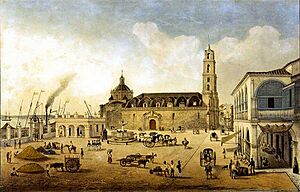Havana facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Havana
La Habana
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
From the top to the left: Línea Street; Barrio chino; Malecón; Palacio de la Revolución; and Castillo del Morro
|
|||
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
City of Columns
|
|||
| Country | |||
| Metro Zone | Greater Havana | ||
| Established | 16 November 1519 (current place) | ||
| Municipalities | 15 | ||
| Government | |||
| • Body | Gobierno Provincial de La Habana | ||
| Area | |||
| • Capital city | 728.26 km2 (281.18 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 59 m (195 ft) | ||
| Population
(2023)
|
|||
| • Capital city | 1,814,207 | ||
| • Rank | 7th in North America 1st in Cuba |
||
| • Density | 2,491/km2 (6,450/sq mi) | ||
| • Urban | 100 % | ||
| Demonym(s) | Habaneros-habaneras | ||
| GDP (PPP, constant 2015 values) | |||
| • Year | 2023 | ||
| • Total | $41.1 billion | ||
| • Per capita | $19,100 | ||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (UTC−05:00) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (UTC−04:00) | ||
| Patron saint | San Cristóbal | ||
| HDI (2019) | 0.834 – very high | ||
| Official name: Old Havana and its Fortification System | |||
| Type: | Cultural | ||
| Criteria: | iv, v | ||
| Designated: | 1982 (6th session) | ||
| Reference #: | 204 | ||
| Region: | Latin America and the Caribbean | ||
Havana (/həˈvænə/; Spanish: La Habana [la aˈβana]) is the capital and largest city in Cuba. It's the main port and a big business hub. Havana is the most populated city and the largest by area in Cuba. It is also the second largest metropolitan area in the Caribbean region. In 2012, about 2.1 million people lived here. The city covers an area of 728.26 km2 (281.18 sq mi).
The Spanish founded Havana in the 16th century. It was a key starting point for Spanish ships exploring the Americas. It also became a vital stop for Spanish ships returning to Spain with treasures. Philip II of Spain made Havana the capital in 1607. Walls and forts were built to protect the city from attacks. Today, Havana is where the Cuban government is located. It also hosts many businesses and over 100 foreign offices. The current governor is Reinaldo García Zapata.
Modern Havana is like three cities in one: Old Havana, Vedado, and the newer suburban areas. The city spreads mostly west and south from the bay. This bay has a narrow entrance and splits into three main harbors: Marimelena, Guanabacoa, and Antares. The Almendares River flows through the city from south to north. It empties into the Straits of Florida a few miles west of the bay.
Havana welcomes over a million tourists each year. In 2010, 1.1 million international tourists visited. Old Havana was named a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1982. The city is famous for its history, culture, architecture, and monuments. Like the rest of Cuba, Havana has a tropical climate.
What's in a Name?
In 1514, the city was first called San Cristóbal de la Habana. This means "Saint Christopher of the Habana." Habana was the name of a local Native American group. Some think the name came from Habaguanex, a chief of the Taíno tribe. When the name came to English, the "b" sound changed to a "v" sound. This is a common change in Spanish. The name Havana became very popular during the Spanish–American War. It also refers to a type of cigar, a color, and a type of rabbit.
Havana's History
The 1500s

Diego Velázquez de Cuéllar first founded Havana in 1514. It was on the southern coast of Cuba, near the Mayabeque River. But attempts to build a city there failed. Between 1514 and 1519, the Spanish tried two more spots on the north coast. The city that became Havana was finally settled in 1519. This spot was next to a natural bay called Puerto de Carenas. The bay was perfect for a harbor, which is why the location changed.
Pánfilo de Narváez gave Havana its full name: San Cristóbal de la Habana. San Cristóbal is the patron saint of Havana. In its early days, Cuba was mostly a base for the Spanish to conquer other lands.
Havana started as a trading port. It was often attacked by buccaneers, pirates, and French raiders. In 1555, the French raider Jacques de Sores attacked and burned the city. These attacks made the Spanish Crown build forts in major cities. This was to protect against pirates and control trade with the West Indies.
Ships from all over the New World brought goods to Havana. From there, they were sent to Spain. The many ships in the bay also helped Havana's farms and factories grow. They needed food, water, and other supplies for their long journeys.
On December 20, 1592, King Philip II of Spain officially made Havana a city. Later, the Spanish Crown called it "Key to the New World and Rampart of the West Indies." Work continued to build and improve the city's defenses.
The 1600s
Havana grew a lot in the 17th century. New buildings were made from wood, the most common material. They mixed different Spanish building styles. The city also built public monuments and religious buildings. Many important structures were finished during this time. These included the convent of St. Augustin and El Morro Castle.
