List of Scottish inventions and discoveries facts for kids
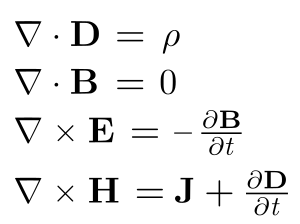
"the most significant event of the 19th century will be judged as Maxwell's discovery of the laws of electrodynamics"
Scottish inventions and discoveries are amazing things, processes, or ideas that were created or found by people from Scotland. Sometimes, an invention is called Scottish because it was made in Scotland, even if the inventor wasn't Scottish. It's often hard to tell the difference between something discovered for the first time and something invented.
Scotland has a long history of creating new things, even before the Industrial Revolution. Some of the most famous Scottish inventions include James Watt's improved steam engine, the bicycle, macadam roads, Alexander Graham Bell's first working telephone, John Logie Baird's television, and Alexander Fleming's discovery of penicillin.
Here's a list of some of the cool inventions and discoveries that are known to be Scottish.
Contents
- Travel and Transport Innovations
- Power and Energy Innovations
- Heavy Industry Innovations
- Agricultural Innovations
- Communication Innovations
- Publishing Firsts
- Culture and Arts Innovations
- Scientific Discoveries
- Sports Innovations
- Medical Innovations
- Household Innovations
- Weapons Innovations
- Miscellaneous Innovations
- See also
Travel and Transport Innovations
Roads and Vehicles
- Macadamised roads: John Loudon McAdam (1756–1836) developed this way of building roads using crushed stones. It's the basic idea for modern roads.
- Pedal bicycle: Both Kirkpatrick Macmillan (1813–1878) and Thomas McCall (1834–1904) are given credit for inventing the pedal bicycle.
- Pneumatic tyre: This air-filled tire was invented by Robert William Thomson and later improved by John Boyd Dunlop (1822–1873).
- Overhead valve engine: David Dunbar Buick (1854–1929) invented this type of engine, which is used in many cars today.
Civil Engineering Marvels
- Tubular steel: Sir William Fairbairn (1789–1874) helped create strong, hollow steel structures.
- The Falkirk Wheel: This amazing rotating boat lift was designed by Nicoll Russell Studios, RMJM, and engineers Binnie, Black, and Veatch. It opened in 2002.
- Patent slip for docking vessels: Thomas Morton (1781–1832) invented a way to pull ships out of the water for repairs.
- Canal design: Thomas Telford (1757–1834) was a master at designing canals.
- Improved dock design: John Rennie (1761–1821) made docks better for ships.
- Improved crane design: James Bremner (1784–1856) made cranes more efficient.
Aviation Innovations
- Aircraft design: Frank Barnwell (1910) helped set the basic rules for designing airplanes at the University of Glasgow.
Shipbuilding Innovations
- Europe's first passenger steamboat: Henry Bell (1767–1830) built the first steamboat for carrying people in Europe.
- First iron-hulled steamship: Sir William Fairbairn (1789–1874) built the first steamship with an iron body.
- First practical screw propeller: Robert Wilson (1803–1882) invented a useful screw propeller for boats.
Power and Energy Innovations
- Improved condensing steam engine: James Watt (1736–1819) made the steam engine much more efficient.
- Thermodynamic cycle: William John Macquorn Rankine (1820–1872) developed important ideas about how heat engines work.
- Coal-gas lighting: William Murdoch (1754–1839) was a pioneer in using gas from coal for lighting.
- Stirling heat engine: Rev. Robert Stirling (1790–1878) invented this type of engine.
- Wave-powered electricity generator: Stephen Salter invented a device to create electricity from ocean waves in 1977.
- Pelamis Wave Energy Converter: Richard Yemm created this "red sea snake" device to harness wave energy in 1998.
Heavy Industry Innovations
- Coal mining in the sea: Sir George Bruce of Carnock (1575) created an artificial island for coal mining in the sea, which was a huge achievement for its time.
- Making cast steel from wrought iron: David Mushet (1772–1847) found a way to make strong steel from iron.
- Hot blast oven: James Beaumont Neilson (1792–1865) invented a method that made iron production much cheaper.
- Steam hammer: James Nasmyth (1808–1890) invented this powerful tool used in factories.
- Wire rope: Robert Stirling Newall (1812–1889) invented wire rope, which is used in many ways, from bridges to elevators.
Agricultural Innovations
- Threshing machine improvements: James Meikle (c.1690-c.1780) and Andrew Meikle (1719–1811) made threshing machines better for separating grain.
- Hollow pipe drainage: Sir Hew Dalrymple, Lord Drummore (1700–1753) developed a system for draining wet soil.
- Scotch plough: James Anderson of Hermiston (1739–1808) invented an improved plough.
- Mechanical reaping machine: Rev. Patrick Bell (1799–1869) invented a machine to harvest crops.
- Fresno scraper: James Porteous (1848–1922) invented this tool for moving earth.
Communication Innovations
- Telephone: Alexander Graham Bell (1847-1922) invented the first practical telephone.
- Print stereotyping: William Ged (1690–1749) invented a way to make copies of printing plates.
- Roller printing: Thomas Bell patented roller printing for textiles in 1783.
- Adhesive postage stamp and postmark: James Chalmers (1782–1853) is credited with these postal innovations.
- Universal Standard Time: Sir Sandford Fleming (1827–1915) helped create the idea of worldwide time zones.
- Light signalling between ships: Admiral Philip H. Colomb (1831–1899) developed a way for ships to communicate using lights.
- Underlying principles of radio: James Clerk Maxwell (1831–1879) laid the scientific groundwork for radio waves.
- Kinetoscope: William Kennedy Dickson (1860-1935) helped invent this early motion picture camera in 1889.
- Teleprinter: Frederick G. Creed (1871–1957) invented the teleprinter, which sent typed messages over wires.
- RADAR: Robert Watson-Watt (1892–1973) made a big contribution to the development of radar.
- Automated teller machine (ATM) and PIN system: James Goodfellow (born 1937) invented the ATM and the Personal Identification Number system.
Publishing Firsts
- First edition of the Encyclopedia Britannica (1768–81): This famous encyclopedia was first published in Scotland.
- First English textbook on surgery (1597).
- First modern pharmacopoeia: William Cullen (1776) wrote a book that became a main guide for classifying and treating diseases in Europe.
- First postcards and picture postcards in the UK.
Culture and Arts Innovations
- Gospel music: The way Scottish Presbyterians sang psalms, called "lining out," is thought to have influenced the "call and response" style of gospel music in the American South.
- Scottish National Portrait Gallery: Designed by Sir Robert Rowand Anderson (1889), this was the world's first building made specifically to be a portrait gallery.
- Ethereal wave, Shoegaze, Future bass, and Hyperpop: Scottish bands and producers like Cocteau Twins, The Jesus and Mary Chain, Rustie, Hudson Mohawke, and Sophie helped create or popularize these music styles.
Scientific Discoveries
- Logarithms: John Napier (1550–1617) invented logarithms, which made calculations much easier.
- Modern Economics: Adam Smith (1776) is known as the "father of modern economics" for his book The Wealth of Nations.
- Modern Sociology: Adam Ferguson (1767) is called the "Father of Modern Sociology" for his work An Essay on the History of Civil Society.
- Hypnotism: James Braid (1795–1860) is known as the "Father of Hypnotherapy."
- Tropical medicine: Sir Patrick Manson is known as the "father of Tropical Medicine."
- Modern geology: James Hutton is called the "Founder of Modern Geology."
- Theory of electromagnetism: James Clerk Maxwell (1831–1879) developed the theory that describes how electricity and magnetism are connected.
- Composition of Saturn's Rings: James Clerk Maxwell (1859) figured out that Saturn's rings are made of many small particles, not solid rings.
- Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution: James Clerk Maxwell (1860) helped create the theory that explains how gas molecules move at different temperatures.
- Popularizing the decimal point: John Napier (1550–1617) helped make the decimal point widely used.
- First theory of the Higgs boson: Peter Higgs, a physicist at the University of Edinburgh, proposed the theory of the Higgs boson particle in 1964.
- Gregorian telescope: James Gregory (1638–1675) invented this type of telescope.
- Discovery of Proxima Centauri: Robert T. A. Innes (1861–1933) discovered Proxima Centauri, the closest star to our Sun.
- Discovery of the Horsehead Nebula: Williamina Fleming (1857–1911) discovered this famous nebula.
- World's first oil refinery: James Young (1811–1883) created the first oil refinery and a process to get paraffin from coal, which helped start the modern oil industry.
