French Air and Space Force facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Air and Space Force |
|
|---|---|
| Armée de l'air et de l'espace | |
 |
|
| Founded |
|
| Country | |
| Type | Air and space force |
| Role | Aerial and space warfare |
| Size |
|
| Part of | French Armed Forces |
| Colours | |
| Engagements |
|
| Commanders | |
| Chief of the Armed Forces | President Emmanuel Macron |
| Chief of Staff of the French Air and Space Force | Général d'armée aérienne Stéphane Mille |
| Insignia | |
| Roundel |  |
| Fin flash |  |
| Aircraft flown | |
| Electronic warfare |
E-3 Sentry |
| Fighter | Rafale, Mirage 2000 |
| Helicopter | AS532 Cougar, Fennec, EC725 Caracal |
| Trainer | Alpha Jet, Pilatus PC-21, SOCATA TBM, Extra EA-300 |
| Transport | Lockheed C-130, Airbus A310, Airbus A330, Airbus A400M, Dassault Falcon 7X, Dassault Falcon 900, Dassault Falcon 2000, Transall C-160, Boeing C-135FR |
The French Air and Space Force (AAE), known in French as Armée de l'air et de l'espace, is France's military branch that operates in the sky and in space. It is a key part of the French Armed Forces.
It started in 1909 as a small part of the French Army. By 1934, it became its own independent military service. In 2020, its name changed to include "Space." This change shows its new focus on missions in outer space.
As of 2021, about 40,500 people work for the French Air and Space Force. They use a variety of aircraft, including fighter jets and transport planes.
The leader of the French Air and Space Force is called the Chief of Staff. This person reports to the Chief of the Defence Staff, who then answers to the civilian Minister of the Armed Forces.
Contents
History of French Airpower
Early Days of Flight
Starting the Air Service
The French Air Service, called Service Aéronautique, began in 1909. This was when the French War Minister bought the first airplane, a Wright Biplane. More planes, like a Bleriot and two Farmans, were added the next year.
By 1910, General Pierre Roques was put in charge of this new "Fifth Service." In 1912, France officially created its air arm. It planned to have three types of aircraft: for scouting, bombing, and fighting other planes.
Inventing the Fighter Plane
France was one of the first countries to build aircraft. At the start of World War I in 1914, France had 148 planes and 15 airships. These planes were used to help ground forces.
During the war, pilots tried to use light weapons against enemy planes. Roland Garros found a way to shoot a machine gun through his plane's propeller. This was a big step in making fighter planes. Later, Anthony Fokker improved this idea with a special gear. This gear allowed machine guns to fire without hitting the propeller.

Forming Fighter Groups
In 1916, during the Verdun Offensive, new ways of fighting were needed. A skilled pilot named Charles de Tricornet de Rose created a special unit. This unit's job was to stop German planes from flying over French lines.
This group, called Groupement de Chasse, was very successful. Famous pilots like Georges Guynemer started their careers here. After this success, France created more large fighter groups. These groups helped in major battles like the Battle of the Somme.
Bringing Airpower Together
As the war continued, France kept bringing more airpower together. By 1918, they had formed large units called Escadres de Combat. Each escadre had many fighter planes.
Later, these escadres were combined into an even bigger unit called the Division Aerienne. This division also included bombing planes and escort planes. This showed how France was becoming very strong in the air.
The Division Aerienne fought in major battles, like the Second Battle of the Marne. By the end of World War I in November 1918, France had 3,608 planes. French airmen had destroyed many enemy planes and balloons. However, many French pilots and observers also lost their lives.
Between the World Wars
After World War I, France continued to develop its air force. In 1922, military aviation became a "special arm" of the French Army. It was not until July 2, 1934, that it became a fully independent military branch.
During this time, the French Air Force also started its first paratrooper units. These units would later become the special forces known as the Air Parachute Commandos. The Air Force also kept a presence in France's colonies around the world.
World War II and Beyond
The French Air Force played a role in World War II, especially during the Battle of France in 1940. After the war, France rebuilt its aircraft industry.
Since 1945, the French Air Force has been involved in several conflicts. These include the First Indochina War and the Algerian War. It has also participated in operations in the Persian Gulf, Afghanistan, Mali, and Iraq.
From 1964 to 1971, the French Air Force was responsible for France's nuclear weapons. This included using Dassault Mirage IV bombers and ballistic missiles.

After 1962, France focused more on nuclear defense. This led to big changes in the Air Force's structure. New commands were created, like the Strategic Air Forces Command. The Dassault Mirage IV was a key plane for nuclear strikes.
In 1994, the special forces unit called Fusiliers Commandos de l'Air was restarted.

The French Air Force began replacing older planes with newer ones. The Airbus A400M transport aircraft and the Dassault Rafale fighter jet were introduced. The first Rafale squadron became