Member states of NATO facts for kids
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is like a big team of 32 countries from Europe and North America that work together to keep each other safe. It was started on April 4, 1949. Most of the countries (30) are in Europe, and two are in North America.
NATO also has ways for its members to work with other countries nearby. These include programs like the Partnership for Peace.
Almost all NATO members have armies. The only one that doesn't have a typical army is Iceland. However, Iceland has a coast guard and special civilian experts who help NATO. Three NATO countries have nuclear weapons: France, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
NATO started with 12 countries. Over the years, more countries joined. Since the end of the Cold War, 16 more countries have joined NATO.
A very important rule in NATO is Article 5. It says that if one member country is attacked, it's like an attack on all of them. Then, all the other members will help the attacked country, even using their armed forces if needed. This rule mainly covers attacks on the main parts of North America and Europe, and all of Turkey. It does not cover faraway places like Hawaii or the Falkland Islands.
NATO also has an "Open Doors" policy. This means that countries like Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, and Ukraine are hoping to join NATO in the future.
Contents
How NATO Started and Grew
NATO was officially created on April 4, 1949. This happened when the North Atlantic Treaty was signed. The first 12 countries to join were: Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
All these countries also signed another agreement in 1951. This agreement made sure that civilians, not just military leaders, had a say in how NATO was run.
Today, NATO has 32 member countries. Besides the first 12, four more joined during the Cold War. These were Greece and Turkey in 1952, West Germany in 1955, and Spain in 1982. Also, when Germany became one country again in 1990, the former East Germany joined NATO.
After the Cold War ended, NATO grew even more. Many countries from Eastern Europe joined. These included the Czech Republic, Hungary, and Poland in 1999. Then, in 2004, Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, and Slovenia joined. Later, Albania and Croatia joined in 2009, Montenegro in 2017, and North Macedonia in 2020. Most recently, Finland joined in 2023, and Sweden joined in 2024.
No country has ever left NATO since it started. However, France did step away from NATO's main military command for a while, from 1966 to 2009.
As of March 7, 2024, NATO covers a huge area of about 27.5 million square kilometers (10.6 million square miles).
NATO Member Countries
Here is a list of the countries that are part of NATO and when they joined.
| Flag | Map | Country Name | Capital City | Joined NATO | Population | Military Spending (as % of GDP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Albania | Tirana | 1 April 2009 | 2,854,710 | 2.03 | |
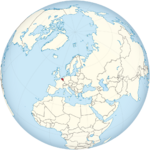 |
Belgium | Brussels | 24 August 1949 | 11,611,419 | 1.30 | |
 |
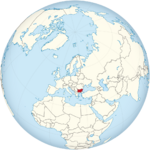 |
Bulgaria | Sofia | 29 March 2004 | 6,885,868 | 2.18 |
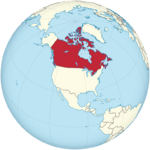 |
Canada | Ottawa | 24 August 1949 | 38,155,012 | 1.37 | |
 |
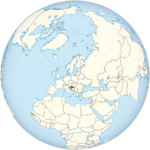 |
Croatia | Zagreb | 1 April 2009 | 4,060,135 | 1.81 |
 |
 |
Czech Republic | Prague | 12 March 1999 | 10,510,751 | 2.10 |
 |
 |
Denmark | Copenhagen | 24 August 1949 | 5,854,240 | 2.37 |
 |
 |
Estonia | Tallinn | 29 March 2004 | 1,328,701 | 3.43 |
 |
 |
Finland | Helsinki | 4 April 2023 | 5,619,399 | 2.41 |
 |
 |
France | Paris | 24 August 1949 | 64,531,444 | 2.06 |
 |
 |
Germany | Berlin | 6 May 1955 (West Germany) 3 October 1990 (Germany) |
83,408,554 | 2.12 |
 |
 |
Greece | Athens | 18 February 1952 | 10,445,365 | 3.08 |
 |
 |
Hungary | Budapest | 12 March 1999 | 9,709,786 | 2.11 |
 |
 |
Iceland | Reykjavík | 24 August 1949 | 370,335 | 0.0 |
 |
 |
Italy | Rome | 59,240,329 | 1.49 | |
 |
 |
Latvia | Riga | 29 March 2004 | 1,873,919 | 3.15 |
 |
 |
Lithuania | Vilnius | 2,786,651 | 2.85 | |
| Luxembourg | Luxembourg | 24 August 1949 | 639,321 | 1.29 | ||
 |
 |
Montenegro | Podgorica | 5 June 2017 | 627,859 | 2.02 |
 |
 |
Netherlands | Amsterdam | 24 August 1949 | 17,501,696 | 2.05 |
 |
 |
North Macedonia | Skopje | 27 March 2020 | 2,103,330 | 2.22 |
 |
 |
Norway | Oslo | 24 August 1949 | 5,403,021 | 2.20 |
 |
 |
Poland | Warsaw | 12 March 1999 | 38,307,726 | 4.12 |
 |
 |
Portugal | Lisbon | 24 August 1949 | 10,290,103 | 1.55 |
 |
 |
Romania | Bucharest | 29 March 2004 | 19,328,560 | 2.25 |
 |
 |
Slovakia | Bratislava | 5,447,622 | 2.0 | |
 |
 |
Slovenia | Ljubljana | 2,119,410 | 1.29 | |
 |
 |
Spain | Madrid | 30 May 1982 | 47,486,935 | 1.28 |
 |
 |
Sweden | Stockholm | 7 March 2024 | 10,467,097 | 2.14 |
 |
 |
Turkey | Ankara | 18 February 1952 | 84,775,404 | 2.09 |
 |
 |
United Kingdom | London | 24 August 1949 | 67,281,039 | 2.33 |
 |
 |
United States | Washington, D.C. | 336,997,624 | 3.38 |
Special Rules for Some Members
Some of the first countries to join NATO, like Denmark, Iceland, and Norway, made special agreements. They decided not to have permanent military bases from other NATO countries, no nuclear weapons, and no Allied military activities on their land unless they invited them. However, Denmark did allow the US to keep an existing base in Greenland.
For many years, from the mid-1960s to the mid-1990s, France decided to have its military work more independently from NATO. But in 2009, France rejoined NATO's main military command. France is still the only NATO member that doesn't fully commit its nuclear submarines to the alliance.
Countries Hoping to Join NATO
As of March 2024, three more countries have officially told NATO they want to join. These are Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, and Ukraine.
- At a big meeting in 2008, NATO members agreed that Georgia and Ukraine "will become members of NATO in the future."
- NATO invited Bosnia and Herzegovina to start a special plan to prepare for membership in April 2010.
Countries That Left NATO (or Didn't Join)
No country has ever officially left NATO. However, some places that used to be controlled by NATO member countries did not join NATO after they became independent.
 Cyprus became independent from the United Kingdom in 1960.
Cyprus became independent from the United Kingdom in 1960. Algeria became independent from France in 1962.
Algeria became independent from France in 1962. Malta became independent from the United Kingdom in 1964.
Malta became independent from the United Kingdom in 1964.
Military Personnel in NATO
This section shows how many people are in the military for each NATO country.
| Country | Active Soldiers | Reserve Soldiers | Other Military Staff | Total Military | Per 1,000 People | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Active | ||||||
| Albania | 5,350 | 2,100 | 2,150 | 9,600 | 3.1 | 1.7 | |
| Belgium | 23,500 | 5,900 | 0 | 29,400 | 2.5 | 2 | |
| Bulgaria | 36,950 | 3,000 | 0 | 39,950 | 5.9 | 5.4 | |
| Canada | 62,300 | 29,100 | 5,800 | 97,200 | 2.5 | 1.6 | |
| Croatia | 16,800 | 21,000 | 3,000 | 40,800 | 9.8 | 4 | |
| Czech Republic | 26,600 | 4,200 | 0 | 30,800 | 2.8 | 2.5 | |
| Denmark | 13,100 | 44,200 | 0 | 57,300 | 9.6 | 2.2 | |
| Estonia | 7,100 | 20,000 | 21,200 | 48,300 | 40.5 | 5.9 | |
| Finland | 23,850 | 233,000 | 2,900 | 259,750 | 46.2 | 4.2 | |
| France | 202,200 | 38,500 | 95,100 | 335,800 | 4.9 | 3 | |
| Germany | 179,850 | 34,100 | 0 | 213,950 | 2.5 | 2.1 | |
| Greece | 132,000 | 289,000 | 7,400 | 428,400 | 41 | 12.6 | |
| Hungary | 32,150 | 20,000 | 0 | 52,150 | 5.3 | 3.3 | |
| Iceland | 0 | 0 | 250 | 250 | 0.7 | 0 | |
| Italy | 161,850 | 14,500 | 178,600 | 354,950 | 5.8 | 2.7 | |
| Latvia | 6,600 | 16,000 | 0 | 22,600 | 12.5 | 3.7 | |
| Lithuania | 16,100 | 12,950 | 18,400 | 47,450 | 18.1 | 6.1 | |
| Luxembourg | 900 | 0 | 600 | 1,500 | 2.2 | 1.3 | |
| Montenegro | 2,710 | 2,800 | 4,100 | 9,610 | 16 | 4.5 | |
| Netherlands | 33,650 | 6,350 | 6,500 | 46,500 | 2.6 | 1.9 | |
| North Macedonia | 8,000 | 4,850 | 7,600 | 20,450 | 9.6 | 3.7 | |
| Norway | 25,400 | 40,000 | 0 | 65,400 | 11.9 | 4.6 | |
| Poland | 164,100 | 37,500 | 14,300 | 215,900 | 5.6 | 4.2 | |
| Portugal | 21,500 | 23,500 | 22,600 | 67,600 | 6.6 | 2.1 | |
| Romania | 69,900 | 55,000 | 57,000 | 181,900 | 10 | 3.9 | |
| Slovakia | 12,800 | 0 | 0 | 12,800 | 2.3 | 2.3 | |
| Slovenia | 6,200 | 950 | 0 | 7,150 | 3.4 | 3 | |
| Spain | 122,200 | 13,800 | 80,500 | 216,500 | 4.6 | 2.6 | |
| Sweden | 14,850 | 21,500 | 0 | 36,350 | 3.4 | 1.4 | |
| Turkey | 355,200 | 378,700 | 160,800 | 894,700 | 10.6 | 4.2 | |
| United Kingdom | 141,100 | 70,450 | 0 | 211,550 | 3.1 | 2.1 | |
| United States | 1,315,600 | 797,200 | 0 | 2,112,800 | 6.2 | 3.8 | |
| NATO | 3,240,410 | 2,233,850 | 688,800 | 6,163,060 | 6.3 | 3.3 | |
How Much Money NATO Countries Spend on Defense
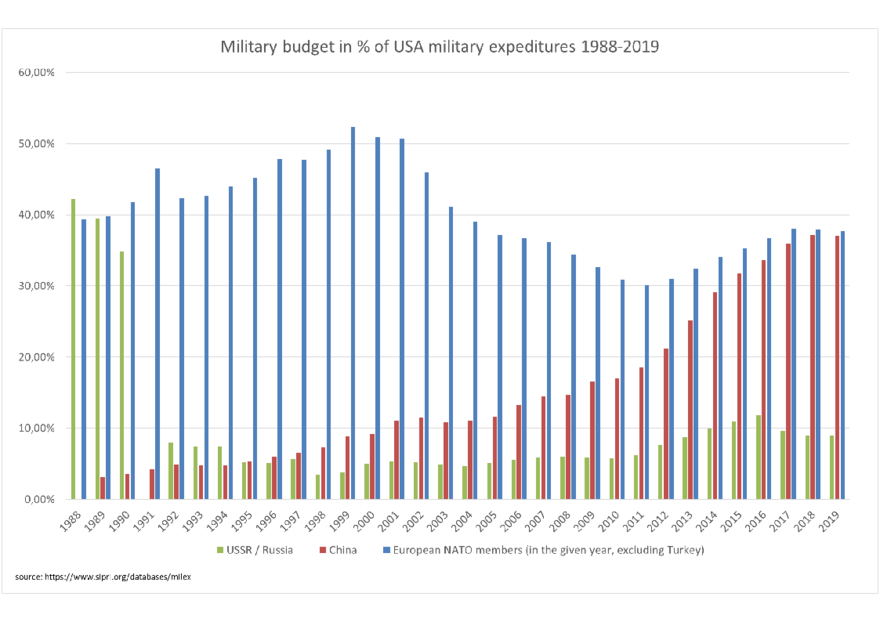
Military spending of the US compared to 31 other NATO member countries (US$ millions). United States (65.63%) All other NATO countries total (34.37%)
Total military spending of NATO member countries except the United States, and Sweden (US$ millions). Greece (1.75%) Estonia (0.28%) Portugal (0.99%) Montenegro (0.03%) Lithuania (0.51%) Norway (2.05%) Turkey (4.42%) Latvia (0.25%) Denmark (1.91%) Croatia (0.34%) North Macedonia (0.062%) Romania (1.32%) Hungary (1.01%) Bulgaria (0.45%) Italy (7.63%) France (13.47%) Poland (7.50%) Spain (4.57%) Slovenia (0.21%) United Kingdom (18.03%) Slovakia (0.62%) Canada (6.56%) Germany (17.26%) Netherlands (3.85%) Other (4.928%)
The United States spends more than twice as much on defense as all other NATO members put together. NATO members have agreed to spend at least 2% of their country's total economic output (called GDP) on defense. However, in 2023, most countries did not meet this goal.
| Member Country | Population | Total Money (GDP in $billions) |
Defense Spending (US$) | Military Staff | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total ($millions) |
% of GDP | Per Person | ||||
| 3,101,621 | 25.43 | 516 | 2.03 | 114 | 7,000 | |
| 11,913,633 | 655.74 | 8,519 | 1.30 | 585 | 21,300 | |
| 6,827,736 | 106.72 | 2,325 | 2.18 | 218 | 26,900 | |
| 38,516,736 | 2,233.83 | 30,495 | 1.37 | 609 | 77,100 | |
| 4,169,239 | 89.90 | 1,624 | 1.81 | 315 | 13,700 | |
| 10,706,242 | 326.13 | 6,834 | 2.10 | 426 | 29,500 | |
| 6,057,361 | 418.58 | 9,940 | 2.37 | 1,479 | 17,300 | |
| 1,202,762 | 41.89 | 1,437 | 3.43 | 690 | 7,500 | |
| 5,614,571 | 302.72 | 7,308 | 2.41 | 1,103 | 30,800 | |
| 62,819,428 | 3,120.35 | 64,271 | 2.06 | 801 | 204,700 | |
| 84,220,184 | 4,610.04 | 97,686 | 2.12 | 911 | 185,600 | |
| 10,497,595 | 249.81 | 7,684 | 3.08 | 648 | 110,800 | |
| 9,670,009 | 231.61 | 4,889 | 2.11 | 349 | 20,900 | |
| 360,872 | 32.89 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 61,021,855 | 2,311.17 | 34,462 | 1.49 | 505 | 171,400 | |
| 1,821,750 | 45.15 | 1,421 | 3.15 | 539 | 8,400 | |
| 2,655,755 | 80.72 | 2,300 | 2.85 | 538 | 18,500 | |
| 660,924 | 60.69 | 785 | 1.29 | 921 | 900 | |
| 602,445 | 8.02 | 162 | 2.02 | 170 | 1,600 | |
| 17,463,930 | 1,162.88 | 21,640 | 1.85 | 1,030 | 41,900 | |
| 2,133,410 | 15.87 | 353 | 2.22 | 127 | 6,100 | |
| 5,600,850 | 482.58 | 10,606 | 2.20 | 1,754 | 24,300 | |
| 37,991,766 | 848.86 | 34,975 | 4.12 | 711 | 216,100 | |
| 10,223,150 | 298.98 | 4,627 | 1.55 | 360 | 28,400 | |
| 18,326,327 | 383.92 | 8,644 | 2.25 | 289 | 66,600 | |
| 5,425,319 | 142.81 | 2,841 | 1.99 | 387 | 15,600 | |
| 2,099,790 | 73.52 | 949 | 1.29 | 339 | 5,900 | |
| 47,051,085 | 1,658.36 | 21,269 | 1.28 | 366 | 117,400 | |
| 10,536,338 | 626.54 | 13,428 | 2.14 | 1,185 | 23,100 | |
| 83,593,483 | 1,090.29 | 22,776 | 2.09 | 310 | 481,000 | |
| 68,502,956 | 3,520.50 | 82,107 | 2.33 | 1,077 | 138,100 | |
| 338,229,980 | 28,719.94 | 967,707 | 3.37 | 2,239 | 1,300,200 | |
| 969,619,192 | 53,976.44 | 1,474,399 | 2.73 | 1,210 | 3,418,600 | |
How People Feel About NATO
A survey in 2016 showed that most people in NATO countries liked NATO. However, many also thought their country's military spending should stay the same.
The survey also asked if their country should help another NATO country with its military if it was attacked. The answers were mixed. About half or fewer people in six of eight countries said their country should use military force. In Germany (58%), France (53%), and Italy (51%), more than half said they should not use military force.
More than half of Americans (56%) and Canadians (53%) were willing to help. Many British (49%) and Polish (48%) people also supported helping. People in Spain were split, with 48% supporting and 47% opposing.
A company called YouGov also checks public opinion about NATO. As of January 6, 2025, 45% of people in the UK strongly support NATO. 31% tend to support it. Older people (65+) support NATO more strongly (59%). Younger people (18-24) tend to support it (34%), but many (33%) are unsure.
A poll in 2025 found that 52% of people in Slovenia supported NATO membership. This is less than the 66% who voted for it in a special vote in 2003.
 | Chris Smalls |
 | Fred Hampton |
 | Ralph Abernathy |