Human impact on the environment facts for kids
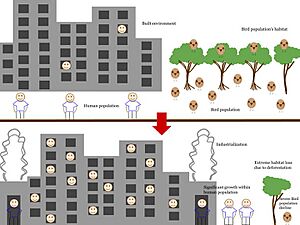
Human impact on the environment means the changes that people make to the natural world. These changes affect everything from the air and water to plants, animals, and entire ecosystems. When we build cities, grow food, and create new things, we change the planet.
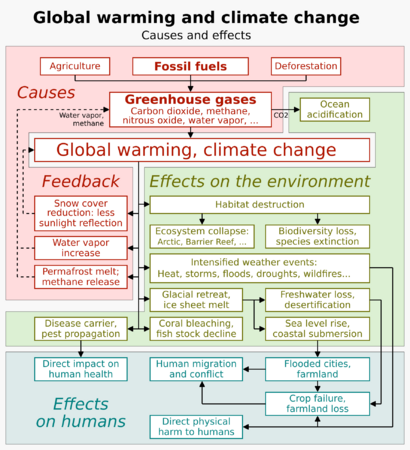
These actions are necessary for our lives, but they can also cause serious problems. Some of these include global warming, environmental degradation (the breakdown of the environment), and biodiversity loss (the disappearance of different types of plants and animals). Human activities that harm the environment include pollution, deforestation (cutting down forests), and using too many natural resources.
Scientists call our current time period the "Anthropocene". This name means the "Age of Humans," because people are now the main force changing the Earth's environment.
Contents
Using More Than Earth Can Provide
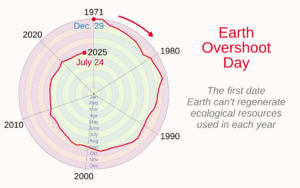
One of the biggest challenges is that humans are using more resources than the planet can provide over the long term. This is called "overshoot."
Using Too Many Resources
Overconsumption happens when people use natural resources, like water, trees, and minerals, faster than the Earth can replace them. We can measure this using an ecological footprint. This tool helps us see if we are living within the planet's limits. Currently, humanity is using about 70% more resources each year than the Earth can regenerate.
People in developed nations often consume resources at a much higher rate than those in developing countries. For example, the amount of oil and metals used by one person in a wealthy country can be over 30 times more than that used by a person in a poorer country.
Our food choices also have a big impact. Raising animals for meat uses a lot of land and water. Because of human activities, the world has lost 83% of all wild mammals and half of all plants.
A Growing Population
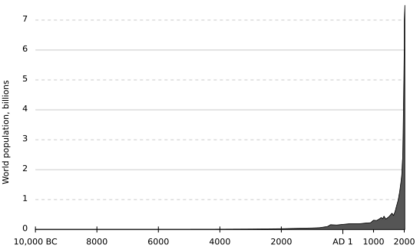
As the world's population has grown, so has our total impact on the environment. More people need more food, water, and energy. In 2017, over 15,000 scientists signed a letter warning that a growing human population is a major driver of environmental problems.
However, the number of people is only one part of the story. How we live is also very important. The main challenge is to find ways for everyone to live well without using up the planet's resources for future generations.
How We Get Our Food
The food we eat has a major effect on the environment. Both farming and fishing can cause harm if not done in a sustainable (long-lasting) way.
Farming's Footprint
Farming is essential for feeding the world, but it can have a big impact. To create farms, large areas of forest are often cleared (deforestation). This destroys the homes of many animals.
Farming also uses large amounts of water for irrigation. In some places, this can cause rivers and lakes to dry up. Fertilizers and pesticides used to help crops grow can sometimes wash into rivers and pollute the water, harming fish and other aquatic life.
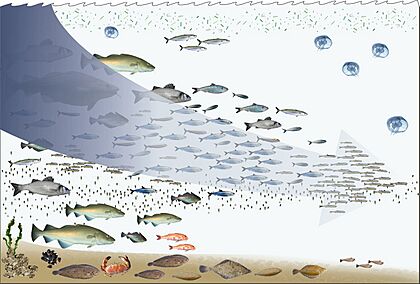
Fishing's Impact
The way we fish also affects the oceans. Overfishing is a major problem. This happens when we catch fish faster than they can reproduce. If this continues, some types of fish could disappear completely. According to a UN report, overfishing is the main reason many ocean species are going extinct.
Another issue is by-catch, which is when fishing nets accidentally catch other sea animals like dolphins, turtles, and sharks. Since 1970, the populations of ocean sharks and rays have dropped by 71%, mostly due to overfishing.
Meat and the Environment
Biomass of mammals on Earth in 2018 Livestock, mostly cattle and pigs (60%) Humans (36%) Wild mammals (4%)
Producing meat, especially beef, has a large environmental footprint. Raising livestock takes up a huge amount of land. In fact, about 26% of the Earth's land that isn't covered by ice is used for grazing animals.
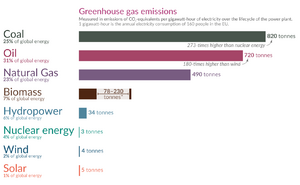
Livestock also produce greenhouse gases, like methane, which contribute to climate change. The entire livestock industry is responsible for about 18% of all human-caused greenhouse gas emissions.
The Problem with Palm Oil
Palm oil is a vegetable oil used in many products, from pizza and chocolate to soap and lipstick. Because it is so popular, huge areas of tropical rainforest, especially in Malaysia and Indonesia, have been cut down to grow oil palm trees.
This deforestation destroys the homes of endangered species like orangutans, tigers, and rhinos. While some palm oil is produced more sustainably, the high demand continues to put forests at risk.
Changing the Natural World
Human activities are changing ecosystems all over the planet. This leads to the loss of habitats and the many species that live in them.
Harming Our Ecosystems
Environmental degradation is the damage or destruction of the environment. This happens through the use of resources like air, water, and soil. It includes the destruction of ecosystems and the extinction of wildlife. A 2021 study found that only about 3% of the planet's land is still ecologically "intact," meaning it has healthy populations of its native animals and very little human disturbance.
Breaking Up Animal Homes

When we build cities, roads, and farms, we often break up large, connected habitats like forests into smaller, isolated pieces. This is called habitat fragmentation.
For animals, this is like having their neighborhood chopped up by highways they can't cross. It makes it harder for them to find food, find a mate, and raise their young. This is a major reason why biodiversity is declining worldwide.
The Loss of Plants and Animals
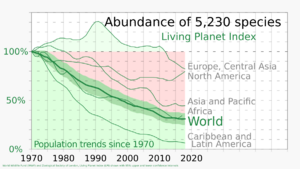
Biodiversity refers to all the different kinds of life on Earth. Sadly, human actions are causing plants and animals to go extinct at a rate 100 to 1,000 times faster than normal. Scientists call this the Holocene extinction, or the sixth mass extinction.
A 2019 global report warned that around one million species of plants and animals are now threatened with extinction. This loss of biodiversity is dangerous because we rely on healthy ecosystems for clean air, water, and food.
Species in the Wrong Place
An invasive species is a plant or animal that is introduced to a new environment where it doesn't belong. Because it has no natural predators in its new home, it can spread quickly and harm the native wildlife.
- Cats: In Australia, feral and domestic cats kill over 1.5 billion native animals each year and are a major cause of mammal extinctions.
- Burmese Pythons: In the Florida Everglades, pythons (originally from Asia) that were released into the wild have eaten so many raccoons, opossums, and other mammals that their populations have crashed.
Climate Change
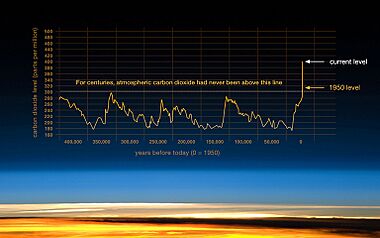
Climate change is one of the most serious environmental issues today. It is caused by the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas for energy. This releases greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO₂), into the atmosphere.
These gases act like a blanket, trapping heat and causing the Earth's temperature to rise. This leads to more extreme weather events like heatwaves, droughts, and floods, as well as rising sea levels.
Pollution's Impact
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment. These harmful materials are called pollutants.
Acid Rain and Oceans
When we burn fossil fuels, chemicals like sulfur and nitrogen are released into the air. These can mix with water in the clouds to create acid rain. Acid rain can harm forests, poison lakes, and damage buildings.
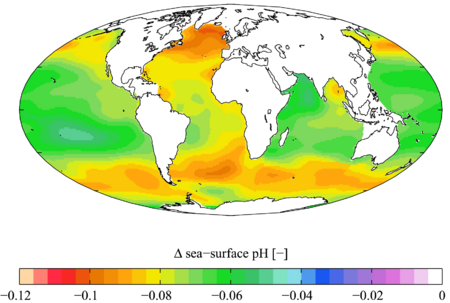
Much of the CO₂ we release also gets absorbed by the ocean. This makes the water more acidic, a process called ocean acidification. This is very harmful to sea creatures with shells, like corals, clams, and oysters.
Plastic Pollution
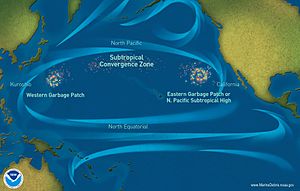
Plastic is a very useful material, but it creates a huge pollution problem because it does not break down naturally. Much of our plastic waste ends up in the ocean.
Scientists estimate that by 2050, there could be more plastic than fish in the oceans by weight. Animals can mistake plastic for food or get tangled in it, which can injure or kill them.
Light Pollution
Light pollution is the excessive use of artificial light at night. The bright lights from our cities can be seen from space and can cause problems for wildlife.
For example, light pollution can confuse migrating birds, causing them to fly off course. It can also disrupt the hunting and breeding habits of many animals that are active at night.
How Our Industries Affect the Planet
The ways we produce energy, make products, and travel all have an impact on the environment.
Getting Energy
Most of our energy comes from burning fossil fuels. Coal mining and burning is especially harmful, as it pollutes the air and water and releases huge amounts of CO₂.
However, we are slowly moving towards cleaner energy sources. Renewable energy from the sun (solar power) and wind (wind power) create very little pollution and are becoming cheaper and more common.
Fast Fashion
"Fast fashion" is a term for clothes that are made and sold very cheaply, so people can buy new styles often. This industry has a major environmental impact.
- It uses a huge amount of water. It can take over 2,700 liters of water to make one cotton t-shirt.
- It creates a lot of waste. Many unsold or returned clothes are simply thrown away in landfills.
- It causes pollution. Dyes and chemicals used to make clothes can pollute rivers. Washing synthetic clothes (made of plastic like polyester) releases tiny plastic fibers called microplastics into the water.
How We Travel
Our main forms of transport, such as cars, trucks, ships, and airplanes, burn petroleum fuels. This releases air pollution and is a major source of the greenhouse gases that cause climate change.
Building more roads and airports also takes up land and can destroy natural habitats. Shifting to electric vehicles and using public transport, biking, and walking more often can help reduce this impact.
See also
- Barriers to pro-environmental behaviour
- Effects of climate change on the water cycle
- Environmental impact of meat production
- Environmental impact of fishing
- Environmental impact of automobiles
- Environmental impact of concrete
- Environmental impact of hydraulic fracturing
- Environmental impact of iron ore mining
- Environmental impact of the coal industry
- Environmental issues
- Human overpopulation
- Overconsumption
- Planetary boundaries
- Sustainability
 | Mary Eliza Mahoney |
 | Susie King Taylor |
 | Ida Gray |
 | Eliza Ann Grier |