Delray Beach, Florida facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Delray Beach, Florida
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
Clockwise, from upper left: Aerial view, Lake House at Morikami Museum and Japanese Gardens, Intracoastal Waterway
|
||
|
||
| Nickname(s):
Delray
|
||
| Motto(s):
"Village By The Sea"
|
||
| Country | ||
| State | ||
| County | ||
| Settled (Linton Settlement) | 1884–1900 | |
| Settled (Delray Settlement) | 1901–1910 | |
| Incorporated (Town of Delray) | October 9, 1911 | |
| Incorporated (Town of Delray Beach) | October 9, 1923 | |
| Incorporated (City of Delray Beach) | May 11, 1927 | |
| Named for | Delray, Detroit | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Commission-Manager | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 16.52 sq mi (42.78 km2) | |
| • Land | 15.92 sq mi (41.24 km2) | |
| • Water | 0.59 sq mi (1.54 km2) | |
| Elevation | 20 ft (6 m) | |
| Population
(2020)
|
||
| • Total | 66,846 | |
| • Density | 4,197.81/sq mi (1,620.74/km2) | |
| (* Population density is rounded up and calculated from 2020 Census Population. It is not supplied by cited reference) | ||
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) | |
| ZIP codes |
33444–33448, 33482–33484
|
|
| Area code(s) | 561, 728 | |
| FIPS code | 12-17100 | |
| GNIS feature ID | 0281485 | |
| Website | www.mydelraybeach.com | |
Delray Beach is a vibrant city located in Palm Beach County, Florida, in the United States. It's known for its beautiful beaches and lively downtown area. As of 2020, about 66,846 people call Delray Beach home. The city is part of the larger Miami metropolitan area, sitting about 52 miles (83 kilometers) north of Miami. It's often called the "Village By The Sea" because of its charming coastal feel.
Contents
History of Delray Beach
How Delray Beach Started
Long ago, the Jaega people lived in the area that is now Delray Beach. Other Native American groups, like the Tequesta Indians, also visited or lived here. We don't have many details about these early settlements.
In 1876, a special building called the Orange Grove House of Refuge was built. Its purpose was to help sailors whose ships had wrecked. It got its name from the many orange trees growing nearby.
The first non-native people to settle here were African Americans from the Florida Panhandle. They bought land and started farming around 1884. By 1894, their community was big enough to open the first school in the area.
In 1894, a U.S. Congressman named William S. Linton bought land and hoped to create a farming town. This new community was named Linton. In 1896, Henry Morrison Flagler extended his Florida East Coast Railway south, and a train station was built in Linton.
The early settlers grew winter vegetables to sell in the northern states. After a big freeze in 1898, many people left. In 1901, the town's name was changed to Delray. This new name came from a neighborhood in Detroit, which was named after a battle in the Mexican-American War.
People from The Bahamas started arriving in the early 1900s. Japanese settlers from the nearby Yamato farming colony also joined in Delray's community events. By 1910, Delray had 904 citizens from many different places.
Growing into a Town
In 1911, Delray officially became an incorporated town in Florida. Factories were built to can pineapples and tomatoes. Pineapples became a very important crop. This is why a neighborhood downtown is still called Pineapple Grove today.
Before 1909, Delray was part of Dade County. Then, Palm Beach County was created, and Delray became part of it. Later, Broward County was formed, placing Delray in the southeastern part of Palm Beach County.
By 1920, Delray's population grew to 1,051 people. In the 1920s, draining the Everglades made it harder to grow pineapples. Also, new train lines brought cheaper pineapples from Cuba, creating more competition.
The Florida land boom of the 1920s brought new wealth to Delray. Tourism and buying and selling land became very popular. Delray used money to build water and sewer lines, paved streets, and sidewalks. Many hotels were built. At this time, Delray was the largest town between West Palm Beach and Fort Lauderdale. However, when the land boom ended in 1926, Delray faced financial challenges.
Delray was separated from the ocean by a canal. In 1923, the area between the canal and the ocean became its own town called Delray Beach. In 1927, Delray and Delray Beach joined together to form one town, which we now know as Delray Beach.
Starting in the mid-1920s, many artists and writers began spending their winters in Delray Beach. Cities like Palm Beach weren't always welcoming to artists, so Delray became a popular spot for creative people. Famous cartoonists like H.T. Webster and Fontaine Fox had offices here. This group of artists and writers helped the city during tough economic times.
During the Great Depression, even though money was scarce, Delray Beach still looked good because of all the new buildings from the boom years. The Artists and Writers Colony helped Delray Beach become famous as a resort town. This time is known as Delray Beach's "golden age of architecture." Many buildings from this period show styles like Art Deco and Mediterranean Revival.
Delray Beach After World War II
During World War II, people in Delray Beach volunteered to watch the beach and ocean day and night. Soldiers also patrolled the beach on horseback. After the war, many veterans who had trained at the nearby Boca Raton Army Airfield came back to live in Delray Beach. The city continued to grow steadily through the 1950s and 1960s.
By the early 1960s, Delray Beach became known for surfing. Its surfing fame grew even more after a shipwreck in 1965. During Hurricane Betsy, a large ship called the Amaryllis got stuck near Singer Island. This created perfect waves for surfing. Even after the ship was removed, Delray Beach remained a popular surfing spot.
In the 1970s, Interstate 95 was finished, and new buildings started appearing west of the city. This growth continued into the 1980s, but downtown Delray and older neighborhoods began to decline.
Towards the end of the 1900s, efforts began to bring life back to historic areas. Buildings like the Colony Hotel and Old School Square were restored. Old School Square, which used to be a school, is now a cultural center. The city also created special Historic Districts to protect its unique architecture.
In 2001, the historic home of Solomon D. Spady, a teacher and principal, was restored. It became the Spady Cultural Heritage Museum, which shares the history of African Americans in Delray Beach. The museum later added a Kid's Cultural Clubhouse and an amphitheater.
Downtown Delray, especially along Atlantic Avenue, has been greatly improved. The Delray Beach Tennis Center has brought many visitors by hosting big tennis events.
In 2012, Rand McNally called Delray Beach "America's Most Fun Small Town." In 2015, Coastal Living magazine named it the 3rd Happiest Seaside Town. And in 2024, USA Today readers voted Delray Beach the Best Beach in Florida!
Geography of Delray Beach
Delray Beach has about 3 miles (4.8 kilometers) of public beachfront along the Atlantic Ocean. To the south, it borders Boca Raton. To the north, it borders Boynton Beach.
West of the city, there's an urban area with many communities that use a Delray Beach postal address, even if they are not officially part of the city. This area is sometimes called "West Delray."
Delray Beach is located in the middle of Florida's Gold Coast region. The city has a total land area of about 15.81 square miles (40.95 square kilometers).
Downtown Area
In the past, downtown Delray was mainly along Atlantic Avenue. Now, it stretches from I-95 all the way to the Atlantic Ocean. It also extends a couple of blocks north and south of Atlantic Avenue.
Climate in Delray Beach
Delray Beach has a tropical climate, which means it's warm all year round. It's known as a tropical rainforest climate because even its driest month still gets enough rain.
Summers in Delray Beach are hot and humid, with temperatures often reaching 87 to 93°F (31 to 34°C). Low temperatures are around 75–78°F (24–26°C). Winters are warm and much drier. Winter high temperatures are usually between 74–83°F (23–28°C), and lows are 57–65°F (14–18°C). Sometimes, cold fronts can bring cooler weather, but they usually don't last long.
The city's location near the ocean and above the Tropic of Cancer gives it this warm climate. Hurricane season runs from June 1 to November 30. The most active time for hurricanes is usually from mid-August to the end of September. Delray Beach has been affected by several hurricanes over the years.
| Climate data for Delray Beach | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 76 (24) |
77 (25) |
79 (26) |
82 (28) |
86 (30) |
89 (32) |
90 (32) |
90 (32) |
88 (31) |
85 (29) |
80 (27) |
76 (24) |
83 (28) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 58 (14) |
59 (15) |
62 (17) |
66 (19) |
71 (22) |
74 (23) |
76 (24) |
76 (24) |
75 (24) |
72 (22) |
66 (19) |
60 (16) |
67 (19) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.75 (95) |
2.55 (65) |
3.68 (93) |
3.57 (91) |
5.39 (137) |
7.58 (193) |
5.97 (152) |
6.65 (169) |
8.10 (206) |
5.46 (139) |
5.55 (141) |
3.14 (80) |
61.39 (1,559) |
| Average precipitation days | 8.8 | 7.8 | 8.8 | 7.4 | 9.8 | 16.9 | 16.9 | 18.1 | 17.7 | 13 | 9.4 | 8.9 | 143.4 |
People of Delray Beach
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1910 | 904 | — | |
| 1920 | 1,051 | 16.3% | |
| 1930 | 2,333 | 122.0% | |
| 1940 | 3,737 | 60.2% | |
| 1950 | 6,312 | 68.9% | |
| 1960 | 12,230 | 93.8% | |
| 1970 | 19,366 | 58.3% | |
| 1980 | 34,329 | 77.3% | |
| 1990 | 47,789 | 39.2% | |
| 2000 | 60,020 | 25.6% | |
| 2010 | 60,522 | 0.8% | |
| 2020 | 66,846 | 10.4% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
Population and Diversity
| Race | Pop 2010 | Pop 2020 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White (NH) | 35,844 | 38,341 | 59.22% | 57.36% |
| Black or African American (NH) | 16,759 | 16,823 | 27.69% | 25.17% |
| Native American or Alaska Native (NH) | 87 | 81 | 0.14% | 0.12% |
| Asian (NH) | 1,088 | 1,281 | 1.80% | 1.92% |
| Pacific Islander or Native Hawaiian (NH) | 27 | 16 | 0.04% | 0.02% |
| Some other race (NH) | 196 | 406 | 0.32% | 0.61% |
| Two or more races/Multiracial (NH) | 752 | 2,131 | 1.24% | 3.19% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 5,769 | 7,767 | 9.53% | 11.62% |
| Total | 60,522 | 66,846 |
In 2020, Delray Beach had 66,846 residents. These people lived in 28,914 households. The city is home to a diverse population, with people from many different backgrounds.
Economy of Delray Beach
Delray Beach is a very popular place for beach vacations in South Florida. It's famous for its many restaurants, shops, nightclubs, art galleries, and hotels. East Atlantic Avenue is especially known for its lively nightlife, dining, and shopping.
One of the city's biggest business spots is the Delray Beach Market. This is a huge food hall and event space, the largest in Florida. It opened in 2021.
New Buildings and Growth
Since about 2003, downtown Delray Beach has seen a lot of new construction. Many new buildings are designed to mix homes with shops and businesses. To handle this growth, the city has also built two new parking garages.
Main Employers
Here are some of the biggest employers in Delray Beach:
| # | Employer | Number of employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Delray Medical Center | 1,280 |
| 2 | Palm Beach County School District | 1,123 |
| 3 | City of Delray Beach | 838 |
| 4 | Seo Every Where | 600 |
| 5 | Annco Services | 400 |
| 6 | Meisner Electric Inc of Florida | 370 |
| 7 | Ed Morse Delray Toyota | 350 |
| 8 | Shullman Technology Group | 350 |
| 9 | Pinecrest Rehabilitation Hospital | 300 |
| 10 | Schumacher Automotive Group | 250 |
Arts and Culture in Delray Beach
Delray Beach has 2 miles (3.2 kilometers) of public beach that everyone can enjoy. Travel Holiday magazine once called Delray Municipal Beach the best beach in the southeastern United States. The city has many parks, athletic fields, and even a skatepark and splash park for fun activities.
Art and Music Scene
Delray Beach offers many places to enjoy art. The Pineapple Grove Arts District, located downtown, is famous for its art galleries and cultural groups. Arts Garage is a place where you can see live music, theater, and art exhibits. The Delray Beach Playhouse, which opened in 1947, puts on plays, musicals, and shows for children.
Old School Square is a cultural center that used to be a school. It now has the Crest Theatre for performances and the Cornell Art Museum in the old elementary school building. There's also The Pavilion, an outdoor space for concerts and other events. The Creative Arts School at Old School Square offers art, photography, and writing classes for all ages.
Atlantic Avenue often hosts art fairs and street festivals.
Museums and Nature Spots

Some museums in Delray Beach focus on history. The Cason Cottage House Museum shows what daily life was like in South Florida from 1915 to 1935. The Spady Cultural Heritage Museum shares the history of African Americans in the area. For something different, the Silverball Museum has over 150 classic pinball machines and arcade games you can play!
Near the public beach, you can find the remains of a British ship called the Inchulva, which sank in 1903. This "Delray Wreck" is now a home for fish and corals, and it's a great spot for snorkeling and scuba diving.
Some historic houses have new uses. The Sundy House is now a luxury eco-resort with a cafe and gardens. The J.B. Evans House is now the Sandoway Discovery Center, a natural history museum with live animals and a shell collection.
Delray Beach is also home to the Morikami Museum and Japanese Gardens. This center celebrates Japanese arts and culture with museum buildings, beautiful Japanese gardens, a bonsai garden, and a Japanese restaurant. They also hold traditional Japanese festivals.
Wakodahatchee Wetlands is a public park with a boardwalk. It's a fantastic place to see many different kinds of birds, as well as turtles, alligators, and other animals in their natural homes.
Sports in Delray Beach
The Delray Beach Open is a professional tennis tournament for men held every year. The Delray Beach Tennis Center has hosted other big tennis events too, like the Fed Cup and the Davis Cup.
