History of the Caucasus facts for kids
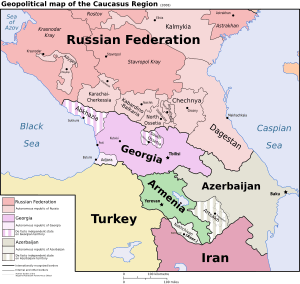
The Caucasus region is a fascinating area located between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. It's a place where Europe and Asia meet, known for its tall mountains, diverse cultures, and long history. The history of the Caucasus can be split into two main parts: the North Caucasus and the South Caucasus.
The North Caucasus was often influenced by groups from the Pontic steppe and Southern Russia. The South Caucasus, which includes modern-day Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia, was more connected to powerful empires like Persia and Anatolia (modern-day Turkey).
Over many centuries, different empires took control of parts of the Caucasus. These included the Achaemenid Empire, Roman Empire, Sassanian Empire, Byzantine Empire, Mongol Empire, and Ottoman Empire. Persian empires, like the Safavids and Qajars, also had a big impact.
In the 1800s, the Russian Empire expanded into the Caucasus. Through treaties like the Treaty of Gulistan (1813) and the Treaty of Turkmenchay (1828), Russia gained control of lands that are now part of Dagestan, eastern Georgia, Azerbaijan, and Armenia from Persia. Russia then conquered the rest of the North Caucasus in wars that lasted from 1817 to 1864.
During Second World War (1939-1945), the Caucasus became a battleground. Nazi Germany tried to capture the region in 1942 because of its important oil fields, especially around Baku. German forces occupied some areas, but they were eventually pushed back by Soviet soldiers after the Battle of Stalingrad (1942–1943).
After the Soviet Union broke apart in 1991, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia became independent countries. Since then, the Caucasus has seen some disagreements over land, leading to the creation of areas like Artsakh, Abkhazia, and South Ossetia, which are not recognized by all countries.



Contents
Ancient Times
The Caucasus region slowly started appearing in historical records during the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age.
Early Kingdoms and Cultures
- Hayasa-Azzi: This was a group of two kingdoms in the Armenian Highlands during the Late Bronze Age. They fought against the powerful Hittite Empire around the 14th century BC. Their conflicts may have played a part in the collapse of the Hittite Empire around 1190 BC.
- Arme-Shupria: Known from Assyrian records starting in the 13th century BC, this kingdom was located in the Armenian Highlands, southwest of Lake Van.
- Diauehi: This was a group of tribes in northeastern Anatolia after the Hittite Empire fell. Some historians think they might have been early Georgians, while others suggest they were early Armenians.
- Nairi: These groups are mentioned in Assyrian and Hittite records between the 13th and 9th centuries BC. The Battle of Nihriya (around 1230 BC) was a major fight between the Hittites and Assyrians involving these groups.
- Urartu: The Kingdom of Urartu became very strong in the mid-9th century BC. It thrived for about 200 years before being taken over by the Median Empire in the early 6th century BC, and then by the Achaemenid Empire.
- Koban Culture: In the North Caucasus, the Koban culture existed from about 1100 to 400 BC. This culture ended around the time the Scythians expanded into the region.
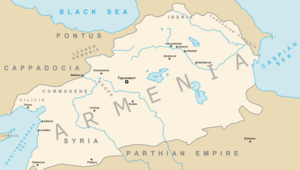
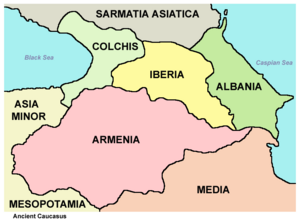
Classical Empires and Kingdoms
Many powerful empires and kingdoms influenced the Caucasus during classical times:
- Urartu
- Kingdom of Colchis
- Persia (including the Medes, Achaemenid Empire, Parthia, and Sassanid Empire)
- Neo-Assyrian Empire
- Kingdom of Armenia (including the Orontid, Artashesian, and Arshakuni dynasties)
- Kingdom of Caucasian Albania
- Kingdom of Caucasian Iberia
- Kingdom of Lazica-Egrisi
- Roman Empire (which briefly controlled parts of Armenia)
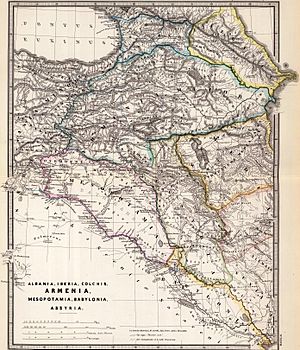
Middle Ages
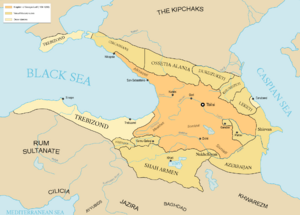
During the Middle Ages, several Armenian kingdoms and principalities, like Bagratid Armenia and Principality of Khachen, helped protect the local Armenian people after the fall of the ancient Kingdom of Armenia.
Caucasian Albania had strong connections with Armenia. The Church of Caucasian Albania shared similar Christian beliefs with the Armenian Apostolic Church.
Major Powers in the Middle Ages
- Sassanian Empire (224 – 651 AD)
- Byzantine Empire (330 – 1453 AD)
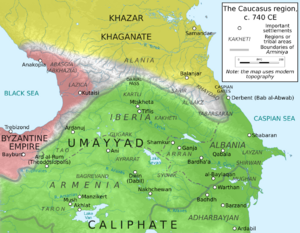
- Khazars (a Turkic people who formed a large kingdom)
- Arab Caliphates: The Rashidun Caliphate, Umayyad Caliphate, and Abbasid Caliphate expanded into the region, bringing Islam.
