Greenwich Village facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Greenwich Village
|
|
|---|---|

Bird's eye view of Greenwich Village, facing towards the Lower Manhattan skyline in 2017
|
|
| Country | |
| State | |
| City | New York City |
| Borough | Manhattan |
| Community District | Manhattan 2 |
| Named for | Groenwijck (Green District) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 0.75 km2 (0.289 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 22,785 |
| • Density | 30,440/km2 (78,840/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Villager |
| Economics | |
| • Median income | $119,728 |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| ZIP Codes |
10003, 10011, 10012, 10014
|
| Area codes | 212, 332, 646, and 917 |
|
Greenwich Village Historic District
|
|

453–461 Sixth Avenue in the Historic District
|
|
| Location | Boundaries: north: W 14th St; south: Houston St; west: Hudson River; east: Broadway |
| Architectural style | various |
| NRHP reference No. | 79001604 |
| Significant dates | |
| Added to NRHP | June 19, 1979 |
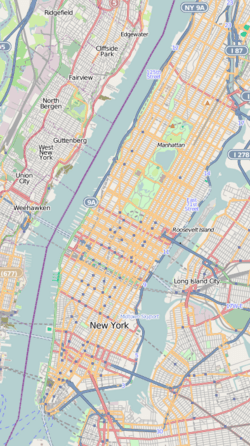
Greenwich Village, often called the Village, is a famous neighborhood in New York City. It's located on the west side of Lower Manhattan. The area is bordered by 14th Street to the north, Broadway to the east, Houston Street to the south, and the Hudson River to the west.
The name "Greenwich" comes from the Dutch word Groenwijck, which means "Green District". For a long time, Greenwich Village was known as a home for artists and a center for new ideas. It played a big role in the Beat Generation and the counterculture of the 1960s. It's also famous for being the birthplace of the modern LGBTQ movement.
Today, Greenwich Village is home to Washington Square Park. It also has two private colleges: New York University (NYU) and The New School. The neighborhood has become quite expensive, with high housing prices.
Contents
- Exploring Greenwich Village's Location
- A Brief History of Greenwich Village
- Preserving Greenwich Village's Heritage
- Greenwich Village's Community and People
- Things to See and Do in Greenwich Village
- Getting Around Greenwich Village
- Education in Greenwich Village
- Notable People from Greenwich Village
- Images for kids
- See also
Exploring Greenwich Village's Location
Greenwich Village is a unique part of Manhattan. It has distinct borders that help define it.
Where is Greenwich Village Located?
The neighborhood is bordered by Broadway to the east. The Hudson River is to the west. Houston Street forms the southern border, and 14th Street is to the north. Washington Square Park and New York University are right in the middle of the area.
Nearby neighborhoods include NoHo and the East Village to the east. SoHo and Hudson Square are to the south. Chelsea and Union Square are to the north. The western part of Greenwich Village is called the West Village.
Understanding the Village's Street Layout
Greenwich Village has a street layout that is different from most of Manhattan. This is because it was once a small, separate village. When New York City grew, the Village kept its original, more winding streets. This gives the neighborhood a special, historic feel.
Many streets here are narrow and curve in interesting ways. This adds to the charm of the area. Unlike most of Manhattan, streets in the Village often have names instead of numbers. For example, West 4th Street runs north-south in the Village. This is unusual because most numbered streets in Manhattan run east-west.
A large part of Greenwich Village is a Historic District. This means that new buildings and changes to old ones are carefully controlled. This helps keep the neighborhood's historic look and feel. Most buildings are mid-rise apartments or old row houses. This is very different from the tall skyscrapers in other parts of Manhattan.
A Brief History of Greenwich Village
Greenwich Village has a long and interesting past. It started as a small settlement and grew into a famous cultural hub.
Early Beginnings of the Village
In the 16th century, the Lenape people called the area "Sapokanikan". This meant "tobacco field". Later, Dutch settlers and enslaved Africans cleared the land. They called their settlement Noortwyck, meaning "North district".
In the 1630s, Governor Wouter van Twiller grew tobacco here. The English took control in 1664. Greenwich Village then grew as a separate hamlet. It was north of the main New York City settlement. In 1644, eleven Dutch African settlers were given land here. This area became known as the Land of the Blacks.
The name "Greenwich" first appeared in 1696. In 1727, a large estate was built by Sir Peter Warren. His house overlooked the North River.
Greenwich Village's Role in Culture and Arts
Greenwich Village became famous as a center for bohemian culture. This means it was known for its artistic and unconventional residents. The neighborhood was a place where new ideas in politics, art, and culture could grow.
Small publishing houses, art galleries, and experimental theaters thrived here. The Stonewall Inn is a very important landmark in the Village. In 1969, protests for equality started there. These Stonewall riots are seen as the beginning of the modern gay rights movement. The Stonewall Inn is now a National Historic Landmark.
The Tenth Street Studio Building was a key place for artists. It opened in 1857. Many famous artists, like Winslow Homer and Frederic Church, had studios there. The Hotel Albert also hosted many important artists and writers. These included Mark Twain and Salvador Dalí.
In 1924, the Cherry Lane Theatre opened. It is New York City's oldest continuously running Off-Broadway theater. It was a place for new playwrights and emerging voices. The Whitney Museum of American Art also started in Greenwich Village in 1931. It was founded by Gertrude Vanderbilt Whitney to showcase American Art.

The Village also had the nation's first racially integrated nightclub, Café Society. It opened in 1938. It featured many talented African American performers. These included Billie Holiday and Lena Horne.
The annual Greenwich Village Halloween Parade started in 1974. It is the world's largest Halloween parade. Millions of people watch it every year.
The Village After World War II

In the 1950s, Greenwich Village became important for the Beat Generation. Writers and artists, known as the Beats, moved here. They wanted to escape social rules and create new art. Famous writers like Jack Kerouac and Allen Ginsberg were part of this movement.
The Village was also a major center for folk music in the 1960s. Music clubs like Gerde's Folk City and The Bitter End hosted many future stars. Bob Dylan, Joan Baez, and Joni Mitchell all performed here. The Village Vanguard and Blue Note are famous for jazz music.
Off-Off-Broadway theater also began in Greenwich Village in 1958. It was a new kind of theater that rejected commercial shows. Coffeehouses like the Caffe Cino were early venues for these plays.
The Village played a key role in the gay liberation movement. The Stonewall riots in June 1969 were a turning point. These protests led to the modern fight for LGBTQ rights in the United States. The Stonewall National Monument was created to honor this history. The world's oldest gay and lesbian bookstore, Oscar Wilde Bookshop, opened here in 1967.
Preserving Greenwich Village's Heritage
Local residents and groups work hard to protect the Village. They want to keep its unique history and architecture.
Efforts to Protect Historic Areas
Since the 1960s, people have fought to preserve the Village. Jane Jacobs, a famous writer, helped protect the area from large development plans. The New York City Landmarks Preservation Commission (LPC) has designated many parts of the Village as historic districts. This means that changes to buildings are limited to keep their original look.
The Greenwich Village Society for Historic Preservation (GVSHP) is a group that works to protect the neighborhood. They have helped create new historic districts. These include the Gansevoort Market Historic District and the Weehawken Street Historic District. These areas protect unique buildings like old warehouses and cobblestone streets.
NYU's Growth and Community Concerns
New York University (NYU) has a large campus in Greenwich Village. The university's growth has sometimes caused disagreements with local residents. People want to make sure new buildings fit the neighborhood's style.
For example, when NYU planned Furman Hall, community groups were concerned. They worried about a tall building near the historic Judson Memorial Church. NYU agreed to make the building shorter and restore historic facades. This showed a willingness to work with the community.
Another project, Founders Hall, also caused debate. NYU decided to keep and restore the facade of St. Ann's Church. This helped blend the new dorm with the old church. These efforts show the ongoing balance between growth and preservation in Greenwich Village.
