1840–1849 Atlantic hurricane seasons facts for kids
The 1840s were a time when many strong storms, called tropical cyclones or hurricanes, formed in the Atlantic Ocean. These storms happen every year, usually between June 1 and November 30. While we don't have details for every single storm from this time, people living along the coast recorded information about the biggest and most impactful hurricanes. This article tells you about the important storms that happened during the 1840s.
Contents
- 1840 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- 1841 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- 1842 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- 1843 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- 1844 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- 1845 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- 1846 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- 1847 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- 1848 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- 1849 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- Related Pages
- Images for kids
1840 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- On June 19, a tropical storm hit near Lake Charles, Louisiana.
- A hurricane caused damage near the mouth of the Rio Grande river. It destroyed villages and led to flooding.
1841 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- A strong tropical storm hit the Florida Panhandle on September 14.
- In early October, a powerful hurricane stayed offshore of the Carolinas. As it moved northeast, it pulled in cold air and changed into a different type of storm called an extratropical storm. This storm then hit New England on October 3.
- It brought a mix of snow and sleet to Connecticut, with snowdrifts reaching up to 5.5 meters (18 feet) in some places.
- The storm wrecked the fishing boats at Georges Bank, and 81 fishermen sadly drowned.
- It also knocked down trees, ripped roofs off houses, and pushed boats onto the shore.
- A factory that made salt along Cape Cod was destroyed, which hurt the local economy.
- In 1842, a monument was built to remember the sailors and fishermen lost at sea during this "October Gale."
- In October, a hurricane hit Cuba, passing close to Havana. After crossing the island, it moved past the Florida Keys, bringing heavy rain but staying offshore.
1842 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- On July 12, a major hurricane hit near Portsmouth, North Carolina. Two ships flipped over, and everyone on board was lost. The storm continued across Virginia before fading away over Maryland.
- On August 2, a tropical storm hit northeastern Florida.
- A second hurricane hit Ocracoke, North Carolina on August 24. It caused livestock to drown and homes to be washed away. It also sank three ships, leading to at least 8 deaths.
- A hurricane nicknamed Antje's hurricane (after a ship it damaged) moved across the Florida Keys on September 4. It then traveled west across the Gulf of Mexico, hitting between Matamoros and Tampico in Mexico. This storm moved west because a strong high-pressure system was to its north.
- A strong tropical storm hit Galveston, Texas on September 17. It caused about $10,000 in damage and killed 40 cattle.
- On September 22, a tropical storm hit the Pensacola, Florida area.
- An October storm from the Pacific Ocean crossed over land at the Isthmus of Tehuntepec and entered the Gulf of Mexico.
- A hurricane passed by Galveston, Texas on October 5, causing flooding and sinking one ship. It continued east, becoming a major hurricane before hitting near St. Marks, Florida. It caused $500,000 in damage before moving out to sea on October 10. This storm is known as the Gulf to Bermuda Hurricane.
- A storm was first seen east of Miami, Florida on October 26. It moved along the coasts of Florida, Georgia, and South Carolina before fading away on October 30, south of North Carolina.
- A storm was first seen southwest of Madeira on October 24. It passed the island on October 26, moving northeast towards Spain. It hit southern Spain on October 29 and moved inland as far as Madrid. It was a strong hurricane (Category 2) near Madeira on October 26. This storm was similar to Hurricane Vince from 2005.
1843 Atlantic Hurricane Season
A major hurricane moved north through the Gulf of Mexico. It hit Port Leon, Florida, on September 13, destroying the town with flooding and storm surge. Fourteen people died. Because of the damage, the town's residents moved the town 5 kilometers (3 miles) north to a new place called New Port, which is now known as Newport, Florida.
1844 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- On June 11, a tropical storm hit near Lake Charles, Louisiana. It moved slowly north, west of the town, and faded away on June 15.
- On August 4, a major hurricane moving through the Gulf of Mexico hit the Rio Grande valley. It moved slowly through the area, causing 70 deaths.
- On September 8, a hurricane moved into Florida south of St. Augustine. It crossed the state, went into the Gulf of Mexico, then turned northeast and hit Florida again on September 9.
- On October 4, a hurricane hit Cuba, causing 101 deaths. It moved northeast, bringing rain and strong winds to the United States coastline but staying offshore. The ship Vigilant was lost off Key West during this hurricane on October 4 and 5.
1845 Atlantic Hurricane Season
No storms were recorded this year.
1846 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- A possible hurricane hit near the mouth of the Mississippi River on April 3, causing heavy rain. It's not certain if it was a tropical storm because of the time of year.
- On September 6, a slow-moving hurricane stayed offshore of Cape Hatteras. It pushed water into the Pamlico Sound. When the hurricane moved north, the winds pushed the water back out, creating two new openings in the land: the Hatteras Inlet and the Oregon Inlet. The Oregon Inlet was named after the first large ship that could pass through it.
- On September 19, a strong gale destroyed 11 ships from Marblehead, Massachusetts, and 65 lives were lost. This might have been a tropical cyclone. After this event, Gloucester became the main center for fishing in New England.
Great Havana Hurricane of 1846
- In October, a very powerful hurricane, possibly a Category 5, moved through the Caribbean Sea. It hit western Cuba on October 10.
- On October 11, it hit the Florida Keys, destroying the old Key West lighthouse and Fort Taylor.
- It then moved north, and on October 13, it hit Tampa Bay as a major hurricane. As the storm approached, it pulled water out of the bay, making the Manatee River so shallow that a horse could walk across it.
- The hurricane crossed Florida and stayed over land as it moved through Georgia, South Carolina, and North Carolina.
- It moved up the Chesapeake Bay, causing a lot of damage through Virginia, Maryland, Washington D.C., and Pennsylvania.
- This storm caused around 163 deaths and widespread damage in all the areas it affected. It is known as the Great Havana Hurricane.
1847 Atlantic Hurricane Season
A hurricane hit Tobago on October 11, causing 27 deaths.
1848 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- On August 18, a tropical storm hit south-central Louisiana, damaging cotton crops.
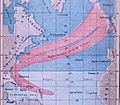
- A hurricane traveled northeast of the Caribbean Sea, through the Bahamas, and then curved into the North Atlantic shipping lanes towards Europe between August 19 and September 2. This storm was one of the first tropical cyclones for which scientists created a path map.
- On September 25, a major hurricane, known as the Great Gale of 1848, hit near what is now Sarasota, Florida. It created a new waterway called New Pass. It made landfall in Tampa Bay, near Fort Brooke and Tampa, where tides rose 4.6 meters (15 feet). It then crossed to the east coast, damaging houses, causing flooding, and affecting shipping.
- On October 11, a major hurricane moving east hit the Florida Panhandle.
- On October 17, a weak hurricane hit the southeast coast of Texas, causing flooding and high tides.
1849 Atlantic Hurricane Season
- A tropical storm may have moved into the area where Arkansas, Louisiana, and Texas meet, as there was a lot of flooding in northern Louisiana that August.
- On September 13, a weak hurricane moved into the Rio Grande river area.
- A hurricane was first seen off the coast of North Carolina in early October. It moved northeast, passing close to but staying offshore of Long Island. On October 6, it made landfall in Massachusetts, causing 143 deaths.
Related Pages
Images for kids
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |