Chihuahuan Desert facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Chihuahuan Desert |
|
|---|---|

Chihuahuan desert landscape in Big Bend National Park
|
|
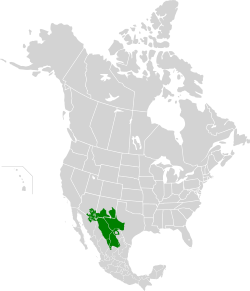
Location map of Chihuahuan Desert
|
|
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Nearctic |
| Biome | Deserts and xeric shrublands |
| Borders |
List
|
| Geography | |
| Area | 501,896 km2 (193,783 sq mi) |
| Countries | Mexico and United States |
| States | |
| Coordinates | 30°32′26″N 103°50′14″W / 30.54056°N 103.83722°W |
| Rivers | Rio Grande |
| Climate type | Hot desert and hot semi-arid |
| Conservation | |
| Conservation status | Vulnerable |
| Global 200 | Yes |
| Protected | 35,905 km2 (13,863 sq mi) (7%) |
The Chihuahuan Desert (also known as Desierto de Chihuahua) is a huge desert area. It covers parts of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. You can find it in West Texas, parts of New Mexico, and a small bit of southeastern Arizona. In Mexico, it covers a large part of Chihuahua, plus areas in Coahuila, Durango, Zacatecas, and Nuevo León.
This desert is the largest desert in North America. It covers about 501,896 square kilometers (193,783 square miles). The Chihuahuan Desert is quite young, having existed for only about 8,000 years.
Contents
Exploring the Chihuahuan Desert

The Chihuahuan Desert has several large mountain ranges. These include the Sierra Madre Oriental, Sierra del Carmen, and Guadalupe Mountains. These mountains create "sky islands." These are cooler, wetter areas right next to or inside the desert. These high places have forests with both pine trees and broadleaf trees.
Cities in the Desert
Few big cities are located within the desert. The largest is Ciudad Juárez in Mexico, with almost two million people. Other important cities include Chihuahua, Saltillo, and Torreón in Mexico. In the US, major cities are El Paso and Albuquerque. Many smaller towns also dot this desert region.
Unique Wildlife and Plants
The World Wide Fund for Nature says the Chihuahuan Desert might be the most diverse desert in the world. This means it has the most types of plants and animals. However, the area has been harmed, mostly by animals grazing too much. Many native grasses have been replaced by woody plants like creosote bush. The Mexican wolf, which used to be common, is now an endangered species. Scientists also predict that climate change could cause many bird, mammal, and butterfly species to be replaced by other species by 2055.
Desert Climate
The Chihuahuan Desert is mostly a rain shadow desert. This means two large mountain ranges block most of the moisture. The Sierra Madre Occidental to the west blocks Pacific Ocean moisture. The Sierra Madre Oriental to the east blocks moisture from the Gulf of Mexico.
Rainfall and Temperatures
The desert usually has a dry climate. It has one main rainy season in late summer. A smaller amount of rain falls in early winter. Most of the rain comes between late June and early October. This is when moist air from the Gulf of Mexico moves into the region. Sometimes, a tropical storm moves inland and brings rain.
The desert is higher up than the Sonoran Desert to its west. Its elevation ranges from about 480 to 1,800 meters (1,575 to 5,900 feet). This higher elevation means the desert has slightly milder summers. Daytime temperatures in June are usually between 32 and 40 degrees Celsius (90 to 104 degrees Fahrenheit). Winters are mild to cool, with occasional freezing temperatures.
The average yearly temperature in the desert is about 13 to 22 degrees Celsius (55 to 72 degrees Fahrenheit). This depends on how high up it is and how far north or south it is. The desert gets about 235 millimeters (9.3 inches) of rain each year. This is more rain than most other warm deserts. Snowfall is rare, except in higher areas.
Desert Plants
The creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) is the most common plant. It grows on rocky and sandy soils in the valleys. Other plants found with creosote bush depend on the soil type and elevation.
Common Plants
- Viscid acacia (Vachellia vernicosa) and tarbush (Flourensia cernua) are common in the northern parts.
- Broom dalea (Psorothamnus scoparius) grows on sandy soils in the west.
- Yucca and Opuntia (prickly pear cactus) are common on slopes and uplands.
- Arizona rainbow cactus (Echinocereus polyacanthus) and Mexican fire-barrel cactus (Ferocactus pilosus) grow near the US–Mexico border.
Grasses and Other Shrubs
Grasses like bush muhly (Muhlenbergia porteri) and blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis) are common. They grow in desert grasslands and near the mountains. Lechuguilla (Agave lechuguilla) is a very important plant. It is one of the plants that shows you are in the Chihuahuan Desert. Honey mesquite (Prosopis glandulosa) and ocotillo (Fouquieria splendens) are also common.
Desert grasslands make up about 20% of this desert. They are often a mix of shrubs and grasses. Early Spanish explorers said they saw grasses "belly high to a horse." These were likely tall grasses like big alkali sacaton (Sporobolus wrightii) and tobosa (Pleuraphis mutica) in floodplains.
Protected Areas
About 7% of the Chihuahuan Desert is protected land. These areas help keep the desert's plants and animals safe.
Examples of Protected Areas
- Buenos Aires National Wildlife Refuge in Arizona.
- Janos Biosphere Reserve and Cañón de Santa Elena Flora and Fauna Protection Area in Chihuahua, Mexico.
- Cuatro Ciénegas Basin and part of Maderas del Carmen Biosphere Reserve in Coahuila, Mexico.
- Mapimí Biosphere Reserve in Durango, Mexico.
- Carlsbad Caverns National Park, White Sands National Park, and Organ Mountains–Desert Peaks National Monument in New Mexico.
- Big Bend National Park and Guadalupe Mountains National Park in Texas.
Images for kids
-
Lechuguilla (Agave lechuguilla) is a key plant of the Chihuahuan Desert.
See also
 In Spanish: Desierto de Chihuahua para niños
In Spanish: Desierto de Chihuahua para niños
- List of deserts by area
- List of ecoregions in the United States (WWF)
- List of geographical regions in Texas
- McKittrick Canyon
- Malpai Borderlands
- Pecos River
- Samalayuca Dune Fields
- Sky islands
- Solitario formation
- Sonoran Desert
- Trans-Pecos
- West Texas






