Victorian literature facts for kids
Victorian literature refers to all the English books, poems, and plays written during the time Queen Victoria was in charge of England, from 1837 to 1901. Many people think this period was a "Golden Age" for English books, especially novels. During this time, the novel became the most important type of writing in English.
Books from the Victorian era show the big changes happening in England. These changes included new scientific discoveries, economic growth, and amazing new technologies. Society also changed, with new social classes appearing and different ideas about religion. Famous writers from this time include Charles Dickens, William Makepeace Thackeray, the three Brontë sisters, Elizabeth Gaskell, George Eliot, Thomas Hardy, and Rudyard Kipling.
Before the Victorian era, writers often focused on feelings and nature. But Victorian writers started looking at real-world problems. Authors like Thomas Carlyle wrote about how the Industrial Revolution made life harder for many people. This inspired other writers, like poet Elizabeth Barrett Browning and novelists Charles Dickens and Thomas Hardy. Elizabeth Barrett Browning wrote about child labor, which helped her become famous even though it was hard for women writers then. Charles Dickens used humor to talk about big problems like how some people were very rich while others were very poor. Thomas Hardy used his stories to question old ideas about religion and society.
Poetry and theatre were also important. Robert Browning and Alfred Tennyson were the most famous poets. Towards the end of the 1800s, plays became popular again. Well-known playwrights included Gilbert and Sullivan, George Bernard Shaw, and Oscar Wilde.
Contents
Amazing Novels of the Victorian Era
Charles Dickens is probably the most famous Victorian novelist. He was great at creating memorable characters. People loved his stories, and he is still one of the most popular authors today. His first novel, The Pickwick Papers, came out when he was only twenty-five. It was a huge hit!
Dickens's books were often published in small parts each month. This made readers excited to see what would happen next. He worked very hard to write entertaining stories. But he also used his books to talk about social problems, like how poor people suffered. Some of his most important books include Oliver Twist (about an orphan boy), A Christmas Carol (a classic holiday story), David Copperfield (a story about growing up), and Great Expectations (another story about a young man's life). Over time, his books became a bit darker, showing a trend in many 19th-century writings.
William Makepeace Thackeray was a big rival to Dickens. He wrote in a similar style but often showed a more critical view of his characters. He also wrote more about middle-class society. His most famous book is Vanity Fair, which tells a story without a clear hero.
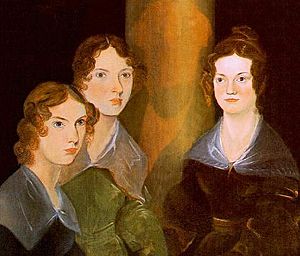
The Brontë sisters—Charlotte, Emily, and Anne Brontë—wrote very unique books. Their works were not always liked by critics at first. Emily's only novel, Wuthering Heights, is a dark and romantic story about love and revenge. Charlotte's Jane Eyre is another major novel with a strong female character and some mysterious elements. Anne's The Tenant of Wildfell Hall was one of the first books to be seen as a feminist novel because it showed a woman trying to escape a bad marriage.
Elizabeth Gaskell also wrote important books. Her famous works include Mary Barton, Cranford, and North and South. These books often showed the lives of working-class people and the challenges of the Industrial Revolution.
George Eliot was the pen name of Mary Ann Evans. Like the Brontë sisters, she used a male name to publish her books. Her notable works include Adam Bede, The Mill on the Floss, and Middlemarch. Her novels often explored deep ideas about morality and society.
Later in the period, Thomas Hardy wrote books like Far from the Madding Crowd, Tess of the d'Urbervilles, and Jude the Obscure. Hardy was known for his stories about country life in England. His books often questioned the changes happening as cities grew bigger.
Victorian Poetry and Plays
Robert Browning and Alfred Tennyson were two of the most important poets in Victorian England. Tennyson was even the "Poet Laureate," meaning he was the official poet for the Queen.
Many Victorian poets loved looking back at history. They were interested in old stories about knights and heroes. They hoped these stories would inspire people to be noble and brave. A great example is Alfred Tennyson's Idylls of the King. This book retold the stories of King Arthur and his knights, mixing them with ideas from Tennyson's own time.