Greenwich Village's Community and People
Greenwich Village is a diverse and lively neighborhood. It has a mix of people and a strong community feel.
Who Lives in Greenwich Village?
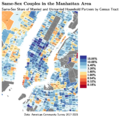
Greenwich Village is part of Manhattan Community District 2. The area has a high percentage of college-educated residents. Most people living here are adults. The neighborhood is known for having many same-sex couples.
The median household income in Greenwich Village is higher than the city average. This means that many residents have good incomes. The area is considered a high-income neighborhood.
Italian-American Heritage
Greenwich Village was once home to a large Italian-American community. Many Italian-Americans moved here in the 1930s. They came from places like Naples and Sicily. For many years, the Village had one of the biggest Italian-speaking communities in the U.S.
Things to See and Do in Greenwich Village
The Village offers many interesting places to visit and activities to enjoy.
Colleges and Schools in the Area
Greenwich Village has several colleges. New York University (NYU) has been here since the 1830s. Its buildings are around Washington Square Park. The New School also has a campus here. Its buildings are known for their modern design. The Cooper Union is located nearby at Astor Place. Pratt Institute also has a campus on 14th Street.
Parks and Recreation

The most famous park is Washington Square Park. It is often called the heart of the neighborhood. The Village also has smaller parks like Christopher Park and Minetta Triangle. There are playgrounds for kids, too.
"The Cage" is a famous basketball court. It's officially called the West Fourth Street Courts. Many basketball and handball players use these courts. It's a popular spot for streetball tournaments. The Grey Art Gallery at NYU shows contemporary art.
Arts and Entertainment Venues
Greenwich Village has a lively performing arts scene. There are many Off Broadway and Off-Off-Broadway theaters. The Blue Man Group performs at the Astor Place Theater. Jazz clubs like the Village Vanguard and the Blue Note host famous musicians. Other music clubs include The Bitter End. The Village even has its own orchestra.
Comedy clubs are also popular here. The Comedy Cellar is where many famous stand-up comedians started their careers.
Important Buildings and Offices
Several publications have offices in the Village. These include American Heritage and Fortune magazines. The National Audubon Society also has its headquarters here. The Salvation Army's former American headquarters is in the northern part of the Village.
Getting Around Greenwich Village
The Village is easy to reach by public transportation.
Subway and Bus Connections
Greenwich Village is served by several New York City Subway lines. These include the Eighth Avenue, Sixth Avenue, Canarsie, and Broadway–Seventh Avenue lines. Key subway stations are 14th Street/Sixth Avenue, 14th Street/Eighth Avenue, West Fourth Street–Washington Square, and Christopher Street–Stonewall.
Local New York City Bus routes also run through the neighborhood. These include the M55, M7, M11, M14, and M20. The PATH train also has stations in Greenwich Village. These are Christopher Street, Ninth Street, and 14th Street.
Education in Greenwich Village
The neighborhood has good schools and libraries.
Local Schools and Colleges
Greenwich Village has a high rate of college-educated residents. Most adults here have a college degree or higher. Elementary school students in the Village miss fewer school days than the city average. High school students also graduate on time more often.
Students in Greenwich Village are zoned for PS 3, Melser Charrette School, and PS 41, Greenwich Village School. They are also zoned for Baruch Middle School 104.
Public Libraries in the Village
The New York Public Library (NYPL) has two branches in Greenwich Village. The Jefferson Market Library is a beautiful building that was once a courthouse. It became a library in 1967. The Hudson Park branch is another library in the area. It was built in 1906.
Notable People from Greenwich Village
Many famous people have lived in Greenwich Village over the years.
