Dust facts for kids
Dust is made of tiny bits of matter. It usually floats in the Earth's air. This dust comes from many places. It can be from soil, or lifted by strong winds. Volcanoes and pollution also create dust. Inside homes and offices, dust is a mix of many things. It has tiny bits of pollen from plants, human and animal hairs, and fibers from clothes and paper. It also contains minerals from outdoor soil, dead human skin cells, and even tiny pieces of burnt meteorites.
Contents
Dust in Our Homes and Its Effect on People
Tiny creatures called House dust mites live indoors wherever people are. Many people with asthma are allergic to dust mites. These mites are too small to see without a microscope. They are like tiny spiders. Dust mites mainly eat dead human skin cells. But they do not live on living people.
Their waste and other things they produce cause allergies. These are a big part of house dust. However, dust mites are quite heavy. So, they do not float in the air for very long. They usually stay on floors and other surfaces. When you walk or move things, they get stirred up. It can take up to two hours for them to settle back down.
Dust mites like dark, warm, and damp places. They grow well in mattresses, bedding, upholstered furniture, and carpets. Their waste contains special chemicals. These chemicals are released when they touch a wet surface. This can happen when a person breathes them in. These chemicals can harm cells in the human body. Dust mites became a bigger problem when humans started using more fabrics. This includes blankets and clothes.
Dust in the Air: Wind-Blown Dust

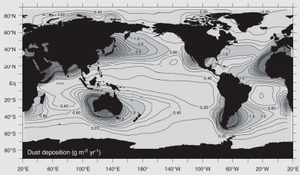
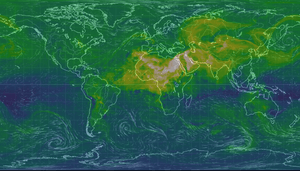
Dust in the air, also called wind-blown dust, comes from dry areas. Strong winds can pick up tiny bits of dirt and sand. This happens in places where the land is easily disturbed. Things like animals grazing, farming, and vehicles can make the land less stable. But not all dusty areas are caused by humans. About one-third of the Earth's land can produce dust. This includes very dry places like the Sahara desert. The Sahara alone is huge, covering 0.9 billion hectares. Other drylands cover 5.2 billion hectares.
Airborne dust forms when sand grains bounce and hit each other. This sends smaller dust particles into the air. This dust travels high up in the troposphere, which is the lowest part of Earth's atmosphere. This airborne dust is called an aerosol. Once in the air, it can change local temperatures. For example, dust from the Sahara can travel all the way to the Caribbean and the Amazon basin. It can affect air temperatures, make the ocean cooler, and change how much rain falls.
Dust in the Middle East
Dust has always been a part of life in the Middle East. But recently, it has gotten much worse. This is due to climate change and more desertification. Desertification means dry land turns into desert. Because many things cause this dust problem, there is no easy answer.
In Iran, dust directly affects over 5 million people. It has become a serious issue for the government. In the Khuzestan area, the air quality has become very bad. The amount of pollution in the air has been more than 50 times the normal level many times a year. New projects, like Project-Dust, are now studying Middle Eastern dust.
Dust from Roads
Dust kicked up by cars on roads can make up 33% of air pollution. Road dust is a mix of many things. It includes tiny particles from car exhausts and factories. It also has bits from tires and brakes. Dust from paved roads, potholes, and construction sites also adds to it.
Road dust is a big reason why tiny particles get into the air. Controlling road dust is a challenge in cities. It's also hard in places with lots of traffic on unpaved roads. This includes mines and landfill dumps.
Road dust can be reduced in several ways. Machines like street sweepers with vacuum cleaners can pick it up. People also spray roads with vegetable oil or water. Cars today produce less pollution. So, more of the dust in the air now comes from existing dust being stirred up.
Coal Dust and Health
Coal dust is very dangerous for coal miners. It can cause a lung disease called pneumoconiosis. This includes black lung disease. Because of this danger, laws have been made to control air quality in workplaces. Also, if there is a lot of coal dust floating in the air in a small space, it can cause an explosion. This is very rare but can happen in closed areas.
