Boeing 727 facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Boeing 727 |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Champion Air Boeing 727-200 Advanced | |
| Role | Narrow-body jet airliner |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Boeing Commercial Airplanes |
| First flight | February 9, 1963 |
| Introduction | February 1, 1964 with Eastern Airlines |
| Status | Not being made anymore, still being used by airlines |
| Primary users | FedEx Express Kelowna Flightcraft Air Charter Cargojet Airways Kalitta Charters |
| Produced | 1963–1984 |
| Number built | 1,832 |
| Unit cost | $4.25 million at first, $22 million in 1982 |
The Boeing 727 is a famous jet airliner. It was built by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. This plane can carry between 149 and 189 passengers. It can fly for about 2,400 to 2,700 nautical miles (4,400 to 5,000 km). The Boeing 727 was designed for shorter flights. It could also take off from shorter runways at smaller airports.
The 727 has three Pratt & Whitney JT8D engines. One engine is at the very back of the plane. The other two are on the sides, near the tail. The 727 is the only plane Boeing has ever made with three engines.
This aircraft was created after the Boeing 707. Both planes share some similar features. The first version, the 727-100, flew in February 1963. Eastern Air Lines was the first company to use it. A longer version, the 727-200, first flew in July 1967. Northeast Airlines started using it in December 1967.
Boeing made the 727 throughout the 1970s. The last 727 was built in 1984. By July 2011, many 727s were still flying. Because the 727 can be quite noisy, some planes have been fitted with special "hush kits." These kits help to make the engines quieter.
Contents
How the Boeing 727 Was Developed
The Boeing 727 was designed to fly to smaller cities. These cities often had airports with shorter runways. Airlines also wanted a plane that could carry fewer passengers.
Different airlines had different ideas. United Airlines wanted a plane with four engines. This would help it fly to airports at high altitude, like in Denver, Colorado. American Airlines wanted a plane with two engines. Eastern Air Lines preferred a plane with three engines for flights to the Caribbean. In the end, the airlines agreed on a "trijet," which means a plane with three engines.
In 1959, some thought Boeing should work with de Havilland Aircraft Company. Both companies were making trijets. Boeing made the 727, and de Havilland made the Hawker Siddeley Trident. The planes were similar, but the 727 was a bit bigger. Boeing decided to use a different engine than de Havilland.
In 1960, Pratt & Whitney offered its new JT8D turbofan engine. United and Eastern airlines liked this engine. So, Pratt & Whitney continued to develop it. Even though Boeing first hesitated, they eventually decided to use the JT8D engines for the 727.
The 727 has special parts on its wings. These parts help the plane get more lift. This means it can take off from shorter runways than many other jet planes.
Later, longer 727s were built. These could carry more passengers. They replaced older planes like the Boeing 707 and Douglas DC-8. They also replaced propeller planes such as the Douglas DC-4, DC-6, DC-7, and the Lockheed Constellation.
Boeing stopped making the 727 in 1984. A total of 1,832 planes were built. Almost all of them were delivered to airlines.
Special Features of the 727
The 727 was made for smaller airports. This meant it needed to be self-sufficient. Boeing added "airstairs" to the plane. These are stairs built right into the aircraft. At first, these stairs could be opened while the plane was flying. However, after a hijacker jumped from a 727, Boeing changed the design. Now, the airstairs cannot be opened during flight.
The 727 also has an auxiliary power unit (APU). This is like a small engine that provides power. It lets the plane run its systems without needing power from the ground. The APU is located near the undercarriage, which is a bit unusual.
One key feature that helped the 727 land on short runways was its wing design. Since there were no engines on the wings, special flaps could be used across the entire wing. These flaps, along with other features, helped create a lot of lift.
Noise Levels
The 727 is known for being one of the louder airliners. Its JT8D engines are "low-bypass" engines. This design makes them much noisier than newer "high-bypass" engines. Boeing considered putting quieter engines on the 727.

Today, all 727s still flying need a "hush kit." This is a device that makes the jet engine quieter. FedEx makes one type of these kits. Many companies have bought them. Some 727s also have Winglets. These are small upward extensions on the wingtips that help improve fuel efficiency.
Because of their noise, 727s (even with hush kits) are banned from some airports in Australia.
History of Use
The 727 was very versatile. It could fly both within a country and to other countries. It was also useful at airports with gravel runways. Because its engines are mounted high on the tail, they are less likely to be damaged by debris on the ground.
The 727 was also used by the military. Since the airstairs could be opened in flight (before the design change), the Central Intelligence Agency used them. They would drop supplies into Vietnam during the war.
The Boeing C-22 was a military version of the 727. The Air National Guard used it to transport people. Three C-22B planes were used by the 201st Airlift Squadron.