- Edward Albee (1928–2016), playwright
- Alec Baldwin (born 1958), actor
- Richard Barone, musician, producer
- Brie Bella (born 1983), wrestler
- Nate Berkus (born 1971), interior designer
- David Blue (1941–1982), folksinger
- Matthew Broderick (born 1962), actor
- Barbara Pierce Bush (born 1981), daughter of former U.S. President George W. Bush
- Francesco Carrozzini (born 1982), film director and photographer
- Jessica Chastain (born 1977), actress
- Ramsey Clark (1927–2021), lawyer and activist
- Patricia Clarkson (born 1959), actress
- Francesco Clemente (born 1952) contemporary artist
- Jacob Cohen (1923–1983), statistician and psychologist
- Anderson Cooper (born 1967), CNN anchor
- Hugh Dancy (born 1975), actor
- Claire Danes (born 1979), actress
- Robert De Niro (born 1943), actor
- Brian De Palma (born 1940), film director and screenwriter
- Floyd Dell (1887–1969), novelist, playwright, poet
- Leonardo DiCaprio (born 1974), actor
- Robert Downey Jr. (born 1965), actor and singer
- Steve Earle (born 1955), musician
- Crystal Eastman (1881–1928), lawyer and leader for woman's suffrage
- Eric Eisner, Hollywood lawyer
- Maurice Evans (1901–1989), British actor
- Andrew Garfield (born 1983), actor
- Hank Greenberg (1911–1986), Hall of Fame baseball player
- John P. Hammond (born 1942), blues singer and guitarist
- Jerry Herman (1931–2019), composer and lyricist
- Dustin Hoffman (born 1937), actor
- Edward Hopper (1882–1967), painter
- Marc Jacobs (born 1963), fashion designer
- Richard Johnson, gossip columnist
- Wes Joice (1931–1997), owner of The Lion's Head
- Max Kellerman (born 1973), sports commentator
- Annie Leibovitz (born 1949), photographer
- Arthur MacArthur IV (born 1938), musician
- Andrew McCarthy (born 1962), actor, writer and television director
- Bob Melvin (born 1961), Major League Baseball player and manager
- Edna St. Vincent Millay, poet and playwright
- Matthew Modine (born 1959), actor and activist
- Julianne Moore (born 1960), actress
- Nickolas Muray (born Miklós Mandl; 1892–1965), Hungarian-born American photographer
- Bebe Neuwirth (born 1958), actress
- Edward Norton (born 1969), actor and filmmaker
- Rosie O'Donnell, actress and comedian
- Mary-Kate Olsen, actress and fashion designer
- Mary-Louise Parker, actress
- Sarah Jessica Parker (born 1965), actress
- Sean Parker (born 1979), entrepreneur
- Edgar Allan Poe (1809–1849), poet and novelist
- Leontyne Price (born 1927), soprano
- Daniel Radcliffe (born 1989), actor
- Gilda Radner (1946–1989), actress and comedian
- Rachael Ray, television personality and cook
- Julia Roberts (born 1967), actress
- Oliver Sacks (1933-2015), neurologist and author
- Susan Sarandon (born 1946), actress
- John Sebastian (born 1944), musician
- Amy Sedaris (born 1961), actress
- James Spader, actor
- Pat Steir (born 1938), painter and printmaker
- Emma Stone (born 1988), actress
- Uma Thurman (born 1970), actress
- Tiny Tim (1932–1996), singer
- Marisa Tomei (born 1964), actress
- Calvin Trillin (born 1935), feature writer for The New Yorker magazine.
- Liv Tyler (born 1977), actress
- Edgard Varèse (1883–1965), French-born composer
- Chloe Webb (born 1956), actress.
- Anna Wintour (born 1949), editor-in-chief of Vogue magazine
Images for kids
Error: no page names specified (help).
- LGBTQ culture in New York City
- NYC Pride March
- New York Halloween Parade
- West Village, Manhattan
- East Village, Manhattan
- SoHo, Manhattan
- Washington Square Park
See also
 In Spanish: Greenwich Village para niños
In Spanish: Greenwich Village para niños
 | Stephanie Wilson |
 | Charles Bolden |
 | Ronald McNair |
 | Frederick D. Gregory |