreal forests/taiga |
Southern Hudson Bay taiga |
Manitoba, Ontario, Quebec |
| Boreal forests/taiga |
Yukon Interior dry forests |
British Columbia, Yukon |
| Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests |
Eastern forest–boreal transition |
Ontario, Quebec |
| Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests |
Eastern Great Lakes lowland forests |
Ontario, Quebec |
| Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests |
Gulf of St. Lawrence lowland forests |
New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Quebec |
| Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests |
New England–Acadian forests |
New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Quebec |
| Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests |
Southern Great Lakes forests |
Ontario |
| Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests |
Western Great Lakes forests |
Manitoba, Ontario |
| Temperate coniferous forests |
Alberta Mountain forests |
Alberta, British Columbia |
| Temperate coniferous forests |
Alberta–British Columbia foothills forests |
Alberta, British Columbia |
| Temperate coniferous forests |
British Columbia mainland coastal forests |
British Columbia |
| Temperate coniferous forests |
Cascade Mountains leeward forests |
British Columbia |
| Temperate coniferous forests |
Central British Columbia Mountain forests |
British Columbia |
| Temperate coniferous forests |
Central Pacific coastal forests |
British Columbia |
| Temperate coniferous forests |
Fraser Plateau and Basin complex |
British Columbia |
| Temperate coniferous forests |
Haida Gwaii forests |
British Columbia |
| Temperate coniferous forests |
North Central Rockies forests |
Alberta, British Columbia |
| Temperate coniferous forests |
Northern transitional alpine forests |
British Columbia |
| Temperate coniferous forests |
Okanagan dry forests |
British Columbia |
| Temperate coniferous forests |
Puget lowland forests |
British Columbia |
| Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands |
Canadian aspen forests and parklands |
Alberta, British Columbia, Manitoba, Saskatchewan |
| Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands |
Montana valley and foothill grasslands |
Alberta |
| Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands |
Northern mixed grasslands |
Manitoba, Saskatchewan |
| Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands |
Northern short grasslands |
Alberta, Saskatchewan |
| Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands |
Northern tall grasslands |
Manitoba |
| Tundra |
Alaska–St. Elias Range tundra |
British Columbia, Yukon |
| Tundra |
Arctic coastal tundra |
Northwest Territories, Yukon |
| Tundra |
Baffin coastal tundra |
Nunavut |
| Tundra |
Brooks–British Range tundra |
Northwest Territories, Yukon |
| Tundra |
Davis Highlands tundra |
Nunavut |
| Tundra |
High Arctic tundra |
Northwest Territories, Nunavut |
| Tundra |
Interior Yukon–Alaska alpine tundra |
Yukon |
| Tundra |
Low Arctic tundra |
Manitoba, Northwest Territories, Nunavut, Quebec |
| Tundra |
Middle Arctic tundra |
Northwest Territories, Nunavut, Quebec |
| Tundra |
Ogilvie–MacKenzie alpine tundra |
Northwest Territories, Yukon |
| Tundra |
Pacific Coastal Mountain icefields and tundra |
British Columbia, Yukon |
| Tundra |
Torngat Mountain tundra |
Newfoundland and Labrador, Quebec |
Marine Ecoregions: Canada's Ocean Zones
Canada is special because it touches three huge ocean areas. These are called marine realms. They include the Arctic Ocean, the Temperate Northern Atlantic, and the Temperate Northern Pacific.
These large ocean realms are divided even further. They contain three main types of marine biomes. Within these biomes, there are fifteen unique marine ecoregions. These divisions are based on the distinct types of sea life found in each area.
Did you know that Quebec is the only province that touches two different ocean realms? It borders both the Arctic and the Temperate Northern Atlantic realms!
Canada's Marine Ecoregions by Biome
Here are the different marine ecoregions found in Canada's waters. They are grouped by their main ocean biome.
| Biome |
Ecoregion |
Province/Territory |
| Arctic |
Baffin Bay-Davis Strait |
Nunavut |
| Arctic |
Beaufort - Amundsen - Viscount Melville - Queen Maud |
Northwest Territories, Nunavut |
| Arctic |
Beaufort Sea continental coast and shelf |
Northwest Territories, Yukon |
| Arctic |
High Arctic Archipelago |
Northwest Territories, Nunavut |
| Arctic |
Hudson Complex |
Manitoba, Nunavut, Ontario, Quebec |
| Arctic |
Lancaster Sound |
Nunavut |
| Arctic |
Northern Grand Banks - Southern Labrador |
Newfoundland and Labrador |
| Arctic |
Northern Labrador |
Newfoundland and Labrador, Nunavut |
| Cold temperate northeast Pacific |
North American Pacific Fjordland |
British Columbia |
| Cold temperate northeast Pacific |
Oregon, Washington, Vancouver coast and shelf |
British Columbia |
| Cold temperate northeast Pacific |
Puget Trough/Georgia Basin |
British Columbia |
| Cold temperate northwest Atlantic |
Gulf of Maine - Bay of Fundy |
New Brunswick, Nova Scotia |
| Cold temperate northwest Atlantic |
Gulf of St. Lawrence - Eastern Scotian Shelf |
New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Quebec |
| Cold temperate northwest Atlantic |
Scotian Shelf |
Nova Scotia |
| Cold temperate northwest Atlantic |
Southern Grand Banks - South Newfoundland |
Newfoundland and Labrador |
See also
- Canadian Arctic tundra
- Forests of Canada
- List of ecoregions in the United States (WWF)


