Territorial evolution of California facts for kids
California, the thirty-first state to join the United States, has a long and interesting history of how its land changed hands. This story involves many different groups, from the first people who lived there for thousands of years to European explorers and settlers. It also includes how the land of Native Americans was taken or limited to special areas called reservations.
Contents
California's Changing Lands: A Timeline
This timeline shows the major changes in who controlled the land that is now California.
Early Times: Before Europeans Arrived (Before 1768)
- First People: The first people arrived on the west coast of North America around 13,000 years BCE (Before Common Era).
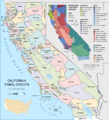
- Native Californians: Many different Native American groups lived in California for thousands of years, each with their own languages and traditions. You can see a map of their territories from around 1492.
- Early European Claims: Even before Europeans explored California, some powerful groups in Europe made claims to unknown lands, including parts of North America.
**Pope's Orders: In 1493, Pope Alexander VI issued a special order called a "papal bull" (Inter caetera). This order divided new lands between Spain and Portugal. **Treaties: The Treaty of Tordesillas (1494) and the Treaty of Saragossa (1529) were agreements between Spain and Portugal that further divided the world for exploration and claiming. **Pacific Ocean Claim: In 1513, Vasco Núñez de Balboa claimed the Pacific Ocean (which he called the "South Sea") and all the lands next to it for Spain.
- First Claims on California Soil:
**Spain's Claim: In 1542, Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo claimed an area near what is now San Diego, California for Spain. He named it San Miguel. **England's Claim: In 1579, Sir Francis Drake claimed an area near Point Reyes for England, calling it New Albion.
Spanish Control (1768-1821)
- Spain Takes Control: From 1768 to 1804, Spain officially claimed a large area called Las Californias. This land was governed by the Viceroyalty of New Spain, which was a Spanish colony in North America.
**Spanish Missions: Starting in 1769, Spain built many missions along the coast. These missions aimed to convert Native Americans to Christianity and teach them Spanish ways. * **Native American Relocation: Many Native Americans were forced to move to these missions between 1769 and 1834. **Land Grants: Spain also gave out large pieces of land, called rancho land grants, to Spanish settlers between 1769 and 1821. **Peace Treaty: The Peace of Paris in 1783 ended the American Revolutionary War and set some borders for the United States.
- Alta California Province: In 1804, Las Californias was divided, and the northern part became the Alta California Province. This province lasted until 1821.
**Russian Presence: From 1812 to 1842, the Russian-American Company built Fort Ross in Northern California. In 1812, Ivan Kuskov claimed parts of the Northern California coast for Russia. **Border Agreement: The Adams–Onís Treaty of 1819 helped define the border between Spanish territories and the United States.
- Mexico's Fight for Freedom: The Mexican War of Independence lasted from 1808 to 1821.
**Argentine Claim: For six days in 1818, Hippolyte Bouchard held Monterey, California for Argentina. **Treaty of Córdoba: This treaty was signed on August 21, 1821, and officially ended Spanish rule in Mexico.
Mexican Control (1821-1848)
- Mexico Takes Over: After the Treaty of Córdoba, the Alta California Province became part of Mexico from 1821 to 1824.
**Mexican Army: The Army of the Three Guarantees played a key role in Mexico's independence in 1821. **Mexican Land Grants: Mexico continued to give out large land grants, known as Mexican rancho land grants, from 1821 to 1846.
- First Mexican Empire: Mexico was briefly an empire from 1821 to 1823.
- Provisional Government: A temporary government ruled Mexico from 1823 to 1824.
- First Mexican Republic: Mexico became a republic from 1824 to 1835.
**Alta California Territory: The 1824 Constitution of Mexico officially established Alta California as a territory from 1824 to 1836. **Border Treaty: The Treaty of Limits (Mexico–United States) in 1828 further defined the border between Mexico and the United States. **Mission Lands: The Mexican secularization act of 1833 took control of the mission lands from the Catholic Church.
- Centralist Republic: Mexico changed its government again, becoming a centralist republic from 1835 to 1846.
**California's "Lone Star": In 1836, there was a small uprising in California, leading to a declaration of independence and the creation of the Lone Star of California flag. **Las Californias Department: Under new laws called Las Siete Leyes (The Seven Laws), Las Californias became a department of Mexico from 1836 to 1846.
- Second Federal Republic: Mexico returned to a federal republic from 1846 to 1848.
**Alta California Territory Restored: The 1824 Constitution was restored, and Alta California became a territory again from 1846 to 1848.
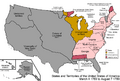
- Mexican-American War: This war between Mexico and the United States lasted from 1846 to 1848.
**California Republic: For 25 days in 1846, a group of American settlers declared the California Republic (also known as the Bear Flag Republic). **U.S. Military Rule: After the war began, the U.S. military governed California from 1846 to 1849. **Treaty of Cahuenga: This treaty, signed on January 13, 1847, ended fighting in California during the war. **Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo: This important treaty, signed on February 2, 1848, officially ended the Mexican-American War. * **Mexican Cession: As a result of the treaty, Mexico gave up a huge amount of land to the United States, known as the Mexican Cession of 1848. This included California.
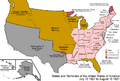
American Control (1848-Present)
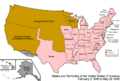
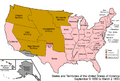
- U.S. Takes Over: From 1848 to 1850, the United States administered Alta California as an "Unorganized territory" after the Mexican Cession.
**Provisional Government: A temporary provisional government for California was set up from 1849 to 1850. **State of Deseret: A group of settlers tried to create their own (unofficial) state called Deseret from 1849 to 1850. **California's Constitution: California created its own constitution on October 13, 1849, which also defined its borders. **Compromise of 1850: This was a series of laws passed by the U.S. Congress to deal with the issue of slavery in new territories, and it included California becoming a state.
- State of California: California officially became a state in 1850.
**Statehood Act: The California Statehood Act was passed on September 9, 1850. **Act for Native Americans: The Act for the Government and Protection of Indians was passed on April 22, 1850. This act had a negative impact on Native Americans in California. * **California Indian Wars: Conflicts between settlers and Native Americans, known as the California Indian Wars, occurred from 1850 to 1880. **Native American Land Rights: The issue of Native American land rights has been ongoing since 1851. * **Land Act: The California Land Act of 1851 dealt with land claims in California. * **Reservations and Cessions: From 1851 to 1892, Native American lands were further restricted to reservations or taken by the government. * **Indian Reorganization Act: The Indian Reorganization Act of 1934 aimed to reverse some of the negative policies towards Native Americans. * **Indian Claims Act: The Indian Claims Act of 1946 allowed Native American tribes to seek compensation for lands taken from them. * **California Act of 1949: This act was part of a policy to end federal recognition of some Native American tribes. * **Rancheria Termination Acts: The California Rancheria Termination Acts, starting in 1956, continued the policy of ending federal recognition for some Native American communities. **Border Disputes: California has had some border disputes with Nevada and Oregon. * **Nataqua Territory: From 1856 to 1861, there was an unofficial territory called Nataqua Territory that claimed parts of California and Nevada. * **Roop County Dispute: A border dispute involving Roop County occurred from 1861 to 1864. **California-Oregon Border: A border dispute between California and Oregon has been ongoing since 1868.
California's Original Borders (1849)
When California became a state, its borders were clearly described in its first constitution.
The boundary of the State of California was set as follows: It starts where the 42nd degree of north latitude crosses the 120th degree of longitude west from Greenwich. From there, it goes south along the 120th degree of west longitude until it meets the 39th degree of north latitude. Then, it runs in a straight line southeast to the Colorado River, where it crosses the 35th degree of north latitude. From that point, it follows the middle of the river's channel down to the border between the United States and Mexico, which was set by a treaty on May 30, 1848. Then, it goes west along that border line to the Pacific Ocean, extending three English miles into the ocean. From there, it follows the Pacific Coast in a northwesterly direction to the 42nd degree of north latitude. Finally, it goes along the 42nd degree of north latitude back to the starting point. This also includes all the islands, harbors, and bays along and next to the Pacific Coast.
Images for kids
 | Tommie Smith |
 | Simone Manuel |
 | Shani Davis |
 | Simone Biles |
 | Alice Coachman |