Weehawken, New Jersey facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Weehawken, New Jersey
|
|
|---|---|
|
Township
|
|

Weehawken (background) and the Hudson River and Midtown Manhattan (foreground) in July 2001
|
|
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | Hudson |
| Incorporated | March 15, 1859 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Faulkner Act (council–manager) |
| • Body | Township Council |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1.48 sq mi (3.82 km2) |
| • Land | 0.78 sq mi (2.03 km2) |
| • Water | 0.69 sq mi (1.79 km2) 46.69% |
| Area rank | 454th of 565 in state 7th of 12 in county |
| Elevation | 3 ft (0.9 m) |
| Population
(2020)
|
|
| • Total | 17,197 |
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
17,207 |
| • Rank | 154th of 565 in state 10th of 12 in county |
| • Density | 21,934.9/sq mi (8,469.1/km2) |
| • Density rank | 8th of 565 in state 6th of 12 in county |
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (Eastern (EDT)) |
| ZIP Codes |
07086–07087
|
| Area code(s) | 201/551 |
| FIPS code | 3401777930 |
| GNIS feature ID | 0882224 |
Weehawken is a township in the northern part of Hudson County, New Jersey. It is located along the Hudson Waterfront and Hudson Palisades, which are cliffs overlooking the Hudson River. In 2020, Weehawken had a population of 17,197 people. This was a big increase from 12,554 people in 2010.
| Top - 0-9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
Weehawken's History
What Does the Name Weehawken Mean?
The name Weehawken comes from the Algonquian language spoken by the Lenape people. They were Native Americans who lived here long ago. The name has many possible meanings. Some think it means "maize land" (corn land). Others believe it means "place of gulls" or "rocks that look like trees." The "rocks that look like trees" likely refers to the tall cliffs called the Palisades.
Three U.S. Navy ships have been named after Weehawken. One famous ship was the USS Weehawken. It was an ironclad ship launched in 1862. It fought for the Union Navy during the American Civil War. Sadly, it sank in a storm in 1863.
How Weehawken Began
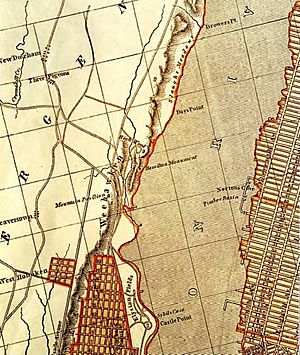
Weehawken's written history started in 1609. That year, Henry Hudson sailed his ship, the Half Moon, down the river now called the Hudson. He anchored in Weehawken Cove. At that time, the area was home to the Hackensack and Tappan tribes of the Lenape people.
European settlers began to arrive in the 1630s. In 1658, Peter Stuyvesant, a Dutch leader, bought land from the Lenape. This land stretched from "the great rock above Wiehacken" to the south. In 1661, Weehawken became part of Bergen, a larger settlement.
In 1674, the British took control of the area from the Dutch. Weehawken became part of East Jersey. Early descriptions of the area talk about thick forests and good land for farming. By 1700, there was ferry service from Weehawken. This ferry was mainly used to transport farm goods to Greenwich Village in Manhattan.
Weehawken officially became a township on March 15, 1859. It was formed from parts of Hoboken and North Bergen.
Weehawken in the Revolutionary War

During the American Revolutionary War, Weehawken was a key lookout spot. Patriots used it to watch the British forces in New York. In 1778, George Washington asked Aaron Burr to send people to Weehawken to observe enemy ships.
A famous event in Weehawken's history is the Burr–Hamilton duel. This duel happened on July 11, 1804. It was a fight between Alexander Hamilton, who was the first U.S. Secretary of the Treasury, and Aaron Burr, who was the Vice President. Hamilton was badly wounded and died the next day. This duel was re-enacted on its 200th anniversary in 2004.
Three years before this, Hamilton's son, Philip Hamilton, also fought a duel in the area. He was defending his father's honor and was fatally wounded.
Weehawken in the 1800s
In the mid-1800s, a wealthy man named James G. King built a large estate called Highwood. He hosted many important people there.
Weehawken became a major transportation center. Ferries, a toll road called the Hackensack Plank Road, and later, the West Shore Railroad, all connected here. Rich people built homes on top of the New Jersey Palisades cliffs. They came to escape the summer heat of New York. Weehawken became a popular place for the wealthy to relax. There were even special lifts and an elevator to help people get up the cliffs. The Eldorado Amusement Park, which opened in 1891, attracted huge crowds.
Weehawken in the 1900s
By the early 1900s, the large estates and amusement parks started to disappear. More private homes were built. Many German, Austrian, and Swiss immigrants moved to Weehawken. They built homes and worked in nearby factories. Weehawken remained mostly a residential town, even as Hudson County grew more industrial. After World War I, many Syrian immigrants also moved to Weehawken. They came to work in the growing textile industry.
Weehawken's Geography
Weehawken is part of the larger New York metropolitan area. It sits on the western shore of the Hudson River, across from Midtown Manhattan. It is also the western end of the Lincoln Tunnel, a major tunnel connecting New Jersey to New York City.
The township covers about 1.48 square miles (3.82 square kilometers). About half of this area is land, and the other half is water.
Weehawken shares borders with Hoboken, Union City, and West New York. Across the Hudson River, it borders the New York City borough of Manhattan.
The tall cliffs called the Palisades shape Weehawken's natural look. Important man-made structures include the Lincoln Tunnel Helix and the tunnel's toll plaza. Weehawken has different neighborhoods: Downtown (also called "The Shades"), the Heights, Uptown (which includes Kingswood Bluff), and the Waterfront. The Waterfront area has been developed for transportation, businesses, and homes.
There are many public staircases and "dead-end" streets throughout the town. Boulevard East is a scenic road in Weehawken. It offers amazing views of the Hudson River and the Manhattan skyline. Local rules prevent very tall buildings from being built. This helps keep the beautiful views clear from higher parts of the town. In 2021, a company donated land on the Palisades cliff to the town. This helps protect its natural beauty and history.
Weehawken's Population
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1860 | 280 | — | |
| 1870 | 597 | 113.2% | |
| 1880 | 1,102 | 84.6% | |
| 1890 | 1,943 | 76.3% | |
| 1900 | 5,325 | 174.1% | |
| 1910 | 11,228 | 110.9% | |
| 1920 | 14,485 | 29.0% | |
| 1930 | 14,807 | 2.2% | |
| 1940 | 14,363 | −3.0% | |
| 1950 | 14,830 | 3.3% | |
| 1960 | 13,504 | −8.9% | |
| 1970 | 13,383 | −0.9% | |
| 1980 | 13,168 | −1.6% | |
| 1990 | 12,385 | −5.9% | |
| 2000 | 13,501 | 9.0% | |
| 2010 | 12,554 | −7.0% | |
| 2020 | 17,197 | 37.0% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 17,207 | 37.1% | |
| Population sources: 1860–1920 1860–1870 1870 1880–1890 1890–1910 1890–1900 1910–1930 1940–2000 2000 2010 2020 |
|||
Population in 2020
In 2020, Weehawken had 17,197 people. The population is made up of many different groups. About 43.8% of the people were White (not Hispanic). About 15% were Asian. About 3.9% were Black or African American. People of Hispanic or Latino background made up about 32.9% of the population.
Population in 2010
In 2010, Weehawken had 12,554 people. There were 5,712 households, which are groups of people living together. About 20.4% of households had children under 18. The average household had 2.20 people.
The median age in Weehawken was 37.2 years old. This means half the people were younger than 37.2, and half were older.
Weehawken's Economy
Weehawken has a shopping area along Park Avenue. This street has many local stores, restaurants, and bars. Along the Hudson River, there are large office buildings and apartments. Weehawken is mostly a residential town, meaning people live there.
However, it also has a business area called Lincoln Harbor. Companies like UBS and Swatch Group USA have offices there. There is also a Sheraton Hotels and Resorts hotel in this area.
Sports in Weehawken
In 2011, there were plans to host a Formula One car race in Weehawken and West New York. It was called the Grand Prix of America. The race was supposed to be 3.2 miles long and attract 100,000 people. It was expected to bring in about $100 million for the local economy. However, the race was never held. It was repeatedly added and then removed from the racing calendar.
Places to See in Weehawken
Weehawken is famous for its amazing views of the New York City skyline. You can see from the Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge all the way to the George Washington Bridge. But there are many other interesting places to visit too:
- Park Avenue: This is the main street for shopping and dining. It has many local businesses.
- Hamilton Park: Located on Boulevard East, this park offers great views. It used to be the site of a fun park called Eldorado Amusement Resort.
- King's Bluff: This historic area has some of Weehawken's most expensive homes. They are built in many different architectural styles.
- Weehawken Water Tower: Built in 1883, this tower looks like a famous building in Florence, Italy. Ships use it as a landmark on the Hudson River.
- Hackensack Plank Road: This old road, first built in 1718, climbs from Downtown to The Heights.
- The "Horseshoe" on Shippen Street: This is a unique cobbled street with two sharp turns. It leads to the original town hall.
- Lincoln Tunnel Helix: This is a circular road that leads into the Lincoln Tunnel.
- Weehawken Public Library: This beautiful building was built in 1904. It became a library in 1942 and was updated in 1999.
- NY Waterway's Weehawken Port Imperial Ferry Terminal: This modern ferry terminal opened in 2006. It's where you can catch ferries to Manhattan.
- Reservoir Park: This park opened in 2015 on the site of an old reservoir. It's a peaceful place to relax.
- West Shore Railroad Tunnel: This tunnel, carved through the cliffs, is now used by the Hudson–Bergen Light Rail.
- Hudson Riverfront 9/11 Memorial: This memorial has two trident-shaped beams from the Twin Towers. It is located along the Hudson River Waterfront Walkway.
- Weehawken Pool: This pool is part of the Weehawken Waterfront Park and Recreation Center, which opened in 2021.
-
9/11 Memorial
Hamilton Monument


The Alexander Hamilton Monument is on Hamilton Avenue. It marks the site of the famous duel between Alexander Hamilton and Aaron Burr. The first memorial was built in 1806. It was a tall marble monument with a plaque. However, people took pieces of it as souvenirs, and it disappeared by 1820.
Later, two stones marked where Hamilton and Burr stood during the duel. In 1870, railroad tracks were built through the site. A large boulder where Hamilton was said to have rested was moved to the top of the Palisades. Today, this boulder is still there, just off Boulevard East.
In 1894, an iron fence was built around the boulder. A bust (a sculpture of a head and shoulders) of Hamilton was added, along with a plaque. Sadly, the bust was thrown over the cliff by vandals in 1934. A new bust was put in place in 1935. The plaque was also stolen later. New historical markers were added on July 11, 2004, the 200th anniversary of the duel.
Education in Weehawken
The Weehawken School District serves public school students from pre-kindergarten through 12th grade. In the 2022–23 school year, the district had about 1,320 students and 130 teachers. This means there were about 10 students for every teacher.
The schools in the district are:
- Daniel Webster School (PreK–2nd grade)
- Theodore Roosevelt School (3rd–6th grade)
- Weehawken High School (7th–12th grade)
The school system is known for its small class sizes and good ratings.
The Weehawken Public Library has about 43,000 books and other items. It is part of a larger library system in Bergen County. The library building was renovated and updated in 1999.
Transportation in Weehawken
Weehawken has about 16 miles of roads. Most of these roads are maintained by the town itself.
Route 495 runs east-west. It connects the Lincoln Tunnel to the New Jersey Turnpike. The Lincoln Tunnel Helix in Weehawken helps traffic get to and from the tunnel.
Public Transportation Options
You can get around Weehawken using buses, ferries, and light rail.
- Bus Service: NJ Transit buses run along major streets like Park Avenue and Boulevard East. These buses connect Weehawken to Manhattan and other parts of Hudson and Bergen Counties.
- Light Rail: The Hudson-Bergen Light Rail (HBLR) has stops at Lincoln Harbor and Port Imperial. You can take the light rail to Hoboken, Jersey City, and Bayonne.
- Ferry Service: From the Port Imperial station, you can transfer to NY Waterway ferries. These ferries take you to Midtown and Lower Manhattan. The main office for NY Waterway is also located in Weehawken.
Media and Culture in Weehawken
Weehawken is part of the New York media market. This means most New York City newspapers are available here. The Jersey Journal is a local newspaper that covers news in Hudson County.
Local weekly papers include the Weehawken Reporter and The Hudson Reporter.
The "Weehawken Sequence" is a famous series of paintings by local artist John Marin. These paintings, from the early 1900s, are considered some of the first abstract art by an American artist.
The Hudson Riverfront Performing Arts Center is a group that wants to build a world-class performing arts center on the waterfront. They have been holding outdoor and indoor events since 2004.
Notable People from Weehawken
Many interesting people have lived in or are connected to Weehawken:
- Adele Astaire (1896–1981), a famous dancer and entertainer.
- Fred Astaire (1899–1987), a well-known Hollywood actor and dancer.
- Karl Bitter (1867–1915), a famous sculptor who had his art studio here.
- Kenneth Burke (1897–1993), a literary theorist, poet, and novelist.
- Helen Castillo, a fashion designer who was born and raised in Weehawken.
- João Gilberto (1931–2019), a Brazilian singer and guitar player, known as a pioneer of bossa nova music.
- Emile Griffith (1938–2013), a professional boxer and World Champion.
- Barry Harris (1929–2021), a jazz pianist and educator.
- Roscoe H. Hillenkoetter (1897–1982), a director of the Central Intelligence Agency.
- John Marin (1870–1953), an early American modernist artist.
- Thelonious Monk (1917–1982), a legendary jazz pianist.
- Kate Pierson (born 1948), a vocalist and founding member of the band The B-52's.
- Jerome Robbins (1918–1998), a famous choreographer, known for West Side Story.
- Wilbur Ross (born 1937), a businessman and former U.S. Secretary of Commerce.
- Gerard Schwarz (born 1947), a conductor.
- Amani Toomer (born 1974), a wide receiver who played for the New York Giants.
- Derrick Ward (born 1980), a running back who played for the New York Giants.
- Daniel Webster (1782–1852), a famous American statesman.
See also
 In Spanish: Weehawken (Nueva Jersey) para niños
In Spanish: Weehawken (Nueva Jersey) para niños