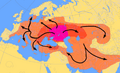
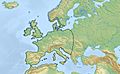
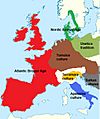
Bronze Age Europe facts for kids
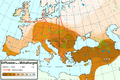
The European Bronze Age was a time when people in Europe started using bronze to make tools, weapons, and jewelry. Bronze is a strong metal made by mixing copper and tin. This period came after the Neolithic (New Stone Age) and before the Iron Age. It began around 3200 BC in some parts of Europe, like the Aegean region, and lasted until about 600 BC in others, like Northern Europe. During this time, many different cultures developed across Europe, each with their own unique ways of life and bronze creations.
| European Bronze Age | |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Contents
History of Bronze in Europe

Early Bronze Discoveries
Scientists found that early bronze was used in the Balkans (southeastern Europe) even earlier than thought. A study in 2013 found a piece of tin bronze from Pločnik (archaeological site) dating back to about 4650 BC! This means people in Europe were making complex bronze items about 1500 years before similar items appeared in the Near East. However, this early bronze making stopped for a while in the Balkans. It was reintroduced much later.
Bronze Age in the Aegean Sea Region
The Aegean Bronze Age started around 3200 BC. This was when people in areas like Crete and mainland Greece began to trade a lot. They brought tin and charcoal to Cyprus, where they mined copper. They mixed these to make bronze. Bronze objects were then traded far and wide. Some bronze items found in the Mediterranean Sea even had tin from as far away as Great Britain!
People at this time were very good at navigation. They could sail across long distances, a skill that wasn't matched again until much later, except by Polynesian sailors.
Around 1500 BC, a huge volcano erupted on the island of Thera. This event caused the Minoan culture to decline. This gave the Mycenaeans from mainland Greece a chance to become powerful. By 1450 BC, they controlled Crete and many other islands. The Mycenaeans were great builders and engineers. They also traded widely across the Mediterranean. Their writing system, called Linear B, gives us the first written records of the Greek language. Their religion included many gods that are still known today, like the Twelve Olympians. Mycenaean society was led by powerful warriors and kings, called wanax.
Bronze Age in Italy
The Bronze Age in Italy is split into four main parts:
- Early Bronze Age (2300–1700 BC)
- Middle Bronze Age (1700–1350 BC)
- Recent Bronze Age (1350–1150 BC)
- Final Bronze Age (1150–950 BC)
On the island of Sardinia, the Nuragic civilization thrived during the second millennium BC. These people built more than 7000 huge stone towers called Nuraghe. They also built special temples, giant tombs called Giants' graves, and holy wells. They made many bronze tools and weapons, and even beautiful bronze statues using a special technique called "lost wax casting." The Nuragic culture continued into the early Iron Age.
Bronze Age in Eastern Europe
The Yamnaya culture was important in Eastern Europe from about 3600 to 2300 BC. These people were mostly nomads, meaning they moved around a lot with their animals. They also did some farming near rivers.
The Catacomb culture came after the Yamnaya. They were known for their special pottery with cord patterns and for using polished battle axes. This culture helped connect Eastern Europe with the West.
Bronze Age in Central Europe
In Central Europe, the early Bronze Age saw the rise of the Unetice culture (1800–1600 BC). Some very rich burials, like one found at Leubingen in Germany, show that some people in the Unetice culture were very powerful and wealthy.
After the Unetice culture came the Tumulus culture (1600–1200 BC). These people buried their dead in large mounds of earth called tumuli or barrows.
The late Bronze Age saw the Urnfield culture (1300–700 BC). This culture is known for burning their dead and placing their ashes in urns (pots) before burying them in large fields. The Lusatian culture in eastern Germany and Poland was part of the Urnfield culture and continued into the Iron Age.
Important sites from this period include:
- Biskupin in Poland
- Nebra in Germany (where the famous Nebra sky disk was found!)
- Zug-Sumpf in Switzerland
- Vráble in Slovakia
Bronze Age in Northern Europe
In northern Germany, Denmark, Sweden, and Norway, people during the Bronze Age made many unique and artistic items. These include lur horns (musical instruments), helmets with horns for ceremonies, and gold jewelry. Some experts believe that an early form of the Germanic languages was introduced to this area around 2000 BC.
Bronze Age in Britain
In Great Britain, the Bronze Age lasted from about 2100 to 700 BC. New people arrived on the islands from mainland Europe. Studies of teeth from graves near Stonehenge show that some of these newcomers came from what is now Switzerland. These new people, often called the Beaker people, brought different customs.
The climate in Britain also changed during this time. It became much wetter, forcing people to move from the hills to the fertile valleys. Large farms for livestock grew in these lowlands, which helped the economy.
Cornwall was a very important source of tin for much of western Europe. Copper was also mined in places like the Great Orme mine in northern Wales. Society became more complex, with different groups and leaders.
A big change was how people buried their dead. In earlier times, many people were buried together in large tombs. But in the Early Bronze Age, people started burying individuals in their own small mounds, also called barrows.
The largest collections of bronze objects in England were found in East Cambridgeshire, especially at Isleham, where over 6500 pieces were discovered!
Bronze Age in Atlantic Europe
The Atlantic Bronze Age (around 1300–700 BC) was a time of strong trade and cultural connections along the Atlantic coasts of Europe. This included parts of Portugal, Spain, France, Great Britain, and Ireland. People in these coastal areas shared similar cultures, often building cliff castles and round houses. Trade routes stretched from Sweden all the way to the Mediterranean Sea.
Ireland's Bronze Age began around 2000 BC when copper was first mixed with tin to make items like flat axes. Before this, people used pure copper. The Irish Bronze Age is divided into:
- Early Bronze Age (2000–1500 BC)
- Middle Bronze Age (1500–1200 BC)
- Late Bronze Age (1200–c. 500 BC)
Ireland is also known for having many Early Bronze Age burials.
Other pages to explore
Images for kids
-
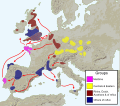
The influence of the Bell Beaker culture.
-
The Trundholm sun chariot from Denmark, around 1400 BC.
-
The Nebra sky disk from Germany, 1800 BC.
-
A bronze boat model from Sardinia, around 1000 BC.
-
A gold diadem from Spain, around 1600 BC.
-
A bronze chariot wheel from Romania, around 1000 BC.
-
A cult chariot model from Serbia, 1300 BC.
-
Gold lunula and discs from Ireland, around 2200 BC.
-
A marble figurine from the Cycladic Islands, 2700 BC.
-
A bronze collar from Sweden, around 1400 BC.
-
A bronze dagger from Switzerland, around 2000 BC.
-
The Valchitran treasure from Bulgaria, around 1300 BC.
-
Bronze axes and armrings from Poland, around 1000 BC.
-
A gold necklace from Belgium, around 1000 BC.
-
A bronze shield from Czech Republic, around 1200 BC.
-
A bronze sword from Austria, around 1300 BC.
-
A gold bull figurine from the North Caucasus, around 3200 BC.