Aluminium facts for kids
Aluminium (or aluminum in American English) is a chemical element. Its symbol is Al, and its atomic number is 13. Aluminum is the most common metal found on Earth. It's famous for being light and for not rusting easily. Aluminum and its alloys (mixtures with other metals) are used in many industries, like transportation, aerospace, and building. They are used to make a huge variety of products and are very important for the world's economy.
Sometimes, it's tricky to say who discovered something first. Friedrich Wöhler is often given credit for getting pure aluminum in 1827. But a Danish scientist named Hans Christian Ørsted made an impure form of it two years earlier, in 1825. So, both are important in its discovery!
Contents
What Makes Aluminum Special?
Aluminum is great at letting electricity and heat pass through it. It's light and strong. You can flatten it into thin sheets (this is called being malleable) or pull it into long, thin wires (this is called being ductile). Even though it reacts easily with other things, it doesn't rust or corrode much.
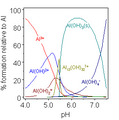
Aluminum stops rusting by forming a very thin layer of aluminium oxide on its surface. This layer acts like a shield, stopping oxygen from reaching the metal. Without oxygen, corrosion can't happen. This thin layer is why aluminum doesn't seem very reactive.
Where We Find Aluminum
Aluminum is the most common metal in the Earth's crust. It's the third most common element overall, after oxygen and silicon. But you won't find pure aluminum metal just lying around in nature. Even though aluminum is common, not all minerals that contain it are good for getting the metal out easily.
Almost all aluminum metal is made from a rock called bauxite. Bauxite forms when certain rocks weather away in tropical areas. In 2017, most bauxite was mined in Australia, China, Guinea, and India.
Making aluminum takes a lot of energy, especially electricity. So, factories that melt bauxite into aluminum (called smelters) are usually built in places where electricity is both plentiful and cheap. In 2012, the biggest aluminum smelters were in China, Russia, Bahrain, United Arab Emirates, and South Africa.
Aluminum was once thought to be a precious metal, even more valuable than gold! This changed as technology got better, making it cheaper and easier to produce pure aluminum.
How We Use Aluminum
Many things are made of aluminum. A lot of it is used in overhead power lines. It's also widely used for window frames and aircraft bodies. In homes, you'll find it in saucepans, soft drink cans, and cooking foil. Aluminum is also used to coat car headlamps and compact discs.
Pure aluminum is very soft. So, a harder metal is almost always added to it to make it stronger. This harder metal is usually copper. Copper/aluminum alloys are used to make ships. The aluminum helps prevent rust, and the copper helps stop barnacles from growing on the ship.
Aluminum compounds are found in deodorants, water treatment plants, food additives, and antacids. Aluminum helps us travel, as it's a part of cars, trucks, airplanes, bicycles, and rockets.
Aluminum is the most used non-ferrous metal (meaning it doesn't contain iron). In 2016, the world made 58.8 million metric tons of aluminum. This was more than any other metal except iron.
When aluminum is mixed with Fe2O3 (iron oxide, or rust) in the right amount, it can make a substance called thermite. Thermite burns very quickly and gets extremely hot. Aluminum is also a main part of the fuel that helps propel rockets into space.
Is Aluminum Harmful?
For most people, aluminum is not as toxic (harmful) as heavy metals. The United States Department of Health and Human Services says aluminum is not a substance that causes cancer. However, some studies suggest that too much aluminum might be linked to certain brain diseases. These diseases can cause problems with thinking and behavior. You can get a lot of aluminum from things like too many antacids, antiperspirants, vaccines, and cosmetics.
The metal is protected by a surface layer of aluminum oxide. This layer forms right away when the metal touches air and is very stable. This is why dishes, pots, and pans can be made of aluminum, and why aluminum foil is safe for packing food. However, acidic foods, like tomatoes, can dissolve this protective oxide layer and some of the aluminum underneath. This isn't dangerous and doesn't weaken the aluminum object. But it can make the food taste a bit off, which is why it's often suggested not to cook very acidic foods in aluminum pots.
Being around aluminum powder or fumes from aluminum welding can cause a lung disease called pulmonary fibrosis. Fine aluminum powder can also catch fire or explode, which is a danger in workplaces.
Did You Know?
- Recycling aluminum uses only one-twentieth (5%) as much energy as making new aluminum from its raw ore.
- Aluminum is the most common metal in the Earth's crust.
- Aluminum and Aluminium are two different names for this metal.
Recycling Aluminum
Getting aluminum back by recycling has become a very important part of the aluminum industry. Recycling wasn't very popular until the late 1960s, when more and more aluminum beverage cans were used. This made people more aware of recycling.
Since making new aluminum needs a huge amount of electricity, recycling aluminum is much cheaper. The cost of recycling aluminum is far less than the cost of making it from bauxite ore.
Cool Facts About Aluminum
- The Earth's crust is made of about 8.2% aluminum. But it needs to be processed to separate it from other compounds and minerals.
- Aluminum weighs one-third less than steel.
- Aluminum does not rust because it does not contain iron.
- Aluminum was used in ancient Greece.
- Napoléon III served meals on aluminum plates because, at the time, it was considered more valuable than silver or gold.
- A new aluminum can can be made as little as 60 days after other aluminum cans are recycled.
- Because of recycling, about 75% of all aluminum ever made is still being used today.
- Aluminum has even been found on the moon.
Images for kids
-
Bauxite, the main rock used to get aluminum. Its reddish-brown color comes from iron minerals.
-
Friedrich Wöhler, the chemist who first fully described pure aluminum metal.
-
The statue of Anteros in Piccadilly Circus, London, made in 1893. It's one of the first statues cast in aluminum.
See also
 In Spanish: Aluminio para niños
In Spanish: Aluminio para niños