The ProWorld Tennis Academy is in Delray Beach. The Delray Beach Tennis Center has 14 clay courts, 6 hard courts, and a large stadium that seats 8,200 people. It offers many programs for both kids and adults. There's also another location, the Delray Swim & Tennis Club, with 24 clay courts.
In 2010, the city even changed its name to Tennis Beach for one week! This was to celebrate being nominated as one of the top tennis towns in the United States.
Media in Delray Beach
Delray Beach has two main daily newspapers, the Palm Beach Post and Sun Sentinel. There are also local publications like the Coastal Star and Delray Newspaper. You can also find lifestyle magazines like Delray Magazine. Local TV stations covering the area include WPTV (NBC), WPBF (ABC), WPEC (CBS), and WFLX (FOX).
Getting Around Delray Beach
Many residents and local businesses in Delray Beach use street-legal golf carts to get around.
Roads and Highways
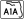 Florida State Road A1A, also called "Ocean Boulevard," runs north-south along the coast.
Florida State Road A1A, also called "Ocean Boulevard," runs north-south along the coast.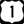 U.S. Route 1, or "Federal Highway," goes through downtown and other areas.
U.S. Route 1, or "Federal Highway," goes through downtown and other areas. Interstate 95 cuts through the city from north to south, with two exits for Delray Beach.
Interstate 95 cuts through the city from north to south, with two exits for Delray Beach. Florida's Turnpike is a toll road that passes through the area west of the city, with an exit at Atlantic Avenue.
Florida's Turnpike is a toll road that passes through the area west of the city, with an exit at Atlantic Avenue.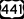 U.S. Highway 441 (State Road 7) runs through residential and business areas west of the city.
U.S. Highway 441 (State Road 7) runs through residential and business areas west of the city.- Other important north-south roads include Congress Avenue, Military Trail, and Jog Road.
 Florida State Road 806, known as "Atlantic Avenue," is the main east-west road and the central street downtown.
Florida State Road 806, known as "Atlantic Avenue," is the main east-west road and the central street downtown.- Linton Boulevard and George Bush Boulevard also connect to State Road A1A and have drawbridges over the Intracoastal Waterway.
Trains
- The Tri-Rail commuter train system and Amtrak both have stops at the Delray Beach Station.
Buses
- PalmTran provides local bus service throughout the area.
Water Travel
You can reach downtown Delray Beach by boat using The Intracoastal Waterway. The city has a public marina where boats can dock. Yacht tours also leave daily from Veteran's Park.
Notable People from Delray Beach
- Leslie Alexander, former owner of the Houston Rockets basketball team
- Kevin Anderson, professional tennis player
- Tommy Armour, professional golfer
- Ashley Biden, daughter of US President Joe Biden
- Michael Binger, professional poker player
- Jim Bishop, journalist and author
- Milton Caniff, cartoonist
- Coco Gauff, professional tennis player
- Larry Haines, actor
- Kevin James, actor and comedian
- Betty Jameson, professional golfer
- Rhi Jeffrey, Olympic gold medalist swimmer
- Clarence Budington Kelland, writer
- Rick Macci, famous tennis coach
- Meg Mallon, professional golfer
- Bam Margera, television personality and skateboarder
- Edna St. Vincent Millay, writer and poet
- George Sukeji Morikami, Japanese pineapple farmer
- Bob Murphy, professional golfer
- Nina Wilcox Putnam, novelist and screenwriter
- Jim Raymond, cartoonist
- Samari Rolle, professional football player
- Gene Sarazen, professional golfer
- Ossie Schectman, professional basketball player
- Albert Seedman, former New York Police Department chief
- Solomon D. Spady, educator
- Louise Suggs, professional golfer
- Gene Tierney, actress
- Sofía Vergara, actress and model
- Anna Leigh Waters, professional pickleball player
- H.T. Webster, cartoonist
- Max Weinberg, drummer and television personality
- Serena Williams, professional tennis player
- Venus Williams, professional tennis player
- Gary Woodland, professional golfer
Sister Cities
Delray Beach has four sister cities around the world:
 Miyazu, Kyoto, Japan - This is where George Morikami, who inspired the Morikami Museum and Japanese Gardens, was born.
Miyazu, Kyoto, Japan - This is where George Morikami, who inspired the Morikami Museum and Japanese Gardens, was born. Moshi, Tanzania
Moshi, Tanzania Aquin, Haiti
Aquin, Haiti Pesaro, Italy
Pesaro, Italy
Images for kids
-
Marina Historic District, listed in the U.S. National Register of Historic Places, 2014
See also
 In Spanish: Delray Beach para niños
In Spanish: Delray Beach para niños