Lowndes County, Georgia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Lowndes County
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|

Lowndes County Courthouse in Valdosta
|
|||
|
|||
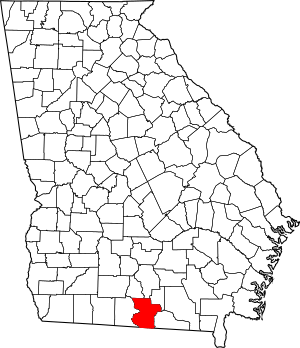
Location within the U.S. state of Georgia
|
|||
 Georgia's location within the U.S. |
|||
| Country | |||
| State | |||
| Founded | December 23, 1825 | ||
| Named for | William Jones Lowndes | ||
| Seat | Valdosta | ||
| Largest city | Valdosta | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 511 sq mi (1,320 km2) | ||
| • Land | 496 sq mi (1,280 km2) | ||
| • Water | 15 sq mi (40 km2) 2.8%% | ||
| Population | |||
| • Estimate
(2022)
|
120,055 | ||
| • Density | 220/sq mi (80/km2) | ||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | ||
| Congressional districts | 1st, 8th | ||
Lowndes County is a county located in the southern part of Georgia, a state in the United States. In 2020, about 118,251 people lived here. The main city and county seat is Valdosta. The county was officially created on December 23, 1825.
Lowndes County is part of the Valdosta metropolitan area, which means it's a busy region with many towns and cities connected together. It's also right next to the border with Florida.
This county is an important place for business, education, and making things in south Georgia. It's well-known for its forest products, like wood for paper (pulpwood) and natural tree sap products (naval stores) such as turpentine and rosin. A large wetland area called Grand Bay, which is about 13,000 acres, is also partly located in Lowndes County.
Contents
History of Lowndes County
Early People and Spanish Influence
Long ago, the land that is now Lowndes County was home to the Timucua people. When Europeans started exploring and settling, this area became part of Spanish Florida. From around 1625 to 1657, the Spanish built a Catholic mission called Santa Cruz de Cachipile here. It was located in the southern part of the county, near what is now Lake Park. Over time, the Timucua people faced many challenges, including illnesses and conflicts, which sadly reduced their population.
Later, the Creek Nation peoples moved into the area. By the early 1800s, they were well established. On December 15, 1818, European Americans formed Irwin County, which included land that had been home to the Creek people. In the 1830s, the government moved most Native Americans from these lands, a process known as Indian Removal.
How the County Began
Lowndes County was officially created by Georgia's government on December 23, 1825. It was formed from parts of Irwin County, Georgia. The county was named after William Jones Lowndes, a well-known lawyer and Congressman from South Carolina. His father, Rawlins Lowndes, was a leader during the American Revolutionary War.
The Coffee Road was an important path that helped settlers move into the area. It was first made by Georgia soldiers to supply troops in Florida during the Creek Wars. This road was the first route through what became Lowndes County.
In the early years, the county's courts met at Sion Hall's tavern on the Coffee Road. The first official county seat (the main town for government) was set up at Franklinville on December 16, 1828. Franklinville was named after Benjamin Franklin, a famous American leader.
In 1830, Lowndes County had about 2,455 people. This included 2,116 white people, 335 enslaved people, and 4 free people of color. As steam-powered boats became popular on the Withlacoochee and Little rivers, more people started living closer to the rivers. In 1833, a new county seat was planned called Lowndesville, but these plans were later changed.
By 1836, a new town called Troupville was chosen as the county seat. A brick courthouse was built there. Troupville grew because people thought a railroad would come through and because the surrounding farmland was good. In 1845, the remaining land in Franklinville was sold.
The last major conflict between Native Americans and white settlers near Troupville happened at Brushy Creek in 1836. After this, very few Native Americans remained in South Georgia.
In 1850, Lowndes County lost some land when Clinch County was formed. The county's eastern border became the Alapaha River. By 1850, the population had grown to 7,714 people, including 5,339 free white people, 20 free people of color, and 2,355 enslaved people. Lowndes County lost more land in 1856 when Berrien and Colquitt counties were created.