Controlling Dust
Controlling Outdoor Dust
Many government environmental agencies, like the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), require businesses to reduce the dust they create. The most common dust control problems happen at new housing developments in cities. In the United States, federal law says that construction sites must get permits. These permits require plans to control dust when they dig or clear land. Simple ways to control dust include spraying water on construction and demolition sites. They also prevent dust from being tracked onto nearby roads.
Controlling dust helps in many ways:
- It lowers health risks like allergies, pneumonia, and asthma attacks.
- It makes it easier to see and improves road safety.
- It leads to cleaner air, cleaner vehicles, and cleaner homes. This helps people stay healthier.
- It helps crops grow better in farming areas.
- It reduces car repair costs. Less dust means filters, bearings, and machines don't get clogged as much.
- It makes driving less tiring and improves how much fuel cars use.
- Each time dust control is applied, it works better. This means less frequent applications are needed over time.
US federal laws also require dust control on empty lots, unpaved parking lots, and unpaved roads. Dust in these places can be controlled by paving them or adding gravel. You can also spray the surface with water, vegetable oils, or other dust suppressants. Water misters can also help settle dust that is already in the air.
Controlling Dust Inside Homes
Dust control means stopping tiny solid particles, smaller than 500 micrometers, from spreading. Dust can be a health risk for children, older people, and those with respiratory illnesses like asthma.
House dust can easily float into the air. So, you need to be careful when cleaning it. A feather duster often just moves the dust around. It makes the dust float and land somewhere else. Products like Pledge and Swiffer are made to trap dust with sticky chemicals.
Special HEPA filters (tested to MIL STD 282) are very good at trapping dust. They can catch 99.97% of dust particles as small as 0.3 micrometers. Not all "HEPA-type" filters work as well. While vacuum cleaners with HEPA filters, water, or cyclones can filter better than those without, they might still release millions of tiny particles into the air. Central vacuum cleaners can be very good at removing dust, especially if they send the air outside.
Air filters vary a lot in how well they work. Laser particle counters are a good way to measure how effective a filter is. Medical tools can test for particles as small as 0.3 micrometers. To test for dust in the air, you can use special filters made from polyvinyl chloride or cellulose ester. These are good for finding dust that can be breathed in (less than 10 micrometers).
Making Surfaces Dust-Resistant
A dust-resistant surface is designed or treated to prevent dust from sticking or causing damage. This can happen during manufacturing or through a repair process. Some materials have a special outer layer that helps dust slide off. Panels or containers with seams might have stronger edges or sealants to protect them from dust.
Dust in Other Places
- Dust makes snowmelt faster in the San Juan Mountains
Dust in Outer Space
Cosmic dust is found everywhere in space. Clouds of gas and dust are the starting points for planets and solar systems. The zodiacal light, which you can see in a very dark night sky, is sunlight reflecting off dust particles orbiting the Sun. The tails of comets are made of dust and gas coming off the comet. Dust also covers planets, and huge dust storms happen on Mars, sometimes covering almost the entire planet. Interstellar dust is found between stars. When there's a lot of it, it forms nebulas and reflection nebulas.
Dust is common throughout our galaxy. Radiation from space heats this dust. The dust then sends out its own radiation in the microwave range. This can affect how we see the cosmic microwave background, which is leftover energy from the Big Bang. Dust in space has a complex way of giving off light.
Studying dust samples from outer space can tell us about the early solar system. Several spacecraft have collected dust. The Stardust spacecraft flew past Comet Wild 2 in 2004. It brought back a capsule of the comet's dust to Earth in 2006. In 2010, the Japanese Hayabusa spacecraft brought back dust samples from an asteroid.
Examples of Dust in the Atmosphere
-
Dry, windy weather sends clouds of dust across south-eastern Australia.
-
A thick dust plume over Kuwait and the north-western tip of the Persian Gulf.
Images for kids
-
Tarps and netting are often used to reduce the amount of dust released from construction sites.
See also
 In Spanish: Polvo para niños
In Spanish: Polvo para niños