Nebula facts for kids
A nebula is a giant cloud in space made of dust, hydrogen gas, helium, and other glowing gases. These clouds are found in galaxies.
The first time someone wrote about a true nebula was in 964 AD. A Persian astronomer named Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi described a "little cloud" near the Andromeda galaxy in his book, Book of Fixed Stars.

Contents
How Nebulae Form
A nebula is mostly made of hydrogen gas and plasma (a superheated gas). A nebula can be the very first step in a star's life, or it can be one of its last stages.
Many nebulae form when gas in space, called the interstellar medium, starts to pull together because of gravity. As this material gets denser, huge stars can form in the middle. These new stars give off strong ultraviolet radiation (a type of light). This radiation makes the gas around them glow, so we can see it.
These glowing nebulae are called H II regions. Their size depends on how big the original gas cloud was. These are places where new stars are born, sometimes forming young groups of stars.
Some nebulae are created after a supernova explosion. This happens when a very big star dies in a huge blast. The material thrown out from the explosion glows because of the energy released. A great example is the Crab nebula in the Taurus constellation. The supernova that made it was seen in 1054 AD. In the center of the Crab Nebula is a neutron star, which is what's left of the exploded star.
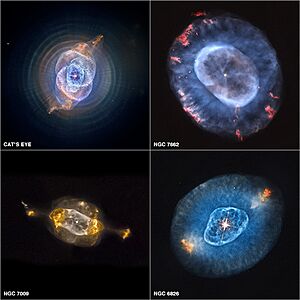
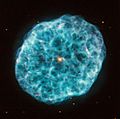
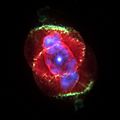
Other nebulae form as planetary nebulae. This is the final stage for smaller stars, like our own Earth's Sun. Stars up to 8-10 times the Sun's mass turn into red giants. They slowly lose their outer layers of gas over time. When a star has lost enough material, its temperature goes up. The ultraviolet radiation it sends out makes the surrounding gas cloud glow. This gas cloud is mostly Hydrogen (97%) and Helium (3%), with tiny amounts of other materials.
In the past, galaxies and star clusters were also called 'nebulae', but that's not how we use the word today. Nebulae can be grouped by how they look and why they glow.
Types of Nebulae
Star-Forming Nebulae
These are large areas of glowing hydrogen gas where new stars are being born. A famous example is the Orion complex. In these nebulae, gravity pulls gas and dust together. This material clumps into bigger and bigger masses, eventually becoming dense enough to form stars. Any leftover material can then form planets and other objects around the new stars.
Emission Nebulae
Emission nebulae make their own light. They are often called H II regions because the glowing gas is mostly ionized hydrogen. This ionized gas glows brightly, giving off light and infra-red radiation.
Reflection Nebulae
Reflection nebulae don't make their own light. Instead, they reflect light from nearby stars, like a cosmic mirror.
Dark Nebulae
Dark nebulae don't glow or reflect light. They are so dense with dust that they block the light from stars or nebulae behind them, making them appear as dark patches in space.
Planetary Nebulae
Planetary nebulae are quite common. They are formed when a red giant star reaches the end of its life. These stars usually become white dwarfs, leaving behind an expanding bubble of glowing gas. We see this as a bright, often circular, nebula.
Supernova Remnants
A supernova happens when a very massive star dies. When the nuclear fusion (the process that powers the star) stops in its core, the star collapses and then explodes. The expanding shell of gas from this explosion forms a supernova remnant. The Crab nebula is a supernova remnant from an explosion that likely happened in 1054 AD. The light and X-rays from supernova remnants come from the glowing, ionized gas. They also give off a lot of radio waves, which are created by fast-moving electrons spiraling in magnetic fields.
Images for kids
-
The "Pillars of Creation" from the Eagle Nebula.
-
NGC 604, a nebula in the Triangulum Galaxy
-
The Oyster Nebula is a planetary nebula in the constellation of Camelopardalis
-
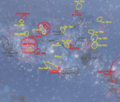
A close-up of the Orion Arm, showing major star groups (yellow), nebulae (red), and dark nebulae (grey) around the Local Bubble.
-
The Omega Nebula, an example of an emission nebula
-
The Horsehead Nebula, an example of a dark nebula.
-
The Cat's Eye Nebula, an example of a planetary nebula.
See also
 In Spanish: Nebulosa para niños
In Spanish: Nebulosa para niños
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |