NATO facts for kids
|
Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord
|
|

Logo
|
|

Flag
|
|
|
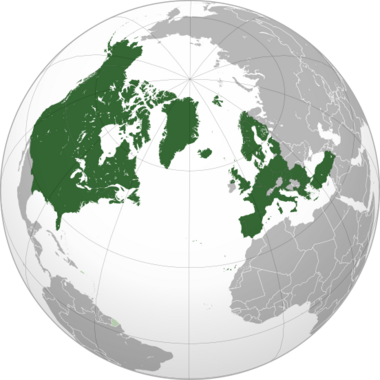
Member states shown in dark green
|
|
| Abbreviation | NATO OTAN |
|---|---|
| Formation | 4 April 1949 |
| Type | Military alliance |
| Headquarters | Brussels, Belgium |
|
Membership
|
|
|
Official languages
|
|
| Mark Rutte | |
|
Chair of the NATO Military Committee
|
Giuseppe Cavo Dragone |
|
Supreme Allied Commander Europe
|
Christopher G. Cavoli |
|
Supreme Allied Commander Transformation
|
Pierre Vandier |
| Expenses (2024) | Total: US$1.474 trillion Excluding the US: US$507 billion |
|
|
|
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is a group of countries that work together to keep each other safe. It's also known as the North Atlantic Alliance. NATO was created after World War II ended. Its main goal is to make sure that if one member country is attacked, all the other members will come to help. This idea is called "collective defense." NATO has been involved in many important events and operations around the world.
Contents
- When Did NATO Start?
- Why Was NATO Created?
- Who Are NATO's Members?
- How Does NATO Work?
- What Does NATO Do?
- NATO's Motto
- Where Is NATO's Headquarters?
- NATO's Military Strength
- NATO's Strategic Ideas
- NATO in the 21st Century
- Key Events in NATO's History
- Fun Facts About NATO
- NATO's Role in the World
- NATO's Structure in Detail
- NATO's Operations in Detail
- Images for kids
- See also
When Did NATO Start?
NATO was officially formed on April 4, 1949. This happened after World War II. Many countries wanted to prevent another big war from happening. So, they decided to create a group where they could all work together for peace and safety.
Why Was NATO Created?
The main reason NATO was created was to protect its member countries. The countries in NATO agreed that if any one of them was attacked, the others would help defend it. This is like a promise: "If you bother one of us, you bother all of us!" During the Cold War, NATO helped balance the power of the Soviet Union. It continued to be important even after the Soviet Union broke apart.
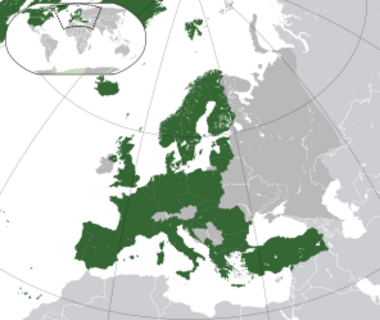
Who Are NATO's Members?
When NATO first started, there were 12 founding countries. These original members were:
- Belgium
- Canada
- Denmark
- France
- Iceland
- Italy
- Luxembourg
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Portugal
- United Kingdom
- United States
Over the years, more countries have joined NATO. Today, there are 32 member countries! The newest country to join was Sweden, on March 7, 2024.
How Does NATO Work?
NATO works because all its member countries agree to cooperate. They hold meetings to talk about important issues and make plans together. The main group that makes decisions in NATO is called the North Atlantic Council (NAC). Think of it as NATO's main office where all the big choices are made.
NATO also has a military side. This means that member countries train their soldiers together. They also share military resources. This helps them be ready to respond to any problems that might come up.
What Does NATO Do?
NATO has done many different things over the years. Here are some examples:
- Peacekeeping: NATO has helped keep peace in various parts of the world. For instance, it sent troops to places like Bosnia and Kosovo. This helped stop conflicts and protect people.
- Training: NATO helps train the military forces of other countries. This makes them better prepared to defend themselves. It also helps them keep their own citizens safe.
- Disaster Relief: NATO has also provided help during natural disasters. For example, it sent aid to countries hit by earthquakes and hurricanes.
NATO's Motto
NATO has a special motto in Latin: "animus in consulendo liber." This means "a mind unfettered in deliberation." It's a way of saying that NATO members are free to think and talk openly. They can share their ideas freely when they are making decisions together.
