Renewable energy in the United States facts for kids
Renewable energy sources in 2022. Renewables were 8.4% of total energy, or 8.3 quads. Biomass (61.1%) Wind (17.8%) Hydro (10.5%) Solar (9.2%) Geothermal (1.4%)
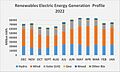
Renewable electricity sources in 2022. Renewables were 21% of total electricity, or 907 TWh. Wind (45.1%) Hydro (26.5%) Solar (21.3%) Biomass (5.4%) Geothermal (1.7%)
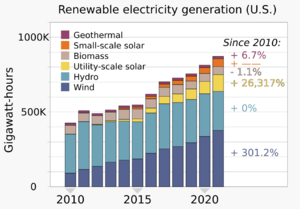
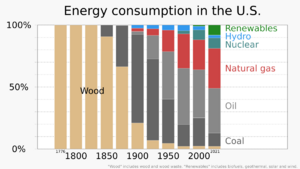
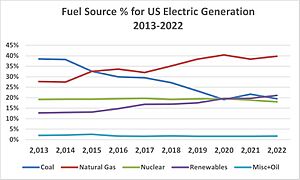
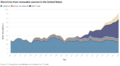
Renewable energy comes from natural sources that refill themselves. These include sunlight, wind, water, and heat from inside the Earth. In 2022, renewable energy made up 8.4% of all energy produced in the United States. It also generated 21% of the country's electricity.
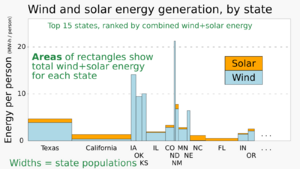
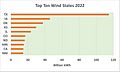
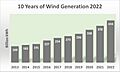
Since 2019, wind power has been the top source of renewable electricity in the U.S. In 2022, wind farms produced 434 terawatt-hours of electricity. This was 10% of the nation's total electricity. By January 2023, the U.S. had enough wind power capacity to generate 141.3 gigawatts (GW). Texas leads the country in wind power. Iowa and Oklahoma are also big wind power states.
Hydroelectric power is the second-largest renewable electricity source. It uses the power of moving water. In 2022, it generated about 6.2% of the nation's electricity. The United States is the fourth-largest producer of hydroelectricity in the world. Only China, Canada, and Brazil produce more.
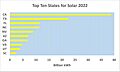
Solar power is also growing fast. In 2022, solar energy provided about 3.4% of the country's total electricity. This was up from 2.8% the year before. Over 260,000 people worked in the solar industry in 2020. Many states use "net metering." This means energy companies buy back extra power from homes with solar arrays. Large solar farms in the U.S. include Mount Signal Solar and Solar Star. The U.S. also uses solar thermal power. This technology uses the sun's heat to make electricity. The Ivanpah Solar Power Facility is a large solar thermal plant.
Other renewable energy sources include geothermal energy. This uses heat from deep inside the Earth. The Geysers in Northern California is the world's largest geothermal power complex.
In 2009, President Barack Obama called for more renewable energy. He wanted to double renewable energy use within three years. By 2011, renewable energy produced more electricity than nuclear power for the first time since 1997. President Joe Biden later set a goal to approve 25 GW of renewable energy projects on public land by 2025. By May 2023, about 37% of this goal had been met.
Contents
- Why We Need Renewable Energy
- Renewable Energy and Carbon Dioxide
- How Renewable Energy Is Growing
- Future Plans for Renewable Energy
- Types of Renewable Electricity Sources
- Solar Water Heating
- Biofuels
- Renewable Energy Research
- Jobs in Renewable Energy
- Policies for Renewable Energy
- Renewable Energy Organizations
- Community Renewable Energy
- Potential Resources
- Images for kids
- See also
Why We Need Renewable Energy
Renewable energy technologies are very diverse. They include solar panels, solar thermal power plants, wind farms, hydroelectricity, geothermal power plants, and ocean power systems. They also include using biomass.
A report called Outlook On Renewable Energy In America explains why the U.S. needs renewable energy. It says America needs energy that is safe and reliable. It should also improve public health and protect the environment. Renewable energy helps fight climate change and creates jobs. It also helps the U.S. lead in new technologies.
One great thing about wind and solar power is that they use little or no water. Other power plants, like those using fossil fuels, need huge amounts of water.
