Tiger facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tiger |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Bengal tiger (P. tigris tigris) | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: |
P. tigris
|
| Binomial name | |
| Panthera tigris |
|

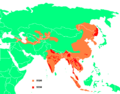
The tiger (Panthera tigris) is the biggest living member of the cat family, called Felidae. Tigers are hunters and eat other animals. They live in different parts of Asia, like India, Bhutan, China, Korea, and Siberian Russia. Tigers usually live alone.
Contents
What Tigers Look Like
Tigers have bright orange fur with black stripes. Their bellies are white. The black stripes often go down to their white undersides. These stripes help them blend in with their surroundings when they are hunting. It's very rare for two tigers to have the exact same stripe pattern.
Sometimes, you might see white tigers. They have white fur with black stripes, or sometimes even pure white fur. These white tigers usually have orange or red eyes. Most Bengal tigers have orange fur. A white tiger cub is born only about once in every 100 million births! The Bengal tiger is a special animal for both Bangladesh and India.
Tigers come in different sizes, depending on their type, called a subspecies. Siberian tigers are the largest. Male Siberian tigers can grow to be at least 9 feet (2.7 metres) long (just their body, not including the tail). They can weigh around 900 lb (410 kg). Female tigers are a bit smaller than males.
Where Tigers Live
Tigers can live in many different kinds of habitats. They mostly need places to hide, water nearby, and enough animals to hunt and eat. For example, Bengal tigers live in many types of forests. These include wet, evergreen forests in Assam and eastern Bengal. They also live in swampy mangrove forests near the Ganges River. You can find them in deciduous forests in Nepal and even in thorn forests in the Western Ghats.
Tiger Types: Subspecies

For a long time, people thought there were five types of tigers still alive. Three other tiger types are now extinct, meaning they no longer exist.
- Here are some tiger subspecies:
- Bali tiger (Panthera tigris balica)
- Bengal tiger (Panthera tigris tigris)
- Caspian tiger (Panthera tigris virgata)
- Chinese tiger (Panthera tigris corbetti)
- Javan tiger (Panthera tigris sondaica)
- Malayan tiger (Panthera tigris jacksoni)
- Siberian tiger (Panthera tigris altaica)
- South China tiger (Panthera tigris amoyensis)
- Sumatran tiger (Panthera tigris sumatrae)
However, in 2017, scientists from the IUCN Cat Specialist Group looked at tiger types again. They decided that tigers in mainland Asia are one type, called P. t. tigris. Tigers on the Sunda Islands are another type, called P. t. sondaica.
Tiger Hybrids
Sometimes, tigers and lions kept in zoos were bred together. This created hybrids called ligers and tigons. These animals have features from both lions and tigers. Today, breeding these hybrids is not encouraged. This is because people want to focus on saving pure tiger species.
A liger is born when a male lion and a female tiger (tigress) have cubs. A tigon is less common. It is born when a female lion (lioness) and a male tiger have cubs.
Tiger Behavior
Tigers are mostly active during the day. They do not often climb trees, but it has been seen. Tigers are very good swimmers. They often take baths in ponds, lakes, and rivers. This helps them stay cool when it's hot.
Tigers can travel long distances. They might move as far as 650 km (400 mi) to find other tiger groups. Adult tigers usually live alone. They set up and protect their own territories. They also have larger areas where they roam freely.
Tigers show their feelings with their faces. For example, a "defense threat" means a tiger is showing its teeth. It will also flatten its ears and make its pupils bigger.
Like other big cats in the Panthera group, tigers can roar. They roar especially when they are angry, during mating season, or after they make a kill. There are two main types of roars. The "true" roar is very loud and can be heard up to 3 km (1.9 mi) away. Tigers sometimes make this roar three or four times in a row. They also have a shorter, harsher "coughing" roar.
When tigers are nervous, they might moan. This sound can be heard from 400 m (1,300 ft) away. Tigers also make a soft, low sound called "chuffing." It's a bit like a smaller cat purring. They make this sound in friendly situations. Other sounds tigers make include grunts, woofs, snarls, miaows, hisses, and growls.
What Tigers Eat: Diet
Tigers eat many kinds of prey, mostly other large mammals. Some of the animals they hunt are deer, monkeys, wild rabbits, wild pigs, tapirs, and buffalo. All tigers are carnivores, which means they only eat meat. Some tigers can eat up to 50 pounds (23 kilograms) of meat in one day. Tigers kill their prey by biting down on its throat until it can no longer breathe.
Tiger Reproduction and Life Cycle
A female tiger's pregnancy lasts from 93 to 114 days. On average, it's about 103 to 105 days. The mother tiger gives birth in a safe place. This could be in tall grass, a thick bush, a cave, or a rocky crack.
Tiger mothers usually have two or three cubs at a time. Sometimes, they can have as many as six. When they are born, cubs weigh between 780 to 1,600 g (1.72 to 3.53 lb). Their eyes are closed at birth.
Around the time they stop drinking their mother's milk (called weaning), the cubs start to go with their mother on her walks. She teaches them how to hunt for themselves. Tiger cubs start hunting on their own when they are about 11 months old. They become fully independent around 18 to 20 months of age. The oldest tiger ever recorded in a zoo lived for 26 years.
Saving Tigers: Conservation
In the 1990s, a new way to help tigers was created. It was called Tiger Conservation Units (TCUs). These are areas of land that can support tiger groups. There are 15 different types of habitats in five large bioregions.
In 2016, experts estimated that there were about 3,890 tigers living in the wild around the world.
The biggest dangers to tigers include losing their homes and their homes being broken into smaller pieces (habitat fragmentation). Also, poaching (illegal hunting) for their fur and body parts has greatly reduced the number of tigers in the wild.
Scientists study tigers in the wild using different methods. They used to estimate tiger numbers by making plaster casts of their pugmarks (paw prints). However, this method was not always accurate. Newer ways to study tigers include using camera traps. Scientists also study DNA from tiger scat (poop). Radio-collaring is another method used to track tigers in the wild. Tiger spray (urine) has also been found to be a good source of DNA.
Cool Facts About Tigers

- Tigers are the biggest cats in the world.
- They can live for up to 25 years.
- A Liger is a mix between a male lion and a female tiger. A Tigon is a mix between a female lion and a male tiger.
- A tiger's pee smells like buttered popcorn!
- Tigers cannot purr, but they can make a sound called "chuff."
- The stripes on a tiger's fur are unique to each tiger. No two tigers have the same stripe pattern.
- The smallest type of tiger is the Sumatran tiger. The largest is the Siberian tiger.
- A tiger's roar is very loud and can be heard from miles away.
Images for kids
-
Tiger hunted by wild dogs (dholes) as illustrated in Samuel Howett & Edward Orme, Hand Coloured, Aquatint Engravings 1807
-
A rewilded South China tiger hunting blesbok in South Africa
-
Tiger hunting on elephant-back, India, 1808
-
Cover of the 1954 edition of Jim Corbett's Man-Eaters of Kumaon, illustrated by Raymond Sheppard
-
Tigers made to perform at Ringling Brothers and Barnum and Bailey Circus
-
The Hindu goddess Durga riding a tiger. Guler school, early 18th century
-
19th-century painting of a tiger by Kuniyoshi Utagawa
-
William Blake's first printing of The Tyger c. 1795
-
An early silver coin of king Uttama Chola found in Sri Lanka shows the Chola Tiger sitting between the emblems of Pandyan and Chera
See also
 In Spanish: Tigre para niños
In Spanish: Tigre para niños
 | Lonnie Johnson |
 | Granville Woods |
 | Lewis Howard Latimer |
 | James West |