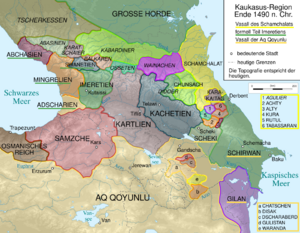
- Kingdom of Georgia (1008 – 1490): This powerful kingdom united many Georgian lands.
* Smaller Georgian kingdoms like Kingdom of Abkhazia and Kingdom of Imereti also existed.
- Persia: Various Persian dynasties, like the Sallarids and Sajids, continued to influence the region.
- Shirvanshah (a local dynasty in Azerbaijan)
- Kingdom of Armenia (Middle Ages)
- Seljuq dynasty (1037 – 1194): Turkic invaders who established a large empire.
- Ilkhanate (1256 – 1335): A Mongol state that ruled over much of the Middle East, including the Caucasus.
- Timurid dynasty (1370 – 1526): Another powerful empire founded by Timur (Tamerlane).
Early Modern History
By the end of the 15th century, the powerful Kingdom of Georgia had broken into smaller kingdoms. These smaller kingdoms were often controlled by either Persia or the Ottoman Empire.
Throughout the 16th century, the Caucasus was a battleground between Persian and Ottoman forces. Both empires wanted to control this important region. In 1555, they signed the Peace of Amasya. This agreement divided the Caucasus into areas of influence. Persia controlled lands east of the Surami Pass, including the Georgian kingdoms of Kartli and Kakheti. The Ottomans controlled areas west of the pass, including the Georgian kingdom of Imereti.
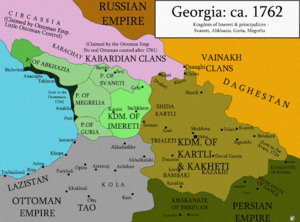
The growing Russian Empire also started to gain land in the North Caucasus in the early 1700s, but these lands were later returned to Persia. After the death of Nader Shah of Persia, the Georgian kingdoms of Kartli and Kakheti united to form the Kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti in 1762. Its king, Erekle II, tried to become independent from Persia.
In 1783, King Erekle II made a deal with the Russian Empire called the Treaty of Georgievsk. Catherine the Great, the Russian empress, wanted to use Georgia as a base against Iran and the Ottoman Empire. However, after her death, the Russians pulled back. The Qajar dynasty in Persia then tried to regain control over the Caucasus. A Persian army defeated the Georgian army in 1795.
In 1801, after the assassination of the Persian ruler Agha Mohammad Khan, Russia took advantage of the chaos and officially took over eastern Georgia (Kartli-Kakheti).
During this time, many people in the Caucasus changed their religion. The Chechens gradually became Sunni Muslims. The Circassians also mostly adopted Islam, influenced by the Crimean Tatars and the Ottoman Empire in the 17th century.
Modern History

Russian Empire and Civil War
- Georgia within the Russian Empire (1801 – 1918): Russia's control over Georgia grew.
* Russo-Persian War (1804 – 13) and Russo-Persian War (1826–28): These wars led to Russia gaining more territory from Persia. * Treaty of Gulistan (1813) and Treaty of Turkmenchay (1828): These treaties officially gave large parts of the Caucasus to Russia. * Caucasian War (1817 – 1864): Russia fought to conquer the remaining independent areas in the North Caucasus. * Ethnic cleansing of Circassians: A tragic event where many Circassians were forced to leave their homes.
- Russian Civil War: After the Russian Revolution, various groups fought for control.
* Democratic Republic of Georgia (1918 – 1921): Georgia briefly became independent. * Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic: A short-lived union of Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan.
Khanates of the Caucasus
After the death of Nader Shah in 1747, many smaller independent states called khanates appeared in the Caucasus. These were ruled by local leaders called khans. The Russian Empire gradually took over these khanates in the early 1800s. Some examples include:
- Baku Khanate
- Erivan Khanate
- Ganja Khanate
- Karabakh Khanate
- Nakhchivan Khanate
- Shaki Khanate (home to the beautiful Palace of Shaki Khans)
- Shirvan Khanate
- Talysh Khanate
Soviet Union Era
- Soviet Union: After the Russian Civil War, the Caucasus became part of the Soviet Union.
* Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic: An early Soviet republic that included Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia. * Later, these became separate Soviet republics: Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic, Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic, and Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic.
- Conflicts before the Soviet collapse:
* First Nagorno-Karabakh War (1988 – 1994): A conflict between Armenians and Azerbaijanis. * Ossetian-Ingush conflict (1989 – 1991): A conflict between two ethnic groups in the North Caucasus.
- Independence: After the Soviet Union dissolved in 1991, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia became independent nations again.
Recent History (1991–present)
Since gaining independence, the Caucasus region has faced several challenges and conflicts:
- War in Abkhazia (1992–1993): A conflict in Georgia.
- First Chechen War (1994 – 1996) and Second Chechen War (1999 – 2006): Wars in the North Caucasus region of Chechnya.
- Russo-Georgian War (2008): A brief conflict between Russia and Georgia.
- 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh War: Another conflict over the Nagorno-Karabakh region.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Historia del Cáucaso para niños
In Spanish: Historia del Cáucaso para niños
- Caucasus Greeks
- North Caucasus
- South Caucasus
- History of Georgia (country)
- History of Armenia
- History of Azerbaijan
- History of Abkhazia
- History of Chechnya
- History of Nagorno-Karabakh
- History of Nakhchivan
- Southern Russia
- Eastern Magyars
- North Caucasian Huns
- Huns
- Khazars
- Western Turkic Khaganate