Where Is NATO's Headquarters?
NATO's main headquarters is located in Brussels, Belgium. Brussels is like the central hub for NATO! This is where many important meetings and decisions happen.
NATO's Military Strength
All the countries in NATO have their own armies, navies, and air forces. When you combine them, they form a very large and powerful military force! In 2022, the total military spending of all NATO members was about 55 percent of the world's total military spending. That shows how strong they are together.
NATO's Strategic Ideas
NATO uses important ideas to guide its actions. One key idea is "deterrence." Deterrence means trying to stop something bad from happening. You do this by showing that you are ready to act if it does. It's like saying, "We want peace, but if you start trouble, we are ready to defend ourselves!"
NATO in the 21st Century
In the 21st century, NATO continues to play a big role in keeping the world safe. It has worked to fight terrorism and prevent cyber attacks. NATO also responds to new challenges that come up in the modern world.
Key Events in NATO's History
- 1949: NATO is founded with 12 member countries.
- 1952: Greece and Turkey join NATO.
- 1955: West Germany joins NATO.
- 1982: Spain joins NATO.
- 1999: Hungary, Poland, and the Czech Republic join NATO.
- 2001: NATO uses Article 5 for the first time after the September 11 attacks. This means an attack on one member is an attack on all.
- 2004: Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, and Slovenia join NATO.
- 2009: Albania and Croatia join NATO.
- 2017: Montenegro joins NATO.
- 2020: North Macedonia joins NATO.
- 2023: Finland joins NATO.
- 2024: Sweden joins NATO.
Fun Facts About NATO
- NATO's official languages are English and French.
- NATO has a special flag with a white star inside a dark blue circle.
- NATO has its own song called the "NATO Hymn."
NATO's Role in the World
NATO is an important organization that helps keep the world secure. By working together, NATO's member countries can respond to problems. They can also protect their citizens and promote peace.
NATO's Structure in Detail
To understand how NATO works, it helps to know its different parts:
- The North Atlantic Council (NAC): This is NATO's main decision-making group. It has representatives from all member countries. The NAC meets regularly to make decisions about NATO's plans.
- The Secretary General: This person is the top official in NATO. They lead the organization and make sure everyone works well together.
- The Military Committee (MC): This is NATO's highest military authority. It includes the top military leaders from all member countries. The MC advises the NAC on military matters.
- Allied Command Operations (ACO): This is the NATO command that handles military operations worldwide. It's like the main office for all of NATO's military actions.
- Allied Command Transformation (ACT): This command works to improve NATO's military abilities. It helps NATO adapt to new challenges and stay modern.
- The NATO Parliamentary Assembly (PA): This group brings together lawmakers from all NATO countries. The PA discusses security issues and helps cooperation between NATO and its members.
NATO's Operations in Detail
NATO has been involved in many different operations:
- Operation Unified Protector: This was a NATO operation in Libya in 2011. Its goal was to protect civilians from attacks. NATO enforced a no-fly zone and carried out air strikes.
- Operation Active Endeavour: This is a NATO operation in the Mediterranean Sea. Its goal is to stop terrorism and other illegal activities. NATO ships patrol the sea and watch shipping.
- Operation Resolute Support: This was a NATO operation in Afghanistan. Its goal was to train and advise Afghan security forces. NATO troops helped the Afghan army and police.
- NATO Response Force (NRF): This is a special force that can be sent quickly to respond to crises. The NRF is made up of troops from all NATO member countries.
Images for kids
-
West Germany joined NATO in 1955.
-
A piece of the Berlin Wall is now displayed outside NATO Headquarters.
-
KFOR-MSU Carabinieri Patrols in front of the Ibar Bridge in Mitrovica, Kosovo, 2019.
-
General Austin S. Miller (right) oversaw the withdrawal of U.S. and NATO forces from Afghanistan.
-
Libyan Army Palmaria howitzers destroyed by the French Air Force near Benghazi in March 2011.
-
Protestors at a February 2022 rally against Russia's invasion of Ukraine in Helsinki.
See also
 In Spanish: OTAN para niños
In Spanish: OTAN para niños
 | Calvin Brent |
 | Walter T. Bailey |
 | Martha Cassell Thompson |
 | Alberta Jeannette Cassell |