In 2009, President Barack Obama spoke about using more renewable energy. He said it would help with energy security and climate change. He wanted the U.S. to "harness the sun and the winds and the soil to fuel our cars and run our factories." His plan called for renewable energy to provide 10% of the nation's electricity by 2012. The goal was 25% by 2025.
A 2024 study showed the benefits of wind and solar energy. Between 2019 and 2022, these sources reduced carbon dioxide (CO₂) by 900 million metric tons. This saved an estimated $249 billion in climate and health costs.
Renewable Energy and Carbon Dioxide
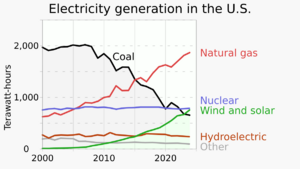
Between 2010 and 2020, the cost of wind, solar, and natural gas dropped a lot. The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) expected carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions to decrease. This was because the country was using less coal and more renewables and natural gas.
Renewable energy can lower CO₂ emissions in three main areas. These are transportation, heating and cooling (like for buildings and factories), and electricity.
How Renewable Energy Is Growing
Renewable Energy in Electricity
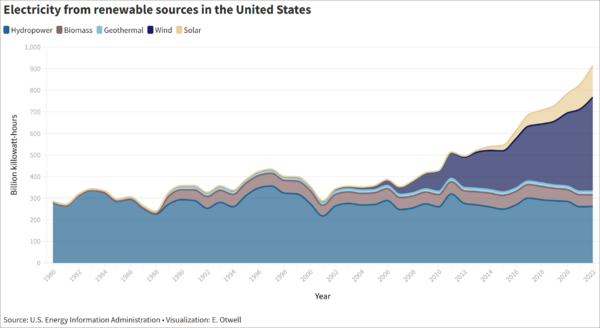
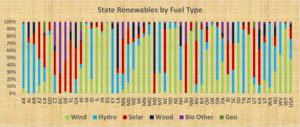
In 2016, renewable energy made up almost 15% of the electricity produced in the U.S. This percentage has grown from just 7.7% in 2001. Most of this growth comes from wind power and, more recently, solar power. Renewable energy in California is very important. About 29% of its electricity comes from renewable sources.
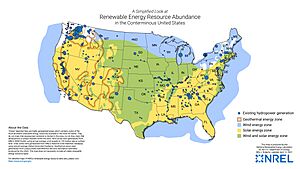
The United States has excellent renewable energy resources. A quarter of the country's land has strong winds. These winds are good enough to generate electricity at a low cost. Less than 5% of federal land suitable for renewable energy could provide carbon-free electricity by 2035.
Many new renewable technologies are becoming as cheap as fossil fuels. Wind, solar, geothermal, and biofuels are growing fast. This growth is lowering costs and improving technology. Wind and solar power are becoming more important than older hydroelectric power. In 2016, wind power made up 37.23% of renewable electricity. Hydroelectric power was 43.62%. Biomass was 10.27%, solar power 6.03%, and geothermal 2.86%.
In 2015, Georgetown, Texas became one of the first U.S. cities to use only renewable energy. They chose this for financial stability.
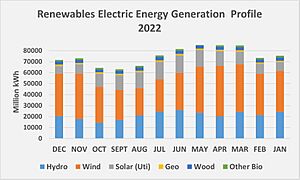
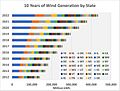
In 2022, wind power generated 434.3 TWh, making up 45.1% of renewable electricity. Hydroelectricity produced 254.8 TWh (26.5%). Solar power generated 205.1 TWh (21.3%). Biomass contributed 51.8 TWh (5.4%), and geothermal 16.1 TWh (1.7%).
Future Plans for Renewable Energy
Experts predict that renewable energy capacity will increase significantly. By early 2024, an additional 55.873 GW of renewable energy capacity was expected to be online. This would bring the total to 277.77 GW, a 23.1% increase from 2018. This growth means more clean electricity for the country.
Types of Renewable Electricity Sources
Hydroelectricity

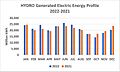
Hydroelectric power was the biggest renewable power source in the U.S. until 2019. Then, wind power took its place. In 2022, it produced 254.79 TWh of electricity. This was about 5.94% of the nation's total electricity. It also provided 26.48% of all renewable power. The U.S. is the third-largest producer of hydroelectricity globally.
The Grand Coulee Dam is the 9th largest hydroelectric power station in the world. Six other U.S. hydroelectric plants are among the world's 50 largest. The amount of hydroelectric power depends on rainfall and water flow. Projects like Hoover Dam and Grand Coulee Dam are famous large construction projects.
| Name | Year of completion | Total capacity (MW) |
|---|---|---|
| Grand Coulee | 1942/1980 | 6,809 |
| Bath County PSP | 1985 | 3,003 |
| Robert Moses Niagara Power Plant | 1961 | 2,675 |
| Chief Joseph Dam | 1958/73/79 | 2,620 |
| John Day Dam | 1949 | 2,160 |
| The Dalles Dam | 1981 | 2,160 |
| Hoover Dam | 1936/1961 | 2,080 |
Wind Power
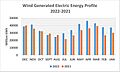
Wind power capacity in the U.S. grew three times larger from 2008 to 2016. By 2016, it supplied over 5% of the country's electricity. In 2019, wind power became the largest source of renewable electricity. By 2022, it made up 10.25% of the nation's total electricity.
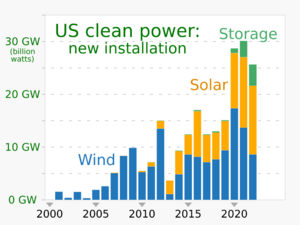
Wind and solar power made up two-thirds of new energy installations in the U.S. in 2015. As of 2023, the U.S. has over 141 GW of installed wind power capacity. Only China has more.
The 1550MW Alta Wind Energy Center in California is the largest wind farm in the U.S. It is the second largest in the world.
In 2015, there were 90,000 jobs in wind operations in the U.S. The wind industry creates many jobs and helps local economies. Wind projects also boost local taxes. They give farmers a steady income from turbines on their land. GE Energy is the biggest U.S. wind turbine maker.
The U.S. has the potential for 10 terawatts (TW) of onshore wind power. It also has 4 TW of offshore wind. The U.S. Department of Energy wants wind power to supply 20% of all electricity by 2030. This includes 4% from offshore wind power. More power lines will be needed to bring wind power from windy states to other areas.
Wind power has grown a lot in Colorado. In 2023, Colorado produced 16,000 GWh from wind. This shows the state's commitment to clean energy.
| Wind farm | State | Current capacity (MW) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alta (Oak Creek-Mojave) | California | 1,320 | |
| Buffalo Gap Wind Farm | Texas | 523 | |
| Capricorn Ridge Wind Farm | Texas | 663 | |
| Cedar Creek Wind Farm | Colorado | 551 | |
| Fowler Ridge Wind Farm | Indiana | 600 | |
| Horse Hollow Wind Energy Center | Texas | 736 | |
| Meadow Lake Wind Farm | Indiana | 500 | |
| Roscoe Wind Farm | Texas | 782 | |
| Shepherds Flat Wind Farm | Oregon | 845 | |
| Sweetwater Wind Farm | Texas | 585 |
Solar Power
- Solar PV utility-scale
- Solar thermal utility-scale
- Estimated distributed solar PV
The U.S. is one of the world's biggest solar power producers. The country helped develop solar farms and new solar technologies.
In 2022, large solar power plants added 145.6 TWh to the electricity grid. Most of this came from photovoltaics (PV). Smaller, distributed solar systems (like on rooftops) also added power. The Energy Information Administration (EIA) has started estimating this contribution. Before 2008, most solar electricity came from thermal systems. But by 2011, PV had become the main source.
Photovoltaics
By the end of 2022, the U.S. had 70.6 gigawatts (GW) of large-scale solar PV capacity. The U.S. has some of the largest solar farms in the world. Mount Signal Solar and Solar Star are examples of huge solar farms in California. Solar Star uses 1.7 million solar panels over a large area. The Desert Sunlight Solar Farm and Topaz Solar Farm are also very big.
Many schools and businesses have solar panels on their roofs. These are often connected to the power grid. They use "net metering" rules. This lets them use electricity at night that they generated during the day. California has many homes with solar panels.
Concentrated Solar Power
By the end of 2016, the U.S. had 1.76 GW of solar thermal power capacity. This type of solar power is usually for large power plants.
Solar thermal power plants work well in sunny areas like the southwestern U.S. They can meet high electricity demands during hot summer afternoons. They can also store energy to use at night.
Some of the largest solar thermal power plants are in the Mojave Desert. The Solar Energy Generating Systems (SEGS) is a group of nine plants built between 1984 and 1991. They use mirrors to focus sunlight and create heat. These plants have a total capacity of 354 MW.