The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood was a group of artists and poets who also drew inspiration from old myths and folklore. Dante Gabriel Rossetti was a famous poet in this group, but his sister Christina is now seen by many as an even stronger poet.
In theatre, funny plays called farces and comic operas were very popular. These often competed with serious plays and even Shakespeare's works. Towards the end of the 1800s, plays by Oscar Wilde became very famous. His play The Importance of Being Earnest (1895) is a brilliant comedy that makes fun of high society. It is still very popular today.
Books for Young Readers
The Victorians are often given credit for "inventing childhood." This happened partly because they worked to stop child labor and started making school mandatory for children. As more children learned to read, books for young people became a big business.
Some famous writers, like Dickens, wrote books for children. But new authors appeared who wrote mainly for kids. These included Lewis Carroll (who wrote Alice's Adventures in Wonderland), Anna Sewell (who wrote Black Beauty about a horse), and R. M. Ballantyne (who wrote The Coral Island). Other authors like Robert Louis Stevenson (who wrote Treasure Island) wrote for adults, but their adventure stories are now often read by children.
At first, many children's books were meant to teach lessons, not just for fun. But as illustrations became more common, children started enjoying reading more. Fairy tales and folk tales also became very popular. There were different types of books and magazines for boys and girls. Girls' stories often focused on family life, while boys' stories were usually about adventures.
Nonfiction: Science, Ideas, and Discovery

The Victorian era was a very important time for science. Scientists tried to describe and classify everything in the natural world. One book, in particular, changed everything: Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species. This book introduced the idea of evolution, which challenged many old beliefs about humans and their place in the world. It took time for people to accept it, but it greatly influenced later thinking and literature.
Many other nonfiction books were important. John Stuart Mill wrote about ideas like liberty and how society should work. The historian Thomas Carlyle wrote influential books like The French Revolution: A History. These books shaped political ideas at the time.
Big reference books were also created. The Oxford English Dictionary, which is now the most important dictionary of the English language, started during this time. The Dictionary of National Biography and a large encyclopedia called Encyclopædia Britannica were also published.
Nature Writing
As cities grew, people became more interested in nature. Writers like Philip Henry Gosse and Sarah Bowdich Lee wrote popular books about the natural world. The Illustrated London News, the world's first illustrated weekly newspaper, often featured articles and pictures about nature.
Supernatural and Fantastic Stories
The late 19th century saw the rise of "Gothic" stories. These tales mixed romance with horror to thrill readers. They often featured things like monsters, ghosts, curses, hidden rooms, and even witchcraft. Gothic stories usually took place in spooky castles or old monasteries, but sometimes the scary characters would appear in cities like London.
This era also saw the creation of famous detective stories and other fantastic tales. Characters like Sherlock Holmes, the famous detective, and villains like Dracula and Edward Hyde (from Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde) became very popular.
How Victorian Literature Influenced the World
Victorian literature had a huge impact beyond England. Writers in the United States and British colonies like Australia, New Zealand, and Canada were all influenced by British books. Even though these writers started to develop their own styles, they are often still considered part of Victorian literature.
Famous American writers from this time include Emily Dickinson, Henry James, Herman Melville, Harriet Beecher Stowe (who wrote Uncle Tom's Cabin), and Mark Twain.
It can be tricky to define "Victorian literature" because the early books are very different from the later ones. Many writers, like Arthur Conan Doyle (who created Sherlock Holmes), Rudyard Kipling, and H. G. Wells (who wrote science fiction), wrote important works during Victoria's reign. However, their style often feels more like the next era, called the Edwardian period.
Images for kids
-
The Brontë sisters wrote fiction rather different from that common at the time.
-
Charles Darwin's work On the Origin of Species affected society, throughout the Victoria era, and still does today.
-
Harriet Beecher Stowe wrote Victorian fiction outside Victoria's domains.
See also
 | Audre Lorde |
 | John Berry Meachum |
 | Ferdinand Lee Barnett |







