Military facts for kids
The military is a group of people whose main job is to protect their country. They are also called the armed forces because they use weapons. The military defends its country from enemies and their armed forces, especially if there is a war. Sometimes, a country's government might also order its military to attack another country. The word "military" comes from an old Latin word, miles, which means warrior.
Contents
What People Do in the Military
There are many different jobs in the military. Some jobs involve fighting, while others support the fighters. People in the military might use weapons, drive special vehicles, or repair equipment. Others learn to fly aircraft, pilot ships, or fix engines.
Most military members wear special uniforms. These uniforms often have a camouflage pattern. This pattern helps them blend in with their surroundings, like a forest or desert, so they are harder to see during combat.
How to Join the Military
There are two main ways people join the military. In many countries, people choose to join because they want to serve. This is called "enlisting" or "volunteering".
In other countries, there are laws that say some people must join the military for a certain time. This is called the draft or conscription. It usually depends on a person's age and how fit they are.
People who have served in the military and then left are called "veterans". Those who have left but can be called back to serve if needed are called reservists.
Different Military Branches
A country's military is usually split into different groups, or branches. Each branch does a different kind of work. The main branches are:
- Army: This force mainly works on land. Soldiers in the Army fight on foot or use land vehicles. They also use helicopters.
- Navy: This force uses ships and boats on the sea. They sometimes have planes too. People in the Navy are often called sailors.
- Air force: This force mainly uses airplanes to operate in the air.
Some countries have more specialized branches:
- Marines: These forces serve on ships but are also trained to fight on land. Their main job is to attack by landing on enemy beaches. They work closely with the Navy but are not sailors. They might also have their own boats, planes, and helicopters.
Some large countries also have small, highly trained groups called special forces. These groups do very difficult and specific missions.
There are also mercenaries, who are soldiers who fight only for money. They don't have much loyalty to the country or group that hires them. Private military contractors (PMCs) are similar, but they work for a civilian company. A warlord might have a private army, which can sometimes be like a group of criminals.
Joining Up and Training
If a person wants to join the military as a volunteer, they "enlist." This means they sign up. They usually need to be 17 or 18 years old. They also have to pass physical fitness tests. These tests show they are healthy enough for military jobs. They must also have good hearing to understand orders and good eyesight to use a rifle.
New people in the military are called "recruits." They go through special training at a camp, sometimes called "boot camp." During this training, recruits have little free time. They learn to understand "orders" or "commands" given by officers. They also learn how to follow these orders correctly.
Recruits do a lot of exercise to get stronger and fitter. They learn about weapons, first aid, and how to use their uniforms and "kit" (their equipment). They also learn how to march, which is walking together in step. This is sometimes called "drill."
By the end of boot camp, recruits know enough to be helpful members of their military group. The training usually ends with a parade. Here, the new recruits show off their marching and other skills to important visitors. Once fully trained, they are ready to protect their country or go to war if needed.
Images for kids
-
NATO military ceremony, Pabrade, Lithuania in November 2014
-
Finnish and American soldiers train together in arctic conditions in Lapland, Finland, as part of Cold Weather Basic Operation Course, January 6–16, 2015
-
Red Ball Express convoy in France
-
Dutch civilians celebrating the arrival of the I Canadian Corps in Utrecht as the Canadian Army liberates the Netherlands from Nazi occupation
-
Arrow-head. Bronze, 4th century BC. From Olynthus, Chalcidice.
-
Naval military forces of France and Britain exchange fire at the Battle of the Chesapeake
-
AIM-7 Sparrow medium range air-to-air missile from an F-15 Eagle
-
Samurai, member of the Japanese warrior caste
-
Swedish king Gustavus Adolphus leading a cavalry charge, 1634
-
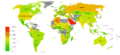
Map of military expenditures as a percentage of GDP by country, 2017.
See also
 In Spanish: Ejército para niños
In Spanish: Ejército para niños