Nevada Solar One generates 64MW of power. It uses special mirrors called parabolic troughs. These heat up tubes of liquid. This plant can also store extra heat in molten salts to use at night.
The Ivanpah Solar Power Facility is a 392 MW solar power plant in California. It opened in 2014. Other large plants include the Solana Generating Station in Arizona and the Mojave Solar Project in California.
Geothermal Power
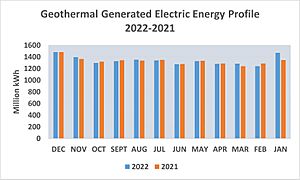
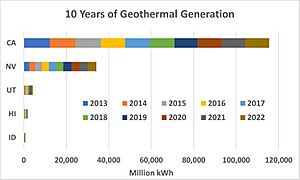
The U.S. leads the world in generating electricity from geothermal energy. In 2022, geothermal energy provided about 16 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity. This was 0.37% of the country's total electricity. As of May 2007, geothermal power was generated in Alaska, California, Hawaii, Nevada, and Utah.
The Energy Policy Act of 2005 helped boost the geothermal industry. It made new geothermal plants eligible for tax credits. It also increased funding for research.
| State | Capacity (MW) |
% of Capacity |
Electric generation (MWh) |
Capacity factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| California | 1838 | 74% | 11,559,591 | 0.718 |
| Nevada | 498.2 | 20% | 3,291,874 | 0.754 |
| Utah | 73 | 3% | 480,928 | 0.752 |
| Hawaii | 43 | 1.7% | 322,592 | 0.856 |
| Oregon | 19.5 | 0.8% | 174,381 | 1.0 |
| Idaho | 10 | 0.4% | 84,436 | 0.964 |
| New Mexico | 1.6 | 0.06% | 12,963 | 0.925 |
| Total | 2483.3 | 100% | 15,926,765 | 0.732 |
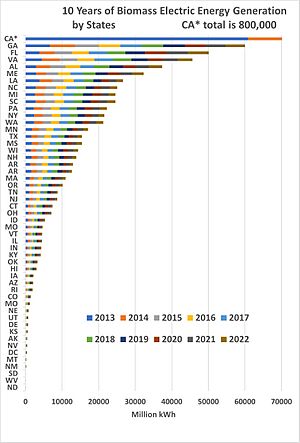
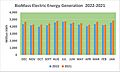
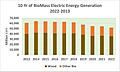
Biomass
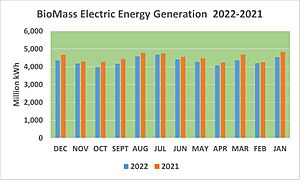
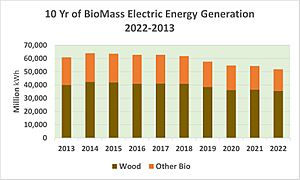
In 2022, biomass generated 51.847 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity. This was 1.21% of the country's total electricity. Biomass was the largest source of renewable primary energy in the U.S. It was the fourth-largest renewable source of electrical power. Wind, hydropower, and solar produced more.
Biomass electricity comes from two main types of fuels:
- Wood and wood-based fuels (like wood chips, bark, and paper waste).
- Other biomass fuels (like municipal solid waste, landfill gas, and agricultural waste).
Wave Power
Wave power uses the energy from ocean waves. It is being developed in several places off the U.S. coasts and in Hawaii. It has moved past the research stage and is now producing reliable energy. So far, it is used where other energy sources are too expensive. But major projects are planned for the future.
Solar Water Heating
In 2006, the U.S. Department of Energy said over 1.5 million homes and businesses used solar water heating. This saved a lot of energy. They predicted another 400 MW of thermal energy would be installed soon.
Solar water heaters can work in any climate. They work better when there is more sunlight and colder incoming water. The colder the water, the more efficiently the system works.
Solar water heaters can reduce the need for regular water heating by about two-thirds. They can pay for themselves in 4 to 8 years through energy savings. For example, Florida homeowners with solar water heaters save 50% to 85% on their water heating bills.
Biofuels
Many cars sold in the U.S. since 2001 can run on fuel with up to 15% ethanol. Older cars can use up to 10% ethanol. Car makers also produce "flexible-fuel" cars. These can use gasoline and ethanol blends up to 85% ethanol (E85). By mid-2006, about 6 million E85-compatible vehicles were on the road.
In 2016, 95% of gasoline sold in the U.S. was mixed with 10% ethanol. The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 aimed for 15.2 billion gallons of biofuels to be used yearly by 2012. This helped expand the market. The USDA also offers grants to gas stations to install pumps for ethanol blends.
The growing ethanol and biodiesel industries create jobs. These jobs are in building, running, and maintaining plants. Most are in rural areas. In 2005, the ethanol industry created almost 154,000 jobs. It also added $5.7 billion to household income.
Renewable Energy Research
Many groups are doing advanced research in renewable energy. These include universities, government labs, and companies. Their research focuses on making renewable energy more efficient and productive.
Two important government labs are Sandia National Laboratories (SNL) and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). Both are funded by the United States Department of Energy. They also work with companies.
Both SNL and NREL have strong solar research programs. NREL's solar program works on photovoltaic (PV) technology, solar thermal energy, and solar radiation. Researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) found a way to store solar energy. They use it to make hydrogen fuel from water. This helps solve the problem of storing solar energy for nighttime use.
In 2012, a company called Semprius Inc. developed a very efficient solar panel. They claimed it could turn 33.9% of sunlight into electricity. This was more than double the previous best rate.
Wind energy research started in the 1970s. NASA developed models to predict wind turbine power. Today, SNL and NREL also research wind energy. They work on better materials, aerodynamics, and sensors.
Many groups research ethanol production. The USDA studies how ethanol production affects food markets. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory researches cellulosic ethanol. This type of ethanol is made from wood, grasses, or non-food plant parts. It does not compete with food supplies.
Over $1 billion of federal money has been spent on hydrogen fuel research. NREL and SNL both have departments for hydrogen research.
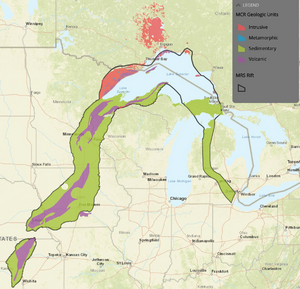
White Hydrogen
White hydrogen is a natural form of hydrogen. It can be found or produced in the Midcontinent Rift System. This could help create a renewable hydrogen economy. Water could be pumped into hot, iron-rich rock to make hydrogen. Then, the hydrogen could be taken out.
Jobs in Renewable Energy
It's hard to know exactly how many jobs renewable energy will create. But it's very likely that the U.S. will see more jobs in the energy sector. This will happen as the country moves to renewable energy.
A study found that renewable energy creates more jobs than fossil fuels for the same amount of energy. Solar and wind energy create the most jobs. This is likely because of the work needed to install them. While some areas might lose jobs in fossil fuels, overall, the U.S. energy sector is expected to gain many jobs.
Studies in Europe have also shown positive job growth from renewable energy. For example, a study in the European Union found that 530,000 jobs were gained during a shift to cleaner energy. Another study in Germany showed similar positive job effects.
Policies for Renewable Energy
The Energy Policy Act of 2005 requires electric companies to allow net metering. This means homes and businesses that generate their own power only pay for the "net" electricity they use. If they produce more than they use, they send it back to the grid. This helps smooth out energy use for sources like solar and wind.
Some places have "feed-in tariffs." This allows people to earn money by producing more renewable energy than they use.
From 2006 to 2014, U.S. households received over $18 billion in tax credits. These were for making homes more energy-efficient or installing solar panels. Most of these credits went to higher-income Americans.
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 included over $70 billion for clean energy programs. This was the largest federal commitment ever for renewable energy and energy saving. These efforts encouraged more companies to use clean energy.
In 2012, President Barack Obama again showed his support for renewable energy. He called for the Defense Department to buy 1,000 MW of renewable energy. He also mentioned plans to approve 10,000 MW of renewable energy projects on public land.
Government subsidies also support energy technologies. In 2016, federal support for renewables was $6,682 million. For fossil fuels, it was $489 million, and for nuclear energy, $365 million.
Most U.S. states now have programs to promote renewable energy. Many have passed new laws about it.
In May 2024, the Biden administration increased taxes on solar cells and electric vehicle batteries from China. These tax increases will happen over three years.
Net Metering
Net metering in the United States is a billing system. It allows customers who generate their own electricity (like with solar panels) to send excess power back to the grid. They get credit for this power. This reduces their electricity bill.
