Animal facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Animals |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Various animals | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| Kingdom: |
Animalia
|
Animals are living things made of many cells. Unlike plants, animals don't use sunlight to make their own food. Instead, they get energy by eating other living things. Some animals are parasites, meaning they live on or in another living thing and get food from it.
Most animals can move around on their own. Animals breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. This process is part of their metabolism, which means all the chemical reactions that keep them alive. Animal cells also have special cell membranes that are different from plants and fungi. The study of animals is called zoology.
Plants are also made of many cells, but they get their energy from light, water, and basic chemicals to grow.
Contents
How Scientists Group Animals

There are many different kinds of animals on Earth. The animals most people know make up only a small part of the animal kingdom. Scientists called biologists group animals based on what they have in common. This system is called biological classification. They believe there are millions of animal species, but only about one million have been identified so far.
Animals are mainly split into two big groups: invertebrates and vertebrates.
- Vertebrates have a backbone (or spine).
- Invertebrates do not have a backbone.
Here are some examples of vertebrates:
- Fish
- Amphibians (like frogs and salamanders)
- Reptiles (like snakes and lizards)
- Birds
- Mammals (like humans, dogs, and whales)
And here are some examples of invertebrates:
- Insects (like bees and butterflies)
- Spiders
- Crustaceans (like crabs and lobsters)
- Molluscs (like snails, clams, and squid)
- Worms
- Jellyfish
In science, humans are considered animals. However, in everyday talk, people often don't think of humans as animals.
Animal Numbers and Where They Live
Scientists have described many animal species. The table below shows how many species are known for some major animal groups. It also shows where they live (on land, in the sea, or in fresh water) and if they live freely or as parasites.
Keep in mind that these numbers are for species that scientists have already found and named. There are likely many more species that haven't been discovered yet! For example, while about 25,000 types of nematodes (roundworms) have been described, some scientists think there could be millions more. In 2011, scientists estimated that there are about 7.77 million animal species in total.
| Phylum | Example | Number of Species |
Land | Sea | Fresh water |
Free- living |
Parasitic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annelids |  |
17,000 | Yes (soil) | Yes | 1,750 | Yes | 400 |
| Arthropods |  |
1,257,000 | 1,000,000 (insects) |
>40,000 (Malac- ostraca) |
94,000 | Yes | >45,000 |
| Bryozoa |  |
6,000 | Yes | 60-80 | Yes | ||
| Chordates |  |
65,000 45,000 |
23,000 |
13,000 |
18,000 9,000 |
Yes | 40 (catfish) |
| Cnidaria |  |
16,000 | Yes | Yes (few) | Yes | >1,350 (Myxozoa) |
|
| Echinoderms |  |
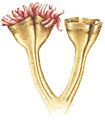
7,500 | 7,500 | Yes | |||
| Molluscs |  |
85,000 107,000 |
35,000 |
60,000 |
5,000 12,000 |
Yes | >5,600 |
| Nematodes |  |
25,000 | Yes (soil) | 4,000 | 2,000 | 11,000 | 14,000 |
| Platyhelminthes |  |
29,500 | Yes | Yes | 1,300 | Yes | >40,000 |
| Rotifers |  |
2,000 | >400 | 2,000 | Yes | ||
| Sponges |  |
10,800 | Yes | 200-300 | Yes | Yes | |
|
|
|||||||
Animal Life Styles
Animals get their food from other living things. This is called heterotrophic nutrition.
- Some animals eat only plants; they are called herbivores.
- Other animals eat only meat; they are called carnivores.
- Animals that eat both plants and meat are called omnivores.
Animals live in many different environments. Over long periods, animals adapt to the habitats they live in through a process called evolution. For example, a fish is perfectly suited for life in water. A spider is adapted to catch and eat insects. A mammal living on the savannahs of East Africa lives a very different life from a dolphin or porpoise hunting fish in the ocean.
The oldest animal fossils found are about 600 million years old, from a time called the Ediacaran period. Animals have been constantly evolving since then. This means the animals we see on Earth today are very different from those that lived long ago. The study of ancient life, including fossils, is called palaeontology.
Images for kids
-
Animals are unique because their early embryo (1) forms a hollow ball called a blastula (2).
-
Predators, like this ultramarine flycatcher, hunt and eat other animals.
-
Hydrothermal vent mussels and shrimps living in deep-sea environments.
-
The blue whale is the largest animal that has ever lived.
-
Ecdysis: A dragonfly has shed its old skin (exuviae) and is expanding its new wings. Like other arthropods, its body is divided into segments.
-
Jean-Baptiste de Lamarck helped create a modern way to classify invertebrates in the early 1800s.
-
Sides of beef in a slaughterhouse.
-
A gun dog retrieving a duck during a hunt.
-
Artistic vision: Still Life with Lobster and Oysters by Alexander Coosemans, painted around 1660.
-
Dickinsonia costata from the Ediacaran biota (about 635–542 million years ago) is one of the earliest known animal species.
-
Anomalocaris canadensis is one of many animal species that appeared during the Cambrian explosion, starting about 539 million years ago. Its fossils are found in the Burgess Shale.
See Also
 In Spanish: Animalia para niños
In Spanish: Animalia para niños