Neornithes facts for kids

The Neornithes are what we call modern birds. They are the common ancestors of all birds alive today, along with all their descendants. There are about 9,000 to 10,000 different kinds of living bird species known around the world!
Bird Families: Palaeognathae and Neognathae
Modern birds are split into two main groups, like two big families. These are the Palaeognathae and the Neognathae.
The Palaeognathae group includes birds like tinamous and large, flightless birds called ratites. Think of ostriches, emus, and kiwis – these are all ratites. The Neognathae group contains all the other birds you can imagine, from tiny hummingbirds to huge eagles!
Scientists generally agree that modern birds first appeared during the Cretaceous period. This was the time when dinosaurs roamed the Earth. The split between the Palaeognathae and Neognathae groups happened before the big event that caused the extinction of most dinosaurs. This event is known as the K/T extinction event.
The very first fossil remains of modern birds might be from about ten million years after the Cretaceous period began. One early fossil, called Gallornis, is thought to be one of the first. However, only a small part of its leg and arm bones have been found.
Scientists have different ideas about when the many different types of Neognathae birds appeared. Some studies, looking at the DNA of birds, suggest they spread out and evolved into many forms during the Cretaceous period. But fossil evidence often points to this happening after the dinosaurs died out, in the early Tertiary period. Scientists are still working to understand how these different pieces of evidence fit together.
Related Pages
Images for kids
-
Archaeopteryx lithographica is often considered the oldest known true bird.
-
Anchiornis huxleyi is an important source of information on the early evolution of birds in the Late Jurassic period.
-
Confuciusornis sanctus, a Cretaceous bird from China that lived 125 million years ago, is the oldest known bird to have a beak.
-
Ichthyornis, which lived 93 million years ago, was the first known prehistoric bird relative preserved with teeth.
-
Didactic model of an avian heart
-
The nictitating membrane as it covers the eye of a masked lapwing
-
The disruptively patterned plumage of the African scops owl allows it to blend in with its surroundings.
-
Red lory preening
-
Restless flycatcher in the downstroke of flapping flight
-
A flock of Canada geese in V formation
-
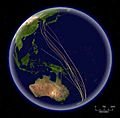
The routes of satellite-tagged bar-tailed godwits migrating north from New Zealand. This species has the longest known non-stop migration of any species, up to 10,200 km (6,300 mi).
-
The startling display of the sunbittern mimics a large predator.
-
Red-billed queleas, the most numerous species of wild bird, form enormous flocks—sometimes tens of thousands strong.
-
Many birds, like this American flamingo, tuck their head into their back when sleeping.
-
Nest of an eastern phoebe that has been parasitised by a brown-headed cowbird
-
A female calliope hummingbird feeding fully grown chicks
-
Reed warbler raising a common cuckoo, a brood parasite
-
Gran Canaria blue chaffinch, an example of a bird highly specialised in its habitat, in this case in the Canarian pine forests
-
Painted tiles with design of birds from Qajar dynasty
-
The California condor once numbered only 22 birds, but conservation measures have raised that to over 500 today.
-
Casuariiformes (cassowaries & emus)
-
Apterygiformes (kiwi)
-
†Aepyornithiformes (elephant birds)
-
Tinamiformes (tinamous)
-
†Dinornithiformes (moa)
-
Galliformes (chickens and relatives)
-
Anseriformes (ducks and relatives)
-
Apodiformes (swifts and hummingbirds)
-
Musophagiformes (turacos)
-
Otidiformes (bustards)
-
Cuculiformes (cuckoos)
-
Columbiformes (pigeons)
-
Pteroclidiformes (sandgrouse)
-
Gruiformes (rails and cranes)
-
Podicipediformes (grebes)
-
Charadriiformes (waders and relatives)
-
Phaethontiformes (tropicbirds)
-
Eurypygiformes (sunbittern and kagu)
-
Sphenisciformes (penguins)
-
Ciconiiformes (storks)
-
Cathartiformes (New World vultures)
-
Accipitriformes (hawks and relatives)
-
Strigiformes (owls)
-
Trogoniformes (trogons and quetzals)
-
Bucerotiformes (hornbills and relatives)
-
Coraciiformes (kingfishers and relatives)
-
Piciformes (woodpeckers and relatives)
-
Falconiformes (falcons)
-
Psittaciformes (parrots)
-
Passeriformes (passerines)
See also
 In Spanish: Aves para niños
In Spanish: Aves para niños