Initiatives
SunShot
In 2011, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) started the SunShot Initiative. This project aimed to cut the cost of solar energy systems by 75% by 2020. The goal was to make solar energy as cheap as other electricity sources without subsidies. The SunShot goal of $1/W was reached in 2017.
Wind Powering America
Wind Powering America (WPA) is another DOE program. It works to increase the use of wind energy. WPA works with farmers, ranchers, Native Americans, and schools.
WPA focuses on states with good wind potential but few wind projects. It provides information about the benefits and challenges of wind technology.
Solar America Initiative
The Solar America Initiative (SAI) was part of a larger plan. It aimed to speed up the development of advanced solar materials. The goal was to make solar power cost-competitive by 2015.
The DOE Solar Energy Technology Program (SETP) worked to achieve SAI goals. It focused on market changes, new device ideas, and manufacturing.
California Solar Initiative
California set a goal to create 3,000 megawatts of new solar electricity by 2017. This was part of the Million Solar Roofs Program. It had $2.8 billion in funding.
The California Solar Initiative offered cash payments for solar PV systems. These payments, plus federal tax breaks, could cover up to 50% of the cost. Other U.S. states also offer financial help for renewable energy.
Green Power Partnership
The EPA's Green Power Partnership recognizes top organizations. These organizations generate their own renewable energy on-site. Together, they produce over 736 million kilowatt-hours of renewable energy each year. This is enough to power more than 61,000 average U.S. homes.
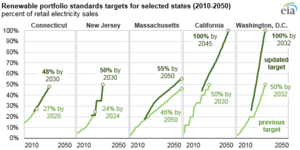
Renewable Portfolio Standards
A Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) is a law. It creates a market for renewable electricity certificates. Electricity companies must get a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources. If they don't, they can buy certificates from other companies that produce renewable energy.
Bans and Restrictions
By February 2024, at least 15% of counties in the U.S. had banned or restricted new wind and solar projects.
Renewable Energy Organizations
The American Council on Renewable Energy (ACORE) is a non-profit group. It works to make renewable energy a main part of America's economy. In 2010, ACORE had over 700 member organizations.
The Environmental and Energy Study Institute (EESI) is an organization that promotes sustainable societies. It works to move society away from fossil fuels. EESI suggests policies that reduce global warming and air pollution. These policies also improve public health and energy security.
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) helps bring new technologies to renewable energy markets. NREL's scientists and engineers work with companies to apply their research.
The Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI) researches and publishes on sustainability. They focus on profitable ways to use energy and resources efficiently.
Community Renewable Energy
Community solar efforts involve local communities in renewable energy projects. The idea is to give communities more control over planning and building these projects. Community-based projects can have many positive social impacts. They can increase acceptance of renewable energy and teach people about clean energy.
Community renewable energy projects need support from institutions. In Europe, there is more institutional support for these projects. This means there are more successful projects there than in the U.S.
In the U.S., there is less institutional support for community-based renewable energy. However, private companies are investing more in community solar and wind projects.
Potential Resources
The U.S. has a huge potential for renewable energy. It could install 11 terawatts (TW) of onshore wind power and 4 TW of offshore wind power. This could generate over 47,000 TWh of electricity. The potential for concentrated solar power in the southwest is also very large. It could generate over 10,000 TWh.
A 2012 report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory looked at the energy potential for each U.S. state.
| Total technical potential | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Resource | Potential capacity (GW) | Potential generation (TWh) |
| Solar | Urban utility-scale PV | 1,200 | 2,200 |
| Rural utility-scale PV | 153,000 | 280,600 | |
| Rooftop PV | 664 | 800 | |
| Concentrating solar power | 38,000 | 116,100 | |
| Total | 192,922 | 399,810 | |
| Wind | Onshore wind power | 11,000 | 32,700 |
| Offshore wind power | 4,200 | 17,000 | |
| Total | 15,178 | 49,760 | |
| Bioenergy | Biomass/biofuel/methane | 62 | 488 |
| Total | 62 | 488 | |
| Geothermal | Hydrothermal power systems | 38 | 300 |
| Enhanced geothermal systems | 3,976 | 31,300 | |
| Total | 4,014 | 31,653 | |
| Hydro | Hydropower | 60 | 259 |
| Total | 60 | 259 | |
| Total | 212,236 | 481,970 | |
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Energía renovable en los Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Energía renovable en los Estados Unidos para niños