- Concept of latent heat, carbon dioxide properties, and heat capacity: French-born Joseph Black (1728–1799) made important discoveries about heat and gases.
- Identifying the nucleus in living cells: Robert Brown (1773–1858) identified the cell nucleus.
- Early incandescent light bulb: James Bowman Lindsay (1799-1862) created an early form of the light bulb.
- Colloid chemistry: Thomas Graham (1805–1869) studied colloids, which are mixtures like milk or fog.
- Kelvin temperature unit: Irishman William Thomson, Lord Kelvin (1824–1907) developed the Kelvin temperature scale.
- Diagrams for chemical bonds: Alexander Crum Brown (1838–1922) created a way to draw chemical bonds.
- Criminal fingerprinting: Henry Faulds (1843–1930) played a key role in developing fingerprinting for crime solving.
- Noble gases: Sir William Ramsay (1852–1916) discovered several noble gases.
- Cloud chamber: Charles Thomson Rees Wilson (1869–1959) invented the cloud chamber to see paths of atoms.
- Statistical graphics: William Playfair created the first line charts, bar charts, and pie charts in the late 1700s and early 1800s.
- First cloned mammal (Dolly the Sheep): This famous cloning was done at The Roslin Institute in 1996 by English scientists Ian Wilmut and Keith Campbell.
- Metaflex fabric: The University of St. Andrews (2010) developed the first fabric that can bend light around an object.
- Tractor beam innovations: St. Andrews University (2013) created the world's first working tractor beam that can pull tiny objects.
Sports Innovations
Scots have helped create and develop many sports:
- Australian rules football: Scots were important in the early development of this game.
- Athletics events: Many modern track and field events, like the shot put and hammer throw, come from the Scottish Highland Games.
- Curling: This sport played on ice with stones originated in Scotland.
- Gaelic handball: The modern game of handball was first recorded in Scotland in 1427.
- Cycling: The invention of the pedal-cycle was a Scottish contribution.
- Golf: Golf as we know it today started in Scotland.
- Ice Hockey: Scottish soldiers in Canada played a game similar to Shinty on frozen lakes, which led to ice hockey.
- Shinty: The rules for this traditional Scottish sport were standardized in the 19th century.
- Rugby sevens: Ned Haig and David Sanderson invented this faster version of rugby in 1883.
- Dugout: The covered bench area for coaches and players was invented by Aberdeen FC Coach Donald Colman in the 1920s.
- First Robot Olympics: The world's first Robot Olympics took place in Glasgow in 1990.
Medical Innovations
- Pioneering surgical anaesthesia with Chloroform: Robert Mortimer Glover first used chloroform in 1842, and Sir James Young Simpson (1811–1870) expanded its use for humans during surgery.
- Saline drip: Dr Thomas Latta used the saline drip in 1831/32.
- Hypodermic syringe: Alexander Wood (1817–1884) invented this syringe for injections.
- First diagnostic ultrasound scanner: Ian Donald (1910–1987) developed the first medical use of ultrasound.
- Independent discovery of smallpox inoculation: Johnnie Notions (c.1730–1803) independently discovered a way to inoculate against smallpox.
- Identifying the mosquito as the carrier of malaria: Sir Ronald Ross (1857–1932) made this crucial discovery.
- Identifying the cause of brucellosis: Sir David Bruce (1855–1931) found the cause of this disease.
- Typhoid fever vaccine: Sir William B. Leishman (1865–1926) discovered the vaccine for typhoid fever.
- Electrocardiography: Alexander Muirhead (1869) contributed to recording the heart's electrical activity.
- Discovery of Staphylococcus: Sir Alexander Ogston (1880) discovered this common bacteria.
- Discovering insulin: John Macleod (1876–1935) was part of the team that discovered insulin, which earned him a Nobel Prize in 1923.
- Penicillin: Sir Alexander Fleming (1881–1955) discovered penicillin, one of the most important antibiotics.
- Pioneering X-ray cinematography: John Macintyre (1896) created the first moving X-ray images.
- First hospital Radiation therapy unit: John Macintyre (1902) set up the first unit for X-ray diagnosis and treatment at Glasgow Royal Infirmary.
- Haldane effect: John Scott Haldane (1907) described how oxygen affects blood.
- First Decompression tables: John Scott Haldane (1908) created tables to help deep-sea divers safely return to the surface.
- Oxygen therapy: John Scott Haldane (1922) helped start the modern use of oxygen therapy.