The plane that was meant to replace the 727 was the Boeing 757. However, the 757 is much larger. So, some airlines replaced their 727s with the 737-800 or the Airbus A320.
Different Types of Boeing 727

There are two main types of the 727. The first is the 727-100, which airlines started using in February 1964. The second type, the 727-200, began service in December 1967.
727-100 Series
The 727-100 made its first flight on February 9, 1963. United Airlines received the very first plane on October 29, 1963.
A total of 571 727-100 planes were built. This includes 407 standard -100s, 53 -100Cs, and 111 -100QCs. The last one was made in October 1972.
- 727-100C: This version could be easily changed. It could be a cargo plane or a passenger plane.
- 727-100QC: QC stands for Quick Change. This is a 727-100C that could be converted into a cargo plane very fast, in about 30 minutes.
- 727-100QF: QF means Quiet Freighter. This type was made especially for United Parcel Service.
727-200 Series

The 727-200 is a longer version of the 727-100. The -200 is about 20 feet (6.1 m) longer than the -100. It measures 153 feet, 2 inches (46.7 meters) long.
The 727-200 first flew on July 27, 1967. Northeast Airlines was the first airline to get a 727-200. Boeing built 310 727-200s. The 727-200 Advanced replaced the original 727-200 in 1972.
- 727-200 Advanced: This type could fly for longer distances. It also had some improvements inside the cabin for passengers.
- 727-200F Advanced: This was a version of the 727-200 Advanced that was designed to carry cargo.
- Super 27: This type was much faster, about 50 mph (80 km/h) quicker. This was because its engines were replaced with more powerful ones. It also had winglets.
Who Uses the Boeing 727 Today?
As of December 2012, about 208 Boeing 727s were still being used. Here are some airlines that had five or more 727s:
- Amerijet International (6 planes)
- Cargojet Airways (9 planes)
- FedEx Express (31 727-200 planes)
- Kalitta Charters (8 planes)
- Kelowna Flightcraft Air Charter (13 planes)
- Linhas Aéreas Suramericanas (6 planes)
- Rio Linhas Aéreas (7 planes)
- Total Linhas Aéreas (6 planes)
- Transmile Air Services (7 planes)
Government and Military Users
The 727 has also been used by several governments and their militaries. For example, the air forces of Belgium, Mexico, and New Zealand have used it. The United States military also used the 727, calling it the C-22.
Some countries that have used the 727 include:
- Benin (Military of Benin) (1)
- Burkina Faso (Force Aérienne de Burkina Faso) (1)
- Colombia (Colombian government, Colombian Air Force) (2)
- Democratic Republic of the Congo (Force Aérienne du Congo) (4)
- Djibouti (Djibouti Air Force)
- Ecuador (Ecuadorian Air Force) (3)
- Mexico (Mexican Air Force, Federal Preventive Police) (9)
- Mongolia (Mongolian Air Force) (2)
Accidents and Safety
As of 2010, the Boeing 727 has been involved in 325 accidents. Some of these were serious, leading to the plane being completely damaged. Over the years, safety features were improved, especially after incidents like the one involving the airstairs.
Orders and Deliveries
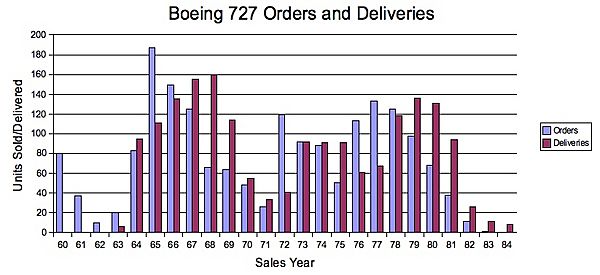 This chart shows how many Boeing 727 planes were ordered and delivered over time.
This chart shows how many Boeing 727 planes were ordered and delivered over time.
727 Models Ordered and Delivered
| Type | Orders | Deliveries |
|---|---|---|
| 727-100 | 407 | 407 |
| 727-100C | 164 | 164 |
| 727-200 | 1245 | 1245 |
| 727-200F | 15 | 15 |
| Total | 1831 | 1831 |
This table shows the total numbers for each type of 727.
Related Planes
- Aircraft related to this one
- Similar aircraft
| Boeing 7x7 aircraft timeline, 1955–now | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950s | 1960s | 1970s | 1980s | 1990s | 2000s | 2010s | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 1961 | 1962 | 1963 | 1964 | 1965 | 1966 | 1967 | 1968 | 1969 | 1970 | 1971 | 1972 | 1973 | 1974 | 1975 | 1976 | 1977 | 1978 | 1979 | 1980 | 1981 | 1982 | 1983 | 1984 | 1985 | 1986 | 1987 | 1988 | 1989 | 1990 | 1991 | 1992 | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 |
| Boeing 707 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 717 (MD-95) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 727 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 737 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 747 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 757 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 767 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 777 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 787 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| = Not being made anymore | = Still being made | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Images for kids
-
Delta Air Lines retired its last 727 from scheduled service in April 2003
-
Northwest Airlines retired its last 727 from charter service in June 2003
-
The initial 727-100 (from Lufthansa here) is 133 ft (41 m) long.
See also
 In Spanish: Boeing 727 para niños
In Spanish: Boeing 727 para niños