The Rise of Valdosta
Many people in Lowndes County were upset when the Atlantic and Gulf Railroad announced in 1858 that its tracks would not go through Troupville. Soon after, the courthouse in Troupville was burned down.
In August 1858, people decided to create a new county called Brooks County from the western part of Lowndes County. Brooks County was formed in December. Then, Echols County, Georgia was also created in December 1858.
In 1859, the county decided to buy land for a new county seat along the railroad line. This new place became Valdosta. The railroad's arrival made Valdosta grow into a major economic center for south Georgia, while Troupville became less important. By 1860, Lowndes County's population was 5,249, including 2,850 free white people and 2,399 enslaved people.
Lowndes County During the Civil War
No battles were fought in Lowndes County during the American Civil War. However, many men from the county joined the Confederate Army. Some of the companies formed here included:
- Company I "Lowndes Volunteers"
- Company G, 26th Regiment Georgia Infantry
- Company D, "Valdosta Guards"
Local State Guard and Militia units were also formed. In 1863 and 1864, some women in the area protested because they couldn't get enough food or supplies. For example, in Stockton, women took yarn from a store when the owner wouldn't accept Confederate money.
In February 1864, some soldiers camped in Valdosta on their way to the Battle of Olustee in Florida. This was the closest fighting came to Valdosta. As the war continued, many people fleeing from other parts of Georgia, like Sherman's March to the Sea, found safety in Valdosta. The family of the famous dentist Doc Holliday was among these refugees.
After the War: Reconstruction and Changes
After the Civil War, during a time called the Reconstruction era, some soldiers from the United States Colored Troops were stationed in Valdosta.
Several years later, in 1871 and 1872, about 112 African American men, women, and children from Lowndes County moved to Arthington, Liberia. This was a colony in West Africa created for free American blacks. Their move was supported by the American Colonization Society. Some stayed there permanently, while a few returned to the United States.
Before 1872, the southern border of Lowndes County and Georgia was a little different. There was a disagreement over the border between Florida and Georgia. In 1872, the United States Congress agreed on a new border line, which is the one we have today.
20th Century and Beyond
In 1899, the town of Remerton, which had a cotton mill, was established. In 1920, Lowndes County lost some land again when Lanier County was created.
During World War II, on September 15, 1941, Moody Air Force Base opened in the county. This brought more federal money and development to the region.
Geography
Lowndes County covers a total area of about 511 square miles. Most of this (496 square miles) is land, and about 15 square miles (2.8%) is water.
The county is part of the Suwannee River basin. This means that the rivers and streams in Lowndes County eventually flow into the Suwannee River. Key rivers in the county include the Withlacoochee River, the Little River, and the Alapaha River.
Neighboring Counties
Lowndes County shares borders with several other counties:
- Berrien County (north)
- Lanier County (northeast)
- Echols County (east)
- Hamilton County, Florida (southeast)
- Madison County, Florida (southwest)
- Brooks County (west)
- Cook County (northwest)
Major Waterways
- Alapaha River
- Alapahoochee River
- Grand Bay Creek
- Little River (Withlacoochee River)
- Withlacoochee River (Suwannee River)
Communities in Lowndes County
Cities
Town
Census-Designated Places
These are areas that are like towns but are not officially incorporated as cities or towns.
- Bemiss
- Moody AFB
Other Communities
These are smaller, unincorporated communities:
- Blanton
- Clyattville
- Franklinville (a historic community)
- Indianola
- Kinderlou
- Mineola
- Old Clyattville
- Olympia (a historic community)
- Ousley
- Naylor
- Troupville (a historic community)
- Twin Lakes
Population Over Time
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1830 | 2,453 | — | |
| 1840 | 5,574 | 127.2% | |
| 1850 | 7,714 | 38.4% | |
| 1860 | 5,249 | −32.0% | |
| 1870 | 8,321 | 58.5% | |
| 1880 | 11,049 | 32.8% | |
| 1890 | 15,102 | 36.7% | |
| 1900 | 20,036 | 32.7% | |
| 1910 | 24,436 | 22.0% | |
| 1920 | 26,521 | 8.5% | |
| 1930 | 29,994 | 13.1% | |
| 1940 | 31,860 | 6.2% | |
| 1950 | 35,211 | 10.5% | |
| 1960 | 49,270 | 39.9% | |
| 1970 | 55,112 | 11.9% | |
| 1980 | 67,972 | 23.3% | |
| 1990 | 75,981 | 11.8% | |
| 2000 | 92,115 | 21.2% | |
| 2010 | 109,233 | 18.6% | |
| 2020 | 118,251 | 8.3% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 120,712 | 10.5% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790-1880 1890-1910 1920-1930 1930-1940 1940-1950 1960-1980 1980-2000 2010 |
|||
Lowndes County is a diverse place. Here's a look at the different groups of people living there, based on the 2020 census:
| Race | Number of People | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| White | 59,306 | 50.15% |
| Black or African American | 43,946 | 37.16% |
| Native American | 312 | 0.26% |
| Asian | 1,908 | 1.61% |
| Pacific Islander | 100 | 0.08% |
| Other/Mixed | 4,807 | 4.07% |
| Hispanic or Latino | 7,872 | 6.66% |
In 2020, there were 118,251 people living in Lowndes County. These people lived in 42,639 households, and 26,536 of these were families.
Courthouses of Lowndes County
The county's former courthouse, built around 1905, is a historic building listed on the National Register of Historic Places. It was the seventh courthouse the county had.
The first courthouse was built in 1828 in Franklinville, the original county seat. In 1834, a new courthouse was built in Troupville. This was replaced by another new courthouse in 1842. Sadly, the 1842 building was destroyed by a fire in June 1858.
The first courthouse in Valdosta was built in 1860. It was made of wood. This building was later sold to help pay for a new one. In 1869, the wooden building used for the courts burned down. For a few years, Lowndes County didn't have an official courthouse. A new brick building was finished in 1874.
By 1900, county leaders decided they needed an even bigger building. The old courthouse was taken down in March 1904, and the seventh courthouse was finished in 1905. This is the beautiful building that many people today call 'the old courthouse.' In 2010, the county government moved to a new judicial complex.
The 1905 Lowndes County Courthouse is known as one of the most beautiful courthouses in Georgia. Today, it's used for many community events, meetings, and public displays.
Education in Lowndes County
Students in Lowndes County attend different schools depending on where they live. If they live outside the Valdosta city limits, they go to schools in the Lowndes County School District. If they live within Valdosta, they attend schools in the Valdosta City School District. The main high schools are Lowndes High School and Valdosta High School.
Valwood School is a private school located in the county.
For higher education, Valdosta State University is in Valdosta.
The South Georgia Regional Library system provides library services to the county's residents.
Transportation
Major Highways
 Interstate 75
Interstate 75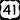 U.S. Route 41
U.S. Route 41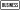
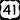 U.S. Route 41 Business
U.S. Route 41 Business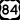 U.S. Route 84
U.S. Route 84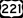 U.S. Route 221
U.S. Route 221 State Route 7
State Route 7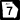 State Route 7 Alternate
State Route 7 Alternate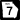 State Route 7 Business
State Route 7 Business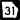 State Route 31
State Route 31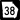 State Route 38
State Route 38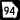 State Route 94
State Route 94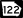 State Route 122
State Route 122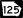 State Route 125
State Route 125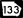 State Route 133
State Route 133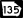 State Route 135
State Route 135 State Route 376
State Route 376 State Route 401 (this is the hidden name for I-75)
State Route 401 (this is the hidden name for I-75)
Walking and Biking Paths
- Azalea City Trail
- VSU Walking Trail System
Railroads
Past Railroads
- Atlantic Coast Line Railroad
- Atlantic and Gulf Railroad
- Atlantic, Valdosta and Western Railway
- Georgia Southern Railroad
- Georgia Southern and Florida Railway
- Plant System
- Savannah, Florida and Western Railway
- Valdosta, Moultrie and Western Railroad
Current Railroads
Today, the railroads in Lowndes County are only used for moving goods (freight). There are no passenger trains like Amtrak that stop directly in the county. The closest Amtrak stops are about 100 miles away in Folkston and Jesup.
- CSX Transportation
- Georgia and Florida Railroad
- Norfolk Southern Railway
- Valdosta Railway
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Lowndes (Georgia) para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Lowndes (Georgia) para niños







