Kevlar facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Kevlar |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
| IUPAC name | Poly(azanediyl-1,4-phenyleneazanediylterephthaloyl) |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | |
| Molar mass | 0 g mol-1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Kevlar is a super strong, heat-resistant synthetic fiber. It's part of a family of materials called aramids, like Nomex and Technora. A chemist named Stephanie Kwolek at a company called DuPont invented Kevlar in 1965.
This amazing material was first used in the early 1970s. It replaced steel in racing tires because it was so strong. Today, Kevlar is often made into ropes or sheets of fabric. These can be used on their own or mixed with other materials to make composite materials.
Kevlar is used in many different things. You can find it in bicycle tires, racing sails, and even bulletproof vests. It's five times stronger than steel for its weight! This makes it perfect for things that need to be tough but light. It's also used for strong mooring lines that hold ships in place, and for drumheads that can handle a lot of hitting.
Another similar fiber called Twaron was created by Akzo in the 1970s. It has the same chemical structure as Kevlar. Teijin now makes Twaron.
Contents
The Story of Kevlar

Kevlar was invented by an American chemist named Stephanie Kwolek. She worked for DuPont. In 1964, her team was looking for a new, lightweight, and strong fiber. They wanted to use it to make lighter, tougher tires. This was because they expected there to be a shortage of gasoline.
Stephanie was working with special liquids that formed liquid crystals. This was very unusual for polymers at the time. One of her solutions looked "cloudy" and "thin." Usually, solutions like this were thrown away. But Stephanie convinced a technician, Charles Smullen, to test it. They were amazed! The fiber they made from it was incredibly strong and didn't break, unlike nylon.
Her bosses quickly realized how important this discovery was. A whole new area of polymer chemistry began because of it. By 1971, the modern version of Kevlar was ready.
In 1971, a man named Lester Shubin had an idea. He suggested using Kevlar to replace nylon in bulletproof vests. Before Kevlar, vests made of nylon offered much less protection. Shubin remembered, "We folded it over a couple of times and shot at it. The bullets didn't go through." This showed how well Kevlar could stop bullets. Shubin received money to research how to use Kevlar in bulletproof vests.
Later, in the 1980s, another type of Kevlar called Kevlar 149 was invented by Jacob Lahijani at DuPont.
How Kevlar is Made
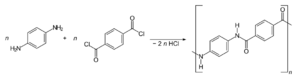
Kevlar is made in a lab from two main chemicals: 1,4-phenylene-diamine and terephthaloyl chloride. They are mixed together in a special liquid. This process creates Kevlar and also produces hydrochloric acid as a side product.
Making Kevlar is expensive. This is because it needs strong sulfuric acid to keep the material dissolved while it's being made and spun into fibers.
There are different types of Kevlar, each made for specific uses:
- Kevlar K-29 is used in things like cables, tires, and brake linings. It can also replace asbestos.
- Kevlar K49 is very strong and is used in ropes and cables.
- Kevlar K100 is a colored version of Kevlar.
- Kevlar K119 is more flexible and can stretch more. It's also better at resisting wear and tear.
- Kevlar K129 is extra strong for things like ballistic vests.
- Kevlar K149 is the strongest type. It's used for armor and in aerospace (like airplanes and spacecraft).
- Kevlar AP is 15% stronger than K-29.
- Kevlar XP is a lighter combination of resin and KM2 plus fiber.
- Kevlar KM2 offers even better protection against bullets for armor.
One important thing to know is that sunlight can damage Kevlar. This is called UV degradation. So, if Kevlar is used outdoors, it usually needs to be protected from the sun.
How Kevlar Works
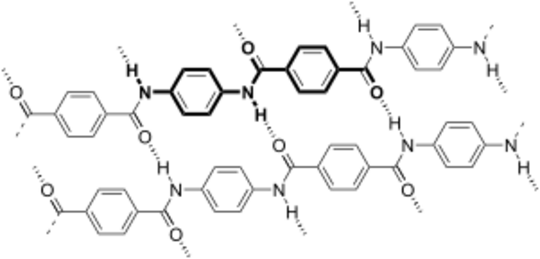
When Kevlar is spun into a fiber, it becomes incredibly strong. Its strength comes from the many tiny bonds between its different chains of molecules. These bonds are like tiny magnets holding the material together. This makes Kevlar much stronger than many other synthetic fibers.
Kevlar molecules are quite stiff and tend to line up in flat, sheet-like structures, similar to how silk protein is organized.
Hot and Cold Facts
Kevlar stays strong even in extremely cold temperatures, down to about -196°C (-321°F). In fact, it might even get a little stronger when it's very cold!
However, at higher temperatures, Kevlar's strength starts to drop. For example, if it's kept at 160°C (320°F) for 500 hours, it loses about 10% of its strength. If it's at 260°C (500°F) for 70 hours, it can lose about half its strength.
What Kevlar is Used For
Science and Space
Kevlar is often used in the field of cryogenics, which is the study of very low temperatures. It's good for this because it doesn't let much heat pass through it, and it's very strong. Scientists use it to hold delicate equipment in place while keeping it super cold.
