Eurasian carp facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Eurasian carp |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Cyprinus
|
| Species: |
carpio
|
 |
|
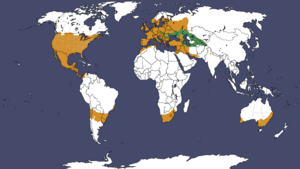
| Native range of C. carpio in green, introduced in orange. | |
The Eurasian or European carp (Cyprinus carpio) is a well-known freshwater fish. It lives in lakes and large rivers across Europe and Asia. Wild populations of this fish are considered vulnerable to extinction. This means they are at risk of disappearing.
However, the common carp has also been raised by people and moved to new places around the world. In many of these new environments, it is seen as a harmful invasive species. It can cause problems for local fish and plants. The common carp is the fish that gives its name to the entire carp family, called Cyprinidae.
Contents
Types of Common Carp
There are two main types, or subspecies, of common carp:
- C. c. carpio lives naturally in many parts of Europe. This includes rivers like the Danube and Volga.
- C. c. yilmaz (also called Deniz carp) comes from Anatolia in Turkey.
In the past, another type from eastern Asia was thought to be a subspecies. It was called C. c. haematopterus (Amur carp). But now, experts believe it is a separate species, called C. rubrofuscus. Common carp can also interbreed with goldfish. The fish that results from this mix is called a Kollar carp.
History of the Common Carp
Common carp first came from Europe and Asia. Now, they have been introduced to almost every part of the world, except the North and South Poles. They are the third most common fish species moved around the world by humans. People have been farming carp for food since the time of the Romans.
The original common carp lived in the Danube River delta about 2,000 years ago. It was shaped like a torpedo and was golden-yellow. It had two pairs of whiskers, called barbels, and scales that looked like a net. Romans started keeping these fish in large, special ponds. This was the beginning of aquaculture, or fish farming.
As farming fish became popular, people started to raise carp in ponds for spawning and growing. The natural home of the common carp also includes the Black Sea, Caspian Sea, and Aral Sea.
Both the European and Asian types of carp have been domesticated. In Europe, monks helped spread carp farming for food between the 13th and 16th centuries. Over time, different kinds of carp appeared due to farming. These include the mirror carp, which has very large, shiny scales. The leather carp has almost no scales. The fully scaled carp looks like the original wild carp.
Koi carp are a special kind of domesticated carp. They are raised for their beautiful colors and are often kept in garden ponds. Koi first appeared in Japan in the 1820s. Their parent species is likely an East Asian carp, possibly C. rubrofuscus.
Common Carp Body and Life
The common carp has a strong body. It often has a dark gold shine, especially on its head. Its body is covered with large, shiny scales. It has big pectoral fins and a long dorsal fin that runs along most of its back. The tail and anal fins can be dark bronze or orange. The carp's mouth points downwards and has two pairs of barbels, with the bottom ones being larger.
Wild common carp are usually thinner than farmed carp. They have red meat and a mouth that sticks out more. Carp can grow very large if they have enough space and food. Farmed carp can grow up to 120 centimetres (47 in) long and weigh over 40 kilograms (88 lb). The oldest carp ever recorded lived for 38 years. The largest carp caught weighed 45.59 kilograms (100.5 lb) in France in 2013. Most common carp are around 40–80 cm (16–31 inches) long and weigh 2–14 kg (4.4–30.9 lb).

Carp Habitat

Common carp can live in many conditions. But they prefer large areas of slow-moving or still water. They like soft, muddy bottoms with lots of plants. Carp are schooling fish, meaning they like to be in groups of five or more.
They naturally live in temperate climates. They prefer fresh or slightly brackish water. The water should have a pH between 6.5 and 9.0 and a low salt level. The best temperature for them is 23 to 30 °C (73–86 °F). They can easily survive winter in a frozen pond as long as there is some water under the ice. Carp can even live in water with very little oxygen by gulping air from the surface.
What Carp Eat (Diet)
Common carp are omnivorous, meaning they eat both plants and animals. They can eat aquatic plants. But they prefer to search the bottom for insects, crustaceans (like tiny zooplankton), crawfish, and worms that live in the mud. Carp feed throughout the day, but they eat the most at night and around sunrise.
Carp Reproduction (Life Cycle)
A female carp lays eggs. A typical adult female can lay 300,000 eggs in one spawning event. Carp usually spawn in the spring when water temperatures rise and it rains. However, they can spawn multiple times in a single season.
Who Eats Carp (Predation)
A single carp can lay over a million eggs in a year. Many eggs and young carp (called fry) are eaten by bacteria, fungi, and many small predators in the pond. Young carp that survive are hunted by other fish like the northern pike and largemouth bass. Several birds, including cormorants, herons, and ospreys, also eat them. Some mammals like otters and mink also prey on carp.
Carp in New Places

Common carp have been introduced to most continents and about 59 countries. In places where they have no natural predators or commercial fishing, they can greatly change their environment. This is because they reproduce quickly and dig through bottom sediments for food. When they feed, they can destroy, pull up, and eat underwater plants. This can seriously harm native duck and fish populations.
Carp were brought to Australia over 150 years ago. But they only became a big problem in the 1960s. They spread quickly through the Murray–Darling basin after big floods in 1974. Now, they are found in almost every Australian territory. In Victoria, common carp are considered a harmful fish. There is no limit to how many a fisher can catch. In South Australia, it is against the law to release this fish back into the wild. One Australian company even makes plant fertilizer from carp.
Scientists have tried to get rid of a small group of carp from Lake Crescent in Tasmania. They did this without using chemicals, and it worked. But it was a long, expensive, and difficult project. This shows how hard it is to safely remove carp once they are settled. One idea to control carp numbers is to use a special virus called koi herpes virus. This virus only affects carp and causes many of them to die. In 2016, the Australian Government planned to release this virus into the Murray–Darling basin. However, in 2020, this plan was found unlikely to work.
The CSIRO has also found a way to change carp genetically. This method makes them only produce male offspring. This "daughterless carp" method looks promising for completely removing carp from Australia's waterways.
Common carp were brought to the United States in 1831. In the late 1800s, the government spread them widely as a food fish. But now, people in the U.S. rarely eat them. They are usually seen as pests. Like in Australia, carp have caused negative environmental effects in the U.S.
In Utah, people are trying to reduce the carp population in Utah Lake by 75 percent. They use nets to catch millions of carp. These carp are then given to people who will eat them or processed into fertilizer. This helps a native fish called the June sucker to recover. Another way to control carp is to trap them in small rivers they use to spawn. Then, they are exposed to a fish poison called rotenone. This method quickly reduces their impact and helps native plants and fish grow back. It also makes it easier for native fish to eat young carp.
Common carp are thought to have come to British Columbia, Canada, from Washington state. They were first noticed in the Okanagan Valley in 1912. Their population grew very quickly. Carp are now found in many river systems in British Columbia.
In 2020, scientists showed something interesting. A small number of fertilized carp eggs can survive being eaten by waterfowl (like ducks) and passing through their digestive system. These eggs can still hatch after being found in the birds' droppings. Birds really like to eat fish eggs. Carp lay hundreds of thousands of eggs at once. This means that even if only a few eggs survive, birds could be helping to spread invasive carp to new places. This could be a big worry for freshwater biodiversity.
Farming Common Carp
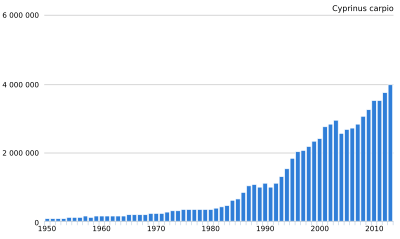
Common carp are a very important farmed fish. In 2015–2016, about 4.67 million tons of common carp were produced globally. This was about 7.4% of all fish caught or farmed in inland waters worldwide. In Europe, common carp made up 1.8% of inland fish production during the same period. It is a major farmed fish in freshwater aquaculture in Europe, especially in central and eastern European countries.
Countries like Russia, Poland, Czech Republic, Hungary, and Ukraine produce most of Europe's carp. The average amount of carp produced in central European fishponds is between 0.3 and 1 ton per hectare. European common carp production reached its highest point in 2009–2010. Since then, it has been slowly decreasing.
Sometimes, carp farming is criticized for causing too many nutrients to build up in freshwater bodies. This is called eutrophication. However, carp farming in fish ponds in Europe likely causes less pollution than most other food production methods in the European Union.
Carp as Food and for Sport

China produces a huge amount of common carp each year. The amount is more than all other fish, like trout and salmon, produced by fish farming worldwide. About three million tons are produced annually in China. This makes up 14% of all farmed freshwater fish. China is by far the largest commercial producer of carp, making about 70% of the world's total. Carp is eaten in many parts of the world, both wild-caught and farmed.
In Central Europe, carp is a traditional part of a Christmas Eve dinner. For example, in Hungary, a special fish soup made with carp is eaten on Christmas Eve. In the Czech Republic, a traditional Christmas Eve dinner includes a thick soup made from carp's head and insides, and fried carp meat with potato salad. A similar meal is eaten in Slovakia, Austria, parts of Germany, and Poland.
In Western Europe, carp are more commonly raised for sport fishing. However, there is still a small market for them as food. Carp are also mixed with other fish to make gefilte fish, which is popular in Jewish cuisine. Common carp are very popular with anglers in many parts of Europe. Their popularity is slowly growing among anglers in the United States and southern Canada. Carp are also popular for spear fishing, bowfishing, and fly fishing.
In the United States, carp are mostly ignored as a food fish. Most shoppers do not buy carp. This is because they prefer fish that are already filleted, rather than cooking a whole fish. Carp have small bones called y-bones, which can make them harder to eat whole.
The Romans farmed carp, and this tradition continued through monasteries in Europe. In China, Korea, and Japan, carp farming began as early as the Yayoi period (around 300 BC to AD 300).
|
See also
 In Spanish: Carpa común para niños
In Spanish: Carpa común para niños