- Transplant rejection: Professor Thomas Gibson (1940s) was the first to understand why the body rejects transplanted tissue.
- Effective tuberculosis treatment: Sir John Crofton helped develop effective treatments for tuberculosis in the 1950s.
- First beta-blocker drugs: Sir James W. Black (1964) developed these drugs, which changed how heart conditions like angina are treated. He won a Nobel Prize in 1988.
- Modern asthma therapy: Sir David Jack (1972) developed modern treatments for asthma.
- Chainsaw: Invented by surgeons John Aitken and James Jeffray to help with difficult childbirths.
- Glasgow Coma Scale: Graham Teasdale and Bryan J. Jennett (1974) created this scale to assess brain injuries.
- Anesthetic drug Propofol: Dr. John B. Glen (1977) discovered and developed Propofol, a widely used surgical anesthetic.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine: Ian Frazer (2006) helped discover this vaccine, which prevents certain cancers.
- Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS): Strathclyde University (2014) developed a laser and nanoparticle test to detect diseases like meningitis.
Household Innovations
- Television: John Logie Baird (1923) invented the television.
- Refrigerator: William Cullen (1748) demonstrated the first artificial refrigeration.
- Flush toilet: Alexander Cumming (1775) improved the flush toilet with a curved pipe to prevent smells.
- Vacuum flask: Sir James Dewar (1847–1932) invented the vacuum flask, which keeps liquids hot or cold.
- Piano footpedal: John Broadwood (1732–1812) invented the piano footpedal.
- Waterproof macintosh: Charles Macintosh (1766–1843) invented the waterproof fabric for raincoats.
- Kaleidoscope: Sir David Brewster (1781–1868) invented the kaleidoscope.
- Keiller's marmalade: Janet Keiller (1797) created the first recipe for Dundee marmalade.
- Modern lawnmower: Alexander Shanks (1801–1845) invented the modern lawnmower.
- Lucifer friction match: Sir Isaac Holden (1807–1897) invented an early friction match.
- Self-filling pen: Robert William Thomson (1822–1873) invented a self-filling pen.
- Cotton-reel thread: J & J Clark of Paisley helped popularize cotton thread on spools.
- Lime cordial: Lauchlan Rose created lime cordial in 1867.
- Bovril beef extract: John Lawson Johnston invented Bovril in 1874.
- Electric clock: Alexander Bain (1840) invented the electric clock.
- Chemical Telegraph: Alexander Bain (1846) also invented an early chemical telegraph.
- Irn-Bru: This popular soft drink is made by Barr's in Scotland and is so popular there that it outsells Coca-Cola and Pepsi.
Weapons Innovations
- Carronade cannon: Robert Melville (1723–1809) invented this short, powerful cannon.
- Ferguson rifle: Patrick Ferguson invented this breech-loading rifle in 1770.
- Lee bolt system: James Paris Lee invented the bolt system used in famous rifles like the Lee-Enfield.
- Ghillie suit: This camouflage suit was first used by the Lovat Scouts.
- Percussion cap: Scottish clergyman Alexander Forsyth invented the percussion cap for firearms.
Miscellaneous Innovations
- Boys' Brigade: Sir William Alexander Smith founded the Boys' Brigade.
- Bank of England: The idea for the Bank of England was developed by William Paterson.
- Bank of France: The idea for the Bank of France was developed by John Law.
- Grand Theft Auto: This famous video game series was developed by Scottish game developers DMA Design (now Rockstar North).
- Colour photography: The first known permanent colour photograph was taken by James Clerk Maxwell (1831–1879).
- Buick Motor Company: Founded by David Dunbar Buick.
- New York Herald newspaper: Founded by James Gordon Bennett, Sr..
- Pinkerton National Detective Agency: Founded by Allan Pinkerton.
- Forbes magazine: Founded by B. C. Forbes.
- Fried chicken: The origins of fried chicken in the American South can be traced back to Scottish cooking traditions.
See also
- List of British innovations and discoveries
- List of English inventions and discoveries
- List of domesticated Scottish breeds
- List of Welsh inventors
- Homecoming Scotland 2009
- Timeline of Irish inventions and discoveries
- Science in Medieval Western Europe
 | Shirley Ann Jackson |
 | Garett Morgan |
 | J. Ernest Wilkins Jr. |
 | Elijah McCoy |

