Socialist International facts for kids

Socialist International logo
|
|
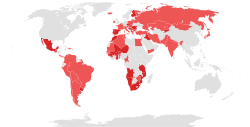
Light red: Countries with a political party affiliated with the Socialist International
Dark red: Countries with the ruling party affiliated with the Socialist International |
|
| Abbreviation | SI |
|---|---|
| Predecessor | Labour and Socialist International |
| Formation | 3 June 1951 |
| Type | International non-governmental organization |
| Purpose | "Strengthen relations between the affiliated parties and to coordinate their political attitudes and activities" |
| Location |
|
|
Region served
|
Worldwide |
|
Membership
|
119 political parties and 13 affiliated organizations |
|
President
|
Pedro Sánchez |
|
Vice-President
|
Temirlan Sultanbekov |
|
Secretary General
|
Benedicta Lasi |
|
Main organ
|
Congress of the Socialist International |
| Secessions | Progressive Alliance |
|
Budget
|
£1.4 million (2014) |
| Website | socialistinternational.org |
The Socialist International (SI) is a global group of political parties. These parties aim to create a fairer society where everyone has a say. They mostly include parties that believe in democratic socialism. This means they want to use democratic ways to achieve socialist goals, like making sure everyone has good healthcare and education.
The SI was officially started in 1951. However, its roots go back to the late 1800s. Today, it has 132 member parties and groups from over 100 countries. Many of its members have been in charge of governments around the world, especially in Europe. In 2013, some parties left the SI to form a new group called the Progressive Alliance.
The current leader of the SI is Pedro Sánchez, who is also the Prime Minister of Spain. The Secretary General is Benedicta Lasi from Ghana. These leaders were chosen at the SI Congress in Madrid, Spain, in November 2022.
Contents
- Understanding the Socialist International's Journey
- Symbol of the Socialist International
- Leaders of the Socialist International
- Meetings of the Socialist International
- Members of the Socialist International
- Groups Connected to the Socialist International
- Other Left-Wing International Groups
- See also
Understanding the Socialist International's Journey
Early Beginnings: First and Second Internationals (1864–1916)
The very first international group for working people was called the International Workingmen's Association. It started in London in 1864. This group brought together different socialist, communist, and anarchist groups, along with trade unions. They wanted to improve conditions for workers. However, disagreements between different groups led to it breaking up in 1876.
Later, in 1889, the Second International was formed in Paris. This was a group of socialist parties. But when World War I started, they had different ideas about the war. This led to the Second International also breaking up in 1916.
Building Bridges: Labour and Socialist International (1919–1940)
After World War I, some parties wanted to restart the Second International. They formed the International Socialist Commission (ISC) in 1919. At the same time, Communist parties created their own group, the Communist International (Comintern), in Moscow.
Some parties didn't want to join either of these groups. So, they formed the International Working Union of Socialist Parties (IWUSP) in Vienna in 1921. Eventually, the ISC and the IWUSP decided to join forces. They created the Labour and Socialist International (LSI) in 1923. This group lasted until 1940, when Nazism grew stronger and World War II began.
The Modern Era: Socialist International (1951–Present)
The Socialist International we know today was formed in Frankfurt in July 1951. It was created to continue the work of the LSI.
After World War II, the SI helped social democratic parties get back on their feet. This was especially true in countries like Portugal (1974) and Spain (1975), where dictatorships ended and democracy returned. For a long time, most SI members were from Europe. But after 1976, the SI started to include more parties from Latin America.
In the 1980s, the SI talked a lot with the United States and the Soviet Union during the Cold War. They discussed important topics like peace and controlling weapons. The SI supported agreements that aimed to reduce nuclear weapons. Leaders from the SI met with US Presidents and Soviet leaders to discuss these issues.

Since then, the SI has welcomed many more parties and groups from Africa, Asia, Europe, and Latin America.
In 2011, some ruling parties were removed from the SI. This happened after protests in countries like Tunisia and Egypt during the Arab Spring. These parties were removed because they were seen as undemocratic.
The Progressive Alliance Split (2013)
In 2013, some important parties, like the Social Democratic Party of Germany, started a new group called the Progressive Alliance. They felt that the SI was not democratic enough and was outdated. They also disagreed with the SI including certain political groups that they saw as undemocratic. For example, they didn't like that the Sandinista National Liberation Front was still a member.
After 2012, many large European parties, such as the British Labour Party, changed their membership status or left the SI. These parties now focus more on the Progressive Alliance. The SI, in turn, has focused more on countries in the "global south" (Africa, Asia, and Latin America).
Connecting with Latin America
For a long time, the Socialist International didn't pay much attention to Latin America. They saw it as a region mainly influenced by the United States. For example, they didn't speak out against the overthrow of the Socialist President Jacobo Árbenz in Guatemala in 1954.
However, after a military takeover in Chile in 1973, the SI realized they needed to get more involved. They started to support groups like the Sandinista National Liberation Front in Nicaragua. These groups were fighting against dictatorships that were supported by the US.
In the 1990s, some non-socialist parties joined the SI. They saw the economic power of European countries and wanted to benefit from these connections. Some critics said that the SI became a place where parties joined just to connect with powerful European politicians. For example, the Institutional Revolutionary Party from Mexico, which ruled for 70 years, joined. In the next decade, many left-wing parties that came to power in Latin America chose to stay separate from the SI.
Symbol of the Socialist International
The symbol of the Socialist International is the fist and rose. This design was first used by the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party in 1977. It's a symbol that many SI member parties use or have used.
Leaders of the Socialist International
Presidents
As of 2025, there have been nine presidents of the Socialist International.
| No. | Portrait | Name (born–died) |
Term of office | Political party | Congress(es) | Country | Vice-president | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Took office | Left office | Time in office | Name | Country | |||||||
| 1 |  |
Morgan Phillips (1902–1963) |
3 July 1951 | 6 July 1957 | 6 years, 3 days | Labour Party | I–IV | ||||
| 2 |  |
Alsing Andersen (1893–1962) |
6 July 1957 | 9 September 1963 | 6 years, 65 days | Social Democratic Party of Denmark | V–VII | ||||
| 3 |  |
Erich Ollenhauer (1901–1963) |
9 September 1963 | 14 December 1963 † | 96 days | Social Democratic Party of Germany | VIII | ||||
| 4 |  |
Bruno Pittermann (1905–1983) |
5 September 1964 | 26 November 1976 | 12 years, 82 days | Socialist Party of Austria | IX–XII | ||||
| 5 |  |
Willy Brandt (1913–1992) |
26 November 1976 | 17 September 1992 | 15 years, 296 days | Social Democratic Party of Germany | XIII–XVIII | ||||
| 6 |  |
Pierre Mauroy (1928–2013) |
17 September 1992 | 10 November 1999 | 7 years, 54 days | Socialist Party | XIX–XX | ||||
| 7 |  |
António Guterres (b. 1949) |
10 November 1999 | 15 June 2005 | 5 years, 217 days | Socialist Party | XXI–XXII | ||||
| 8 |  |
George Papandreou (b. 1952) |
30 January 2006 | 25 November 2022 | 16 years, 300 days | Panhellenic Socialist Movement | XXII–XXV | ||||
| Movement of Democratic Socialists | |||||||||||
| 9 |  |
Pedro Sánchez (b. 1972) |
25 November 2022 | Incumbent | 3 years, 107 days | Spanish Socialist Workers' Party | XXVI | Temirlan Sultanbekov | |||
Honorary Presidents
These are people who have been given special recognition by the Socialist International:
- Mustapha Ben Jafar, Tunisia
- Rubén Berríos, Puerto Rico
- Philippe Busquin, Belgium
- Cuauhtémoc Cárdenas, Mexico
- Mohamed El Yazghi, Morocco
- Alan García, Peru
- Anita Gradin, Sweden
- Elazar Granot, Israel
- Tarja Halonen, Finland
- Mahamadou Issoufou, Niger
- Anker Jørgensen, Denmark
- Lionel Jospin, France
- Neil Kinnock, United Kingdom
- Horacio Serpa, Colombia
- Enrique Silva Cimma, Chile
- Mário Soares, Portugal
- Hans-Jochen Vogel, Germany
Secretaries General
The Secretary General manages the daily work of the Socialist International.
- Julius Braunthal, Austria (1951–1956)
- Bjarne Braatoy, Norway (1956–1957)
- Albert Carthy, United Kingdom (1957–1969)
- Hans Janitschek, Austria (1969–1976)
- Bernt Carlsson, Sweden (1976–1983)
- Pentti Väänänen, Finland (1983–1989)
- Luis Ayala, Chile (1989–2022)
- Benedicta Lasi, Ghana (since 2022)
Meetings of the Socialist International
The Socialist International holds regular meetings called Congresses. Here are some of the places where they have met:
- 1951 (1st): Frankfurt, West Germany.
- 1952 (2nd): Milan, Italy.
- 1953 (3rd): Stockholm, Sweden.
- 1955 (4th): London, United Kingdom.
- 1957 (5th): Vienna, Austria.
- 1959 (6th): Hamburg, West Germany.
- 1961 (7th): Rome, Italy.
- 1963 (8th): Amsterdam, Netherlands.
- 1964 (9th): Brussels, Belgium.
- 1966 (10th): Stockholm, Sweden.
- 1969 (11th): Eastbourne, United Kingdom.
- 1972 (12th): Vienna, Austria (2nd time).
- 1976 (13th): Geneva, Switzerland.
- 1978 (14th): Vancouver, Canada.
- 1980 (15th): Madrid, Spain.
- 1983 (16th): Albufeira, Portugal.
- 1986 (17th): Lima, Peru.
- 1989 (18th): Stockholm, Sweden (2nd time).
- 1992 (19th): Berlin, Germany.
- 1996 (20th): New York City, United States.
- 1999 (21st): Paris, France.
- 2003 (22nd): São Paulo, Brazil.
- 2008 (23rd): Athens, Greece.
- 2012 (24th): Cape Town, South Africa.
- 2017 (25th): Cartagena, Colombia.
- 2022 (26th): Madrid, Spain (2nd time).
Members of the Socialist International
The Socialist International has different types of members: full members, consultative parties, and observer parties.
Full Members
There are 92 full member parties. These parties are actively involved in the SI's work. Some examples include:
- Socialist Party of Albania
- Social Democratic Party
- MPLA
- Socialist Party
- Democratic Labour Party
- Social Democratic Party of Finland
- Socialist Party
- National Democratic Congress
- Indian National Congress
- Labour Party
- Spanish Socialist Workers' Party
Consultative Parties
There are 19 consultative parties. These parties are still connected to the SI but might have a less active role. Some examples are:
- Botswana Democratic Party
- Movement for Democratic Renewal and Development (Djibouti)
- United Democratic Party
- African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde
- Polisario Front (Sahrawi Republic)
Observer Parties
There are 8 observer parties. These parties are new to the SI or have a less formal connection. Some examples include:
- Labour Party
- Labour Party of Kenya
- Vetëvendosje (Kosovo)
- Labour Party (United Kingdom)
Groups Connected to the Socialist International
The SI also works with other organizations that share similar goals.
Fraternal Organisations
These are closely related groups:
- International Falcon Movement – Socialist Educational International (focuses on education)
- Socialist International Women (focuses on women's rights)
Associated Organisations
These groups work with the SI on various issues:
- Arab Social Democratic Forum
- Euro-Latin American Forum of Progressive and Socialist Parliamentarians
- International Federation of the Socialist and Democratic Press
- International Jewish Labor Bund
- International Labour Sports Confederation
- International League of Religious Socialists
- International Social Democratic Union for Education
- World Labour Zionist Movement
- National Democratic Institute
- Party of European Socialists
- Social Democratic Group of the Latin American Parliament
Other Left-Wing International Groups
The Socialist International is one of many groups that have tried to unite left-wing political movements across the world. Here are some others:
- International Workingmen's Association, the First International (1864–1876)
- Second International (1889–1916)
- Labour and Socialist International (1923–1940)
- Communist International, also known as Comintern (1919–1943)
- Fourth International (started in 1938)
See also
 In Spanish: Internacional Socialista para niños
In Spanish: Internacional Socialista para niños