At CERN, a big science lab, a thin window made of Kevlar was used. This window separated a vacuum (empty space) from a place with normal air pressure. It was strong enough to hold the pressure difference and was very thin.
Keeping People Safe
Kevlar is famous for being used in personal armor. This includes combat helmets, ballistic face masks, and ballistic vests (bulletproof vests). The helmets and vests used by the United States military, for example, use Kevlar. It's also used to protect the crews inside armoured fighting vehicles. Even parts of large ships like Nimitz-class aircraft carriers use Kevlar for protection.
Outside the military, firefighters wear uniforms with Kevlar for high heat resistance. Police officers and security teams also wear Kevlar body armor.
Kevlar is also used to make gloves, sleeves, jackets, and other clothes that protect people from cuts, scrapes, and heat. Gear made with Kevlar is often lighter and thinner than gear made from older materials.
Motorcyclists wear clothing with Kevlar padding to protect their shoulders and elbows. In fencing, athletes wear Kevlar in their protective jackets and masks. Speed skaters sometimes wear Kevlar under their clothes to prevent injuries from sharp skates if they fall.
Sports Gear
In Japanese archery (kyudo), Kevlar can be used for bow strings instead of more expensive hemp. It's also a main material for the lines that hold up paragliders. Some bicycle tires have a Kevlar lining inside to help prevent punctures.
In table tennis, thin layers of Kevlar are added to paddles to make them bounce more and weigh less. Tennis racquets are sometimes strung with Kevlar. It's also used in sails for high-performance racing boats.
In 2013, Nike started using Kevlar in some of its shoes. They used it in basketball shoes to make the front part less stretchy than traditional nylon. This helped the shoes fit better. Adidas also used Kevlar in the laces for some of their football boots.
Many companies, like Continental AG, make bike tires with Kevlar to protect them from getting flat. Folding bicycle tires also use Kevlar instead of steel in their edges, which makes them lighter and easier to store.
Music Instruments
Kevlar is used in loudspeaker cones, especially for bass and mid-range sounds, because it has good acoustic properties. It's also used as a strong part of fiber optic cables that carry audio data.
For string instruments like violins, Kevlar can be used in the bows. It gives the bow strength, flexibility, and stability. Kevlar is also used for tailcords, which connect the tailpiece to the endpin of string instruments.
Marching snare drums sometimes use Kevlar for their drumheads. This allows the drumhead to be pulled very tight, making a clear sound. Kevlar is also found in some woodwind instrument reeds, mixed with other materials to act like natural cane reeds.
Cars and Vehicles
Kevlar is sometimes used in parts of cars, especially high-performance cars like the Ferrari F40.
Chopped Kevlar fibers have been used to replace asbestos in brake pads. Kevlar brakes release fewer harmful fibers into the air than asbestos brakes.
Other Cool Uses

Wicks for fire dancing props often contain Kevlar. While Kevlar itself doesn't soak up fuel well, it's mixed with other materials like fiberglass or cotton. Kevlar's high heat resistance means these wicks can be used many times.
Sometimes, Kevlar is used instead of Teflon in some non-stick frying pans.
Kevlar fiber is used in ropes and cables. The fibers are kept straight inside a polyethylene sleeve. These cables have been used in suspension bridges, like the one in Aberfeldy, Scotland. They're also used to strengthen cracking concrete cooling towers. Kevlar is widely used as a protective outer layer for optical fiber cables, keeping them safe from damage.
Scientists at Georgia Institute of Technology used Kevlar fabric as a base for an experiment to make clothes that produce electricity. They wove tiny zinc oxide nanowires into the fabric. If successful, this new fabric could generate electricity just from movement!
A large retractable roof made of Kevlar was a key part of the design for the Olympic Stadium, Montreal for the 1976 Summer Olympics. However, it had many problems and was replaced later.
Kevlar can also be found as a strong layer in rubber bellows and hoses. This makes them good for high-temperature uses and gives them extra strength. It's also used as a braided layer on the outside of hoses to protect them from sharp objects.
Some cellphones, like certain Motorola and OnePlus models, have a Kevlar backplate. It's chosen because it's tough and doesn't block phone signals.
Kevlar fiber mixed with epoxy resin can be used in parts for marine current turbines (which generate electricity from ocean currents) or wind turbines. This is because they are very strong for their weight.
Strong Composite Materials
Aramid fibers, like Kevlar, are often used to make composite materials stronger. They are frequently combined with carbon fiber and glass fiber. The material that holds these fibers together is usually a strong epoxy resin.
You can find these strong composite materials in many places. They are used in the bodies of Formula 1 cars, helicopter rotor blades, and sports equipment like tennis, table tennis, badminton, and squash rackets. They are also in kayaks, cricket bats, and field hockey, ice hockey, and lacrosse sticks.
Kevlar 149, which is the strongest and most organized type of Kevlar, is sometimes used in aircraft construction. For example, it might be used in the front edge of airplane wings. This is because Kevlar is less likely to break than carbon or glass fiber if a bird hits it.
See also
 In Spanish: Kevlar para niños
In Spanish: Kevlar para niños
- Innegra S
- Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene
- Twaron
- Vectran
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |