Romanticism facts for kids
Romanticism (also called the Romantic era or Romantic period) was a big change in how people thought about art, literature, and music. It happened in Europe during the late 1700s and early 1800s.
This movement focused on strong feelings, using your imagination, and the beauty of nature. It also valued human life, freedom to express yourself, being an individual, and old stories like legends and fairy tales. Romanticism was a way of reacting against the strict rules of the Age of Enlightenment. It also pushed back against the changes brought by the Industrial Revolution, which made life more about factories and science.
Romantic ideas were strongest in arts like music and literature. But they also influenced how people studied history, how they learned in schools, and how they looked at the natural world.
Contents
Famous Romantics in Europe
Romanticism spread across Europe. Many artists, writers, and musicians became famous for their work during this time.
Romanticism in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom was one of the first places to have factories and new scientific ideas. Because of this, Romanticism there often showed a strong connection to nature and feelings. Some important figures were:
- William Wordsworth
- Samuel Taylor Coleridge
- Lord Byron
- Percy Bysshe Shelley
- William Blake
- Robert Burns
- Walter Scott
- J. M. W. Turner
Romanticism in Germany
At the same time as Britain, Germany also had a strong Romantic movement. Key ideas in German Romanticism included traveling, the beauty of nature, and old German mythology. Some famous people from this period were:
- Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (when he was younger)
- Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel
- Friedrich Schiller
- Ludwig van Beethoven
- The Brothers Grimm
Related Topics
Images for kids
-
Philipp Otto Runge, The Morning, 1808. This painting shows the beauty of a new day.
-
William Blake, The Little Girl Found, from Songs of Innocence and Experience, 1794. Blake was a poet and artist who explored imagination.
-
John William Waterhouse, The Lady of Shalott, 1888. This painting is based on a poem by Alfred, Lord Tennyson.
-
William Wordsworth (pictured) and Samuel Taylor Coleridge helped start the Romantic Age in English literature in 1798 with their book Lyrical Ballads.
-
Portrait of Lord Byron by Thomas Phillips, c. 1813. Byron was a famous poet whose characters often showed strong emotions.
-
Robert Burns in Alexander Nasmyth's portrait of 1787. Burns was a Scottish poet known for his folk-inspired works.
-
Adam Mickiewicz on the Ayu-Dag, by Walenty Wańkowicz, 1828. Mickiewicz was a major Polish Romantic poet.
-
Juliusz Słowacki, a Polish poet and one of the "Three National Bards" of Polish literature. He was a key figure in the Polish Romantic period.
-
El escritor José de Espronceda, portrait by Antonio María Esquivel (c. 1845) (Museo del Prado, Madrid). Espronceda was a Spanish Romantic poet.
-
Portuguese poet, novelist, politician and playwright Almeida Garrett (1799–1854).
-
Thomas Cole, The Course of Empire: The Savage State (1 of 5), 1836. Cole's series explored the rise and fall of civilizations.
-
Thomas Jones, The Bard, 1774. This painting combines Romantic ideas with Welsh national pride.
-
Ludwig van Beethoven, painted by Joseph Karl Stieler, 1820. Beethoven's music is a great example of Romanticism.
-
Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres, Portrait of Niccolò Paganini, 1819. Paganini was a famous violinist.
-
Frédéric Chopin in 1838 by Eugène Delacroix. Chopin was a famous Romantic composer.
-
Akseli Gallen-Kallela, The Forging of the Sampo, 1893. This Finnish artist found inspiration in his country's old stories.
-
Hans Gude, Fra Hardanger, 1847. This painting shows the beauty of the Norwegian landscape.
-
The November Uprising (1830–31) in Poland against the Russian Empire. Romanticism often inspired feelings of national pride and freedom.
-
Hameau de la Reine, Palace of Versailles (1783–1785). This "hamlet" was built for Queen Marie Antoinette to enjoy a simpler, more natural life.
-
Royal Pavilion in Brighton by John Nash (1815–1823). This building shows a mix of styles, including Romantic influences.
-
Cologne Cathedral (1840–80). Many Romantic artists were inspired by medieval architecture.
-
Grand Staircase of the Paris Opera by Charles Garnier (1861–75).
-
Basilica of Sacré-Cœur by Paul Abadie (1875–1914).
-
Thomas Cole, Childhood (1842), one of four scenes in The Voyage of Life. This series explores different stages of life.
-
Felix Mendelssohn, 1839. Mendelssohn was a German Romantic composer.
-
Robert Schumann, 1839. Schumann was another important German Romantic composer.
-
Franz Liszt, 1847. Liszt was a Hungarian composer and pianist.
-
Hector Berlioz by Gustave Courbet, 1850. Berlioz was a French Romantic composer.
-
Giovanni Boldini, Portrait of Giuseppe Verdi, 1886. Verdi was a famous Italian opera composer.
-
Richard Wagner, c. 1870s. Wagner was a German composer known for his operas.
-
Giacomo Meyerbeer, 1847.
-
Gustav Mahler, 1896. Mahler was a late-Romantic composer.
-
Joseph Vernet, 1759, Shipwreck. This painting shows the dramatic power of nature.
-
Joseph Wright, 1774, Cave at evening, Smith College Museum of Art, Northampton, Massachusetts.
-
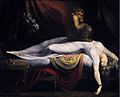
Henry Fuseli, 1781, The Nightmare. This painting explores dark and imaginative themes.
-
Philip James de Loutherbourg, Coalbrookdale by Night, 1801. This painting shows a key place of the English Industrial Revolution at night.
-
Théodore Géricault, The Charging Chasseur, c. 1812. This painting shows a dramatic moment of action.
-
Eugène Delacroix, Collision of Moorish Horsemen, 1843–44. Delacroix was a leading French Romantic painter.
-
Eugène Delacroix, The Bride of Abydos, 1857, based on a poem by Byron.
-
James Ward, 1814–1815, Gordale Scar. This painting captures the wildness of nature.
-
John Constable, 1821, The Hay Wain. Constable was famous for his peaceful landscape paintings.
-
J. C. Dahl, 1826, Eruption of Vesuvius. This painting shows the powerful forces of nature.
-
Isaac Levitan, Pacific, 1898, State Russian Museum, St.Petersburg.
-
J. M. W. Turner, The Burning of the Houses of Lords and Commons (1835), Philadelphia Museum of Art. Turner was known for his dramatic and colorful paintings.
-
Ivan Aivazovsky, 1850, The Ninth Wave, Russian Museum, St. Petersburg. This painting shows the power of the ocean.
-
John Martin, 1852, The Destruction of Sodom and Gomorrah, Laing Art Gallery. Martin was known for his epic and dramatic scenes.
-
Frederic Edwin Church, 1860, Twilight in the Wilderness, Cleveland Museum of Art. This painting captures the beauty of American wilderness.
-
Albert Bierstadt, 1863, The Rocky Mountains, Lander's Peak. Bierstadt painted grand landscapes of the American West.
See also
 In Spanish: Romanticismo para niños
In Spanish: Romanticismo para niños