In 1649, a deadly sickness came from Cartagena, Colombia. It affected one-third of Havana's people. In 1674, work began on the City Walls to make Havana stronger. These walls were finished by 1740.
By the mid-18th century, Havana had over 70,000 people. It was the third-largest city in the Americas. Only Lima and Mexico City were bigger.
The 1700s

In the 18th century, Havana was Spain's most important port. It had places where ships could be repaired. By 1740, it was Spain's biggest shipyard and the only drydock in the New World.
The British captured the city during the Seven Years' War. This happened on June 6, 1762. A British fleet of over 50 ships and 11,000 soldiers landed east of Havana. The British quickly started trading with their colonies in North America and the Caribbean. This changed Cuban society very fast. Less than a year later, the Peace of Paris was signed. Britain gave Havana back to Spain in exchange for Florida.
After getting the city back, the Spanish made Havana the most fortified city in the Americas. They built the Fortress of San Carlos de la Cabaña. This was the third-biggest Spanish fort in the New World. On January 15, 1796, the remains of Christopher Columbus were brought to the island. They stayed there until 1898. Then, they were moved to Seville's Cathedral after Spain lost Cuba.
The 1800s
As trade grew in the early 1800s, Havana became a rich and stylish city. Its theaters hosted famous actors. Wealthy people built grand new classical mansions. During this time, Havana was known as the Paris of the Antilles.
In 1837, Cuba's first railroad was built. It was 51 km (32 mi) long and connected Havana to Bejucal. This railroad moved sugar from the Güines valley to the harbor. Cuba became the fifth country in the world to have a railroad. Throughout the century, Havana gained more cultural places. One was the Tacón Theatre, which was very luxurious.
In 1863, the city walls were taken down. This allowed the city to grow bigger. By the end of the 19th century, Spanish rule in the Americas was ending in Havana.
The sinking of the U.S. battleship Maine in Havana's harbor in 1898 led to the Spanish–American War.
The 1900s
Cuba's first president, Tomás Estrada Palma, led from 1902 to 1906. His time was known for honest government.
In July 1940, during World War II, the Havana Conference took place. Twenty-one American nations, including Cuba, agreed to manage their own lands that were taken by the Axis powers.
By 1958, Cuba was quite advanced for Latin America. However, there were economic issues. Many people, especially graduates, struggled to find jobs. The middle class, which was similar to that in the United States, became unhappy.

After the revolution of 1959, the new government led by Fidel Castro worked to improve public services. They also focused on housing and official buildings. However, after Castro took over private businesses and industries, and the U.S. put an embargo on Cuba, shortages hit Havana hard. By 1966–68, the Cuban government owned all private businesses.
An economic downturn happened after the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991. The Soviet Union had given Cuba billions of dollars, and this support ended. Many thought the government would fall, like other Soviet-backed countries.
The 2000s
After years of economic struggles, the government turned to tourism for money. Foreign investors helped remodel old buildings into new hotels. In Old Havana, many streets and squares have been fixed up for tourists. But Old Havana is a big city, and only a small part has been restored.
On January 27, 2019, a very strong tornado hit Havana. It killed eight people and injured over 190. It was rated an EF4, making it the strongest tornado in Cuba since 1940.
How Havana is Governed
The governor of Havana is Reinaldo García Zapata. He was elected on January 18, 2020.
Havana is run by a city-provincial council. The governor is the main leader. This means Havana acts as both a city and a province of Cuba. The city does not have much independence. It relies on the national government for its budget and political direction.
Voters choose representatives for Municipal Assemblies every five years. These assemblies are in charge of each of the city's boroughs. They elect the borough presidents and vice presidents, who are like mayors. There is only one political party, the Communist Party. However, members of the Communist Party often run against each other. Candidates do not have to be party members. They are chosen by citizens in open meetings.
The city's borders touch Mayabeque Province to the south and east. They also touch Artemisa Province to the west. This is because the old rural La Habana Province was changed in 2010.
Where is Havana?
Location
Havana is on Cuba's northern coast, along the Straits of Florida. This is south of the Florida Keys, where the Gulf of Mexico meets the Atlantic Ocean. The city mostly spreads west and south from the bay. The bay has a narrow entrance and splits into three main harbors: Marimelena, Guanabacoa, and Atarés. The Almendares River flows through the city from south to north. It enters the Straits of Florida a few miles west of the bay.
The city sits on low hills that gently rise from the water. A notable high point is a 60-meter (200-foot) limestone ridge. This ridge slopes up from the east and ends at La Cabaña and El Morro. These are sites of old Spanish forts that overlook the eastern bay. Another important hill to the west holds the University of Havana and the Castillo del Príncipe (Havana).
Weather in Havana
Havana has a tropical climate. This weather is made milder by the island's location in the trade wind belt. Warm ocean currents also help. Havana's climate is mostly a tropical savanna climate (Aw). It is very close to a tropical rainforest climate (Af) and a tropical monsoon climate (Am).
Average temperatures are around 22 °C (72 °F) in January and February. They reach about 28 °C (82 °F) in August. The temperature rarely drops below 10 °C (50 °F). The lowest temperature ever recorded in Havana was 1 °C (34 °F). Rainfall is heaviest in June and October. It is lightest from December to April. The city gets about 1,200 mm (47 in) of rain each year.
Hurricanes sometimes hit the island. However, they usually strike the south coast. Damage in Havana is often less than in other parts of the country. The most recent hurricane-strength storm near Havana was Hurricane Ian in 2022.
Tornadoes are rare in Cuba. But on January 28, 2019, a very strong EF4 tornado hit the eastern part of Havana. This tornado caused a lot of damage. It destroyed at least 90 homes. It also killed four people and injured 195. By February 4, the death toll rose to six.
The table below shows average temperatures:
| Climate data for Havana (1961–1990, extremes 1859–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 33.0 (91.4) |
34.5 (94.1) |
35.3 (95.5) |
37.0 (98.6) |
37.3 (99.1) |
35.4 (95.7) |
36.6 (97.9) |
37.7 (99.9) |
38.2 (100.8) |
39.6 (103.3) |
34.0 (93.2) |
33.2 (91.8) |
39.6 (103.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 25.8 (78.4) |
26.1 (79.0) |
27.6 (81.7) |
28.6 (83.5) |
29.8 (85.6) |
30.5 (86.9) |
31.3 (88.3) |
31.6 (88.9) |
31.0 (87.8) |
29.2 (84.6) |
27.7 (81.9) |
26.5 (79.7) |
28.8 (83.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 22.2 (72.0) |
22.4 (72.3) |
23.7 (74.7) |
24.8 (76.6) |
26.1 (79.0) |
27.0 (80.6) |
27.6 (81.7) |
27.9 (82.2) |
27.4 (81.3) |
26.1 (79.0) |
24.5 (76.1) |
23.0 (73.4) |
25.2 (77.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 18.6 (65.5) |
18.6 (65.5) |
19.7 (67.5) |
20.9 (69.6) |
22.4 (72.3) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.8 (74.8) |
24.1 (75.4) |
23.8 (74.8) |
23.0 (73.4) |
21.3 (70.3) |
19.5 (67.1) |
6.0 (42.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 6.0 (42.8) |
11.9 (53.4) |
10.0 (50.0) |
15.1 (59.2) |
15.4 (59.7) |
20.0 (68.0) |
19.0 (66.2) |
20.0 (68.0) |
20.0 (68.0) |
18.0 (64.4) |
14.0 (57.2) |
10.0 (50.0) |
6.0 (42.8) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 64.4 (2.54) |
68.6 (2.70) |
46.2 (1.82) |
53.7 (2.11) |
98.0 (3.86) |
182.3 (7.18) |
105.6 (4.16) |
99.6 (3.92) |
144.4 (5.69) |
180.5 (7.11) |
88.3 (3.48) |
57.6 (2.27) |
1,189.2 (46.84) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 5 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 6 | 5 | 80 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 75 | 74 | 73 | 72 | 75 | 77 | 78 | 78 | 79 | 80 | 77 | 75 | 76 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 217.0 | 203.4 | 272.8 | 273.0 | 260.4 | 237.0 | 272.8 | 260.4 | 225.0 | 195.3 | 219.0 | 195.3 | 2,831.4 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 7.0 | 7.2 | 8.8 | 9.1 | 8.4 | 7.9 | 8.8 | 8.4 | 7.5 | 6.3 | 7.3 | 6.3 | 7.8 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 6 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 10 |
| Source 1: World Meteorological Organisation, Climate-Charts.com | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Meteo Climat (record highs and lows), Deutscher Wetterdienst (sun) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 °C (73 °F) | 23 °C (73 °F) | 24 °C (75 °F) | 26 °C (79 °F) | 27 °C (81 °F) | 28 °C (82 °F) | 28 °C (82 °F) | 28 °C (82 °F) | 28 °C (82 °F) | 27 °C (81 °F) | 26 °C (79 °F) | 24 °C (75 °F) |
City Districts
The city is divided into 15 municipalities, also called boroughs. These are further split into 105 wards called consejos populares.
- Playa: Includes Santa Fe, Siboney, Cubanacán, Ampliación Almendares, Miramar, Sierra, Ceiba, Buena Vista.
- Plaza de la Revolución: Includes El Carmelo, Vedado-Malecón, Rampa, Príncipe, Plaza, Nuevo Vedado-Puentes Grandes, Colón-Nuevo Vedado, Vedado.
- Centro Habana: Includes Cayo Hueso, Pueblo Nuevo, Los Sitios, Dragones, Colón.
- La Habana Vieja: Includes Prado, Catedral, Plaza Vieja, Belén, San Isidro, Jesús María, Tallapiedra.
- Regla: Includes Guaicanimar, Loma Modelo, Casablanca.
- La Habana del Este: Includes Camilo Cienfuegos, Cojímar, Guiteras, Alturas de Alamar, Alamar Este, Guanabo, Campo Florido, Alamar-Playa.
- Guanabacoa: Includes Mañana-Habana Nueva, Villa I, Villa II, Chivas-Roble, Debeche-Nalon, Hata-Naranjo, Peñalver-Bacuranao, Minas-Barreras.
- San Miguel del Padrón: Includes Rocafort, Luyanó Moderno, Diezmero, San Francisco de Paula, Dolores-Veracruz, Jacomino.
- Diez de Octubre: Includes Luyanó, Jesús del Monte, Lawton, Vista Alegre, Goyle, Sevillano, La Víbora, Santos Suárez, Tamarindo.
- Cerro: Includes Latinoamericano, Pilar-Atares, Cerro, Las Cañas, El Canal, Palatino, Armada.
- Marianao: Includes CAI-Los Ángeles, Pocito-Palmas, Zamora-Cocosolo, Libertad, Pogoloti-Belén-Finlay, Santa Felicia.
- La Lisa : Includes Alturas de La Lisa, Balcón Arimao, El Cano-Valle Grande-Bello 26 y Morado, Punta Brava, Arroyo Arenas, San Agustín, Versalles-Coronela.
- Boyeros: Includes Santiago de Las Vegas, Nuevo Santiago, Boyeros, Wajay, Calabazar, Altahabana-Capdevila, Armada-Aldabó.
- Arroyo Naranjo: Includes Los Pinos, Poey, Víbora Park, Mantilla, Párraga, Calvario-Fraternidad, Guinera, Eléctrico, Managua, Callejas.
- Cotorro: Includes San Pedro-Centro Cotorro, Santa Maria del Rosario, Lotería, Cuatro Caminos, Magdalena-Torriente, Alberro.
People of Havana
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1750 | 70,000 | — |
| 1931 | 728,500 | +940.7% |
| 1943 | 868,426 | +19.2% |
| 1953 | 1,139,579 | +31.2% |
| 1970 | 1,786,522 | +56.8% |
| 1981 | 1,929,432 | +8.0% |
| 2002 | 2,171,671 | +12.6% |
| 2012 | 2,106,146 | −3.0% |
| 2018 | 2,131,480 | +1.2% |
By the end of 2012, about 19.1% of Cuba's population lived in Havana. The city's population was 2,106,146. People in Havana live for about 76.81 years on average.
Havana's population grew quickly in the first half of the 20th century. It reached 1 million people by 1943. Since the 1980s, the city's population has grown slowly. This is due to balanced development, a low birth rate, and people moving abroad.
Ethnic Groups
According to the 2012 census, here's the breakdown of Havana's population by "skin color":
- White: 58.4% (mostly of Spanish background)
- Mestizo or Mulatto (mixed race): 26.4%
- Black: 15.2%
- Asian: 0.2%
There are not many mestizos in Havana or Cuba. This is different from many other Latin American countries. The native Taíno people almost disappeared early in the Spanish conquest due to diseases.
The Cuban government controls who can move into Havana. This is because the city is very crowded. It has almost 20% of the country's population. There are many internal migrants to Havana, often called "palestinos" (Palestinians). Most of these come from the eastern region of Oriente.
Havana has a notable minority of Chinese people. Most of their ancestors came from Canton in the mid-19th century. They were brought by Spanish settlers from the Philippines to work. After their contracts, many settled in Havana. Before the revolution, there were over 200,000 Chinese people. Today, about 100,000 people have Chinese ancestors. There are also about 3,000 Russians living in the city. Most are women married to Cubans who studied in the Soviet Union.
Religions
Roman Catholics are the largest religious group in Havana. Havana is one of three main Catholic areas on the island. Its patron saint is San Cristóbal (Saint Christopher). The main cathedral is dedicated to him. The city has also welcomed three popes: Pope John Paul II (1998), Pope Benedict XVI (2012), and Pope Francis (2015).
Havana's Jewish community became smaller after the Revolution. Before, it had over 15,000 Jews. Many had escaped Nazi persecution. After Castro took power in 1959, many left Cuba for Miami or Israel. The city once had five synagogues, but now only three remain. In 2007, the New York Times estimated about 1,500 known Jews lived in Havana.
Havana's Economy
Havana has a varied economy. It includes traditional areas like manufacturing, construction, and transportation. Newer areas like biotechnology and tourism are also growing.
The city's economy first grew because of its great location. This made it an early trade center in the New World. Sugar and the slave trade first brought wealth to the city. Later, after Cuba became independent, Havana became a famous resort. Even though the government tried to spread industry across the island, Havana remains the main industrial center.
The traditional sugar industry is mostly elsewhere on the island. But light manufacturing, food processing, and chemical factories are in Havana. Other important industries include shipbuilding, vehicle making, and alcoholic drinks like rum. Textiles and tobacco products, especially the famous Habanos cigars, are also key. Havana is still Cuba's main port. About 50% of Cuba's imports and exports go through Havana. The port also supports a large fishing industry.
In 2000, almost 89% of the city's workers were employed by government agencies or businesses. Havana generally has the highest incomes and human development in Cuba. After the Soviet Union collapsed, Cuba focused on tourism. Tourism is now Havana's and Cuba's main source of income.
Shops and Money
After the Revolution, Cuba's free-enterprise system changed. Most businesses in Havana are now run by the state.
In Old Havana and Vedado, there are small private businesses. These include shoe repair shops or places that make clothes. Banking is also controlled by the state. The National Bank of Cuba, located in Havana, manages Cuba's economy. Its branches often use buildings that were once private banks.
In the late 1990s, Vedado became the main business area. It grew a lot between 1930 and 1960. During that time, Havana was a major spot for U.S. tourists. Many tall hotels, casinos, restaurants, and fancy shops were built there. Many of these buildings show the Art Deco style.
Today, Vedado is Havana's financial district. Major banks, airline offices, shops, and many business headquarters are there. The University of Havana is also located in Vedado.
Tourism
Havana has always been a popular place for tourists. Between 1915 and 1930, it attracted more tourists than any other place in the Caribbean. This was largely because Cuba is close to the United States.
When Cuba – United States relations worsened and the U.S. put a trade embargo on the island in 1961, tourism dropped sharply. It did not return to old levels until 1989. The government did not want much tourism at first. But in 1982, Cuba allowed foreign investment.
This led to new companies that attracted foreign money for hotels. The number of tourists grew from 130,000 in 1980 to 326,000 by the end of that decade.
Havana has also been a popular place for health tourism for over 20 years. Foreign patients come to Cuba, especially Havana, for many treatments. These include eye-surgery and treatments for neurological problems like multiple sclerosis. Many patients are from Latin America.
Havana attracts over a million tourists each year. In 2010, 1,176,627 international tourists visited. This was a 20% increase from 2005.
Getting Around Havana
Airports
Havana is served by José Martí International Airport. This airport is about 11 kilometers (7 mi) south of the city center. It is the main hub for Cuba's national airline, Cubana de Aviación. The airport is Cuba's main gateway for international and domestic flights. It connects Havana to the rest of the Caribbean, North, Central, and South America, Europe, and one destination in Africa.
The city also has Playa Baracoa Airport. This is a smaller airport west of the city. It is used for some domestic flights, mainly by Aerogaviota.
Trains
Havana has a network of train lines for local, city-to-city, and long-distance travel. The railways are owned by the government and run by FFCC (Ferrocarriles de Cuba – Railways of Cuba). The FFCC connects Havana to all provinces in Cuba. The Havana Suburban Railway serves the city. The main train stations are Central Rail Station, La Coubre Rail Station, Casablanca Station, and Estación de Tulipán.
In 2004, about 11 million passengers used the trains. The busiest route is between Havana and Santiago de Cuba, which is about 836 kilometers (519 mi) away. In the 2010s, new Chinese and Russian-made coaches were added for long-distance and suburban trains.
In the 1980s, there were plans for a Metro system in Havana. It would have been similar to Moscow's Metro. Studies were well underway. The Cuban press even showed the project and its route. But with the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991, the project was stopped.
Interurban Trains
An interurban line, called the Hershey Electric Railway, was built in 1917. It runs from Casablanca (across the harbor from Old Havana) to Hershey and then to Matanzas.
Old Tram System
Havana had a tram system until 1952. It started as a horsecar system in 1858. It was later electrified in 1900. But fewer people used the trams, and the system went out of business in 1950. The remaining cars were sold to Matanzas in 1952.
Roads
The city has a large road network. It includes wide avenues, main streets, and major access roads. Examples are the Autopista Nacional (A1), Carretera Central, and Via Blanca. The road network has been growing since Spanish times. However, it needs a lot of repairs now. Major highways (Template:Controlled-access highway) include:
- A1 – Autopista Nacional, from Havana to Santa Clara and Sancti Spiritus.
- A4 – Autopista Este-Oeste, from Havana to Pinar del Río.
- Via Blanca, to Matanzas and Varadero.
- Havana ring road (Spanish: Primer anillo), which starts at a tunnel [es] under the entrance to Havana Harbor.
- Autopista del Mediodia, from Havana to San Antonio de los Baños.
- An autopista from Havana to Melena del Sur.
- An autopista from Havana to Mariel.
Learning in Havana
The national government is in charge of all education. There are good primary, secondary, and vocational schools across Cuba. Education is free and required at all levels except higher learning, which is also free.
The University of Havana, in the Vedado section, was founded in 1728. It was seen as a top university in the Western Hemisphere. After the Revolution, the university and all other schools became government-owned. Since then, other universities have opened. One is the Higher Learning Polytechnic Institute José Antonio Echeverría. Many Cuban engineers study there today.
The Cuban National Ballet School has 4,350 students. It is one of the largest and most respected ballet schools in the world.
Famous Places in Havana
- Habana Vieja: This is the original part of Havana. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Plaza Vieja: A square in Old Havana. It used to host events like executions, parades, and bullfights.
- Fortress San Carlos de la Cabaña: A large fortress on the east side of Havana bay. Its walls, built in the late 18th century, are very impressive.
- El Capitolio Nacional: Built in 1929, this huge building was once for the Senate and House of Representatives. Its dome stands out in the city. Inside is La Estatua de la República, the third largest indoor statue in the world. Today, it houses the Cuban Academy of Sciences and the National Museum of Natural History.
- El Morro Castle: A fortress guarding the entrance to Havana bay. It was built to protect the harbor from pirates.
- Fortress San Salvador de la Punta: A small fortress built in the 16th century at the western entrance to Havana harbor. It was important for Havana's defense. It has about twenty old guns and military items.
- Christ of Havana: Havana's 20-meter (66 ft) marble statue of Christ (1958). It overlooks the city from the east side of the bay.
- The Great Theatre of Havana: An opera house famous for the National Ballet of Cuba. It also hosts the National Opera. The main concert hall, García Lorca, is the biggest in Cuba.
- The Malecon/Sea wall: An avenue that runs along the city's north coast by the seawall. It is Havana's most popular avenue, known for its sunsets.
- Hotel Nacional de Cuba: An Art Deco hotel famous in the 1950s for gambling and entertainment.
- Museo de la Revolución: Located in the former Presidential Palace. The yacht Granma is on display behind the museum.
- Necrópolis Cristóbal Colón: A cemetery and outdoor museum. It is one of the most famous cemeteries in Latin America, known for its beauty. Built in 1876, it has nearly 1 million tombs.
Havana's Culture
City Symbols
Havana's coat of arms has three castles. These represent the three forts that defended the city: the Fuerza Castle, the Morro Castle, and the Punta Castle. The key means that Havana was the gateway to the New World. The shield is supported by an oak branch and a laurel wreath. The oak shows the nation's strength, and the laurel wreath means honor and glory. These symbols represent human rights.
Building Styles
Havana has many different building styles. These range from castles built in the 16th century to modern high-rise buildings. Many old buildings have fallen apart or been torn down since 1959. For example, the Plaza del Vapor, built in 1835, was demolished in 1959. Building collapses are not rare, causing injuries and deaths due to lack of care.
Spanish Style

Wealth came into and through Havana from Spain. This was because Havana was a key stop between the new world and old world. So, Havana became the most heavily fortified city in the Americas. Most early buildings are military forts. Examples include La Fortaleza de San Carlos de la Cabana (1558–1577) and the Castillo del Morro (1589–1630). These show the power and wealth of that time.
Old Havana was also protected by a defensive wall. It started in 1674 but was finished in 1767. By then, the city had already grown beyond its walls. This led to the new neighborhood of Centro Habana. Havana's Spanish buildings show influences from different styles and cultures. These include Mudéjar, Spanish, Italian, Greek, and Roman styles. The San Carlos and San Ambrosio Seminary (18th century) is a good example of early Spanish-influenced architecture. The Havana Cathedral (1748–1777) is a great example of Cuban Baroque style.
The Iglesia del Espíritu Santo was dedicated in 1638. It has notable paintings and catacombs. It is one of Havana's oldest churches. Its simple stone design is very beautiful. The church was rebuilt in 1648. In the Spanish era, it was very important. A special rule from 1772 meant that anyone seeking safety could find it there.
The Alameda de Paula was Cuba's first public walkway. It was designed in 1776. It had two rows of poplar trees and benches. It became an important social and cultural place in Havana. It was the model for the Paseo del Prado, designed in 1925. It was named Alameda de Paula because it was near the old Hospital and Iglesia of San Francisco de Paula. In 2000, the Havana promenade was restored and extended.
Towards the end of the 17th century, the hospital for women and the church of San Francisco de Paula began construction. These buildings were expanded in 1731. In 1776, it was Havana's most important hospital. Many famous doctors trained there. Both buildings were destroyed by a hurricane in 1730. They were rebuilt in 1745 in the Baroque style we see today.
Neoclassical Style
Neoclassicism came to Havana in the 1840s. At that time, gas streetlights and the railroad were introduced. In the late 18th century, sugar and coffee production grew fast. This helped shape Havana's most important architectural style. Many rich people in Havana were inspired by French styles. You can see this inside grand houses like the Aldama Palace, built in 1844. This is Cuba's most important neoclassical house. It shows the design of many homes from this time.
In 1925, Jean-Claude Nicolas Forestier, a city planner from Paris, moved to Havana. He worked with architects for five years. He wanted to balance the old buildings with the tropical landscape. He connected the city's roads and highlighted important landmarks. His ideas greatly influenced Havana. The peak of Neoclassicism was with the building of the Vedado district (started in 1859). This area has many well-designed neoclassical buildings.
The Palacio de Villalba was built in 1875. It was designed by Eugenio Rayneri y Sorrentino. Around 1880, the mansion was owned by the Count of Casa Moré. Later, it became a building with many apartments. In 1951, some parts were used for housing. The Spanish Center and the Israeli Center of Cuba were once located there.
The Palacio de Villalba is a strong example of Cuban Neoclassicism. Its design is similar to the Aldama Palace. But while Aldama Palace uses simple columns, Villalba Palace has more detailed Roman and Renaissance designs. The neoclassical style can also be seen in the window covers.
The Palacio de Aldama is a neoclassical mansion built in 1840. It is located in Havana, Cuba. Its main front, with columns, spans one block.
The Royal Palm Hotel is at the corner of San Rafael and Industria. It was first called "Edificio Luis. E. del Valle." It was named after the sugar owner who built it. Later, it was sold and became the famous Royal Palm Hotel. The shops on the ground floor are still there today. The building was restored in 2000.
Art Deco Style
The Bacardi Building (Edificio Bacardí) is a famous Havana landmark. It was designed by Esteban Rodríguez-Castells and Rafael Fernández Ruenes. It was finished in 1930. The building is in the Art Deco style, which was popular in the early 20th century. The Bacardi Building was built as the main office for the Bacardi Rum Company. The government took it over in the early 1960s. In 2001, an Italian company restored the building. Its inside still has the original marble and granite decorations. It is seen as one of the best Art Deco buildings in Latin America.
The López Serrano Building was designed by Ricardo Mira in 1929. It was the tallest residential building in Cuba until the FOCSA Building was built in 1956. The building was built for José Antonio López Serrano, a publisher.
Modernist Style
Modernist architecture changed much of Havana. Famous examples include the Havana Hilton Hotel (1958), the Radiocentro CMQ Building (1955), and the Edificio del Seguro Médico, Havana (1958).
Hotel Tryp Habana Libre is one of Cuba's larger hotels. It is in Vedado, Havana. The hotel has 572 rooms in a 25-floor tower. It opened in 1958 as the Habana Hilton. The hotel was famously where Fidel Castro and other revolutionaries stayed in 1959. The Habana Hilton cost $24 million to build. It was designed by Welton Becket with local architects Lin Arroyo and Gabriela Menéndez.
The Radiocentro CMQ Building was once a radio and television production center and office building. It is in El Vedado, Havana. It was inspired by Raymond Hood's 1933 Rockefeller Center in New York City. The theater opened on December 23, 1947. It was called Teatro Warner Radiocentro. Today, the building is the main office for the Cuban Institute of Radio and Television (ICRT).
The FOCSA Building is a residential block in the Vedado neighborhood. It was named after the construction company. The architects were Ernesto Gómez Sampera, Mercedes Diaz, and Martín Domínguez Esteban. The building was finished in 1956. It was designed to be like a small city within a city. It had 400 apartments, garages, a school, a supermarket, and a restaurant on the top floor. At the time, it was the tallest concrete building in the world without a steel frame.
The Edificio del Seguro Médico is a business building in El Vedado, Havana. It was built between 1955 and 1958. It was designed by Antonio Quintana Simonetti. It had apartments and offices for the National Medical Insurance Company.
City Layout
Modern Havana can be seen as three cities in one: Old Havana, Vedado, and the newer suburban areas. Old Havana has narrow streets and balconies. It is the traditional center for business, industry, and fun. It is also a residential area.
To the west, a newer part called Vedado has become a rival to Old Havana for business and nightlife. The Capitolio Nacional marks the start of Centro Habana. This is a working-class neighborhood between Vedado and Old Havana. Barrio Chino and the Real Fabrica de Tabacos Partagás, one of Cuba's oldest cigar factories, are in this area.
A third part of Havana includes the richer residential and industrial areas. These spread mostly to the west. Marianao is one of the newer parts of the city, from the 1920s. After the revolution, some fancy suburban homes became schools, hospitals, or government offices. Private country clubs became public recreation centers. Miramar, west of Vedado, is still Havana's exclusive area. It has mansions, foreign embassies, and shops for wealthy visitors. The International School of Havana is in Miramar.
In the 1980s, many parts of Old Havana began a big restoration project. This was to help Cubans appreciate their past and attract more tourists. With foreign help, large parts of Habana Vieja have been fixed up. Most major squares (Plaza Vieja, Plaza de la Catedral, Plaza de San Francisco, and Plaza de Armas) and main tourist streets are almost finished.
Art in Havana
The Museo Nacional de Bellas Artes de La Habana is a Fine Arts museum. It shows Cuban and international art. The museum has one of the largest collections of paintings and sculptures from Latin America. It is the biggest in the Caribbean. It is part of the Cuban Ministry of Culture. It has two locations near Havana's Paseo del Prado. One is for Cuban art, and the other is for art from around the world. It has over 45,000 art pieces. Since 1995, the Ludwig Foundation of Cuba has been in Vedado. It is a non-profit group that helps spread and protect Cuban art. Famous artists linked to Havana include Federico Beltrán Masses, Víctor Manuel García Valdés, and Wifredo Lam.
Performing Arts
Across from Havana's Central Park is the Baroque Gran Teatro de La Habana. This important theater was built in 1837. It is now home to the National Ballet of Cuba and the International Ballet Festival of Havana. The building's front has stone and marble statues. There are also sculptures by Giuseppe Moretti that show kindness, education, music, and theater. The main theater is the García Lorca Auditorium. It has 1,500 seats. Famous artists like the tenor Enrico Caruso and ballerina Anna Pavlova have performed there.
Alicia Alonso was a Cuban prima ballerina assoluta and choreographer. Her dance company became the Ballet Nacional de Cuba in 1955. Alonso was born near Havana in 1920. She is best known for her roles in Giselle and the ballet version of Carmen .
Radio and TV
CMQ
CMQ was a Cuban radio and television station in Havana. It was popular in the 1940s and 1950s. It offered music and news. It later grew into radio and television networks.
The company started on March 12, 1933. Ten years later, on August 1, 1943, Goar Mestre bought half of it. At first, it only broadcast in Havana. Later, it expanded across the country.
Cuba was one of the first Latin American countries to have television. In December 1946, station CM-21P did an experimental live broadcast.
Regular TV broadcasting began in October 1950. This was with Gaspar Pumarejo's Unión Radio TV. Then, Goar Mestre Espinosa's CMQ-TV started on channel 6 on December 18, 1950. CMQ officially launched on March 11, 1951. By 1954, CMQ-TV had seven stations. With the CMQ network, Cuba was the second country in the world, after the United States, to have a national TV network.
In the early 1950s, a popular TV show helped CMQ become the top station. On March 12, 1948, the radio studio moved to the Radiocentro building in El Vedado.
Festivals
Film Festival
The Havana Film Festival is a Cuban event that promotes Latin American filmmakers. It is also known as the International Festival of New Latin American Cinema of Havana. It takes place every December in Havana, Cuba.
The first festival was held on December 3, 1979. More than 600 film directors from Latin America attended. The Cuban Institute of the Cinematographic Art and Industry (ICAIC) started it.
The festival aims to bring Latin American filmmakers together. It also helps share their films, documentaries, and cartoons with the world. In 2013, Iván Giroud was reappointed as the festival's president. He had served before from 1994 to 2010.
Sports in Havana
Many Cubans love sports, especially baseball. Havana's team in the Cuban National Series is Industriales. It is one of the most successful teams in the league. In the past, Havana was also represented by other teams.
The city has several large sports stadiums. The biggest is the Estadio Latinoamericano, where Industriales plays. Entry to sports events is usually free. People also play games in neighborhoods across the city. Beach clubs offer water sports and have restaurants and dance halls.
- Havana hosted the 11th Pan American Games in 1991. New stadiums and facilities were built for this event.
- Havana hosted the 1992 IAAF World Cup in Athletics.
- Havana tried to host the 2008 Summer Olympics and 2012 Summer Olympics, but was not chosen.
- Havana hosted the Centrobasket basketball tournament three times: in 1969, 1989, and 1999.
Famous People from Havana
Sister Cities
See also
 In Spanish: La Habana para niños
In Spanish: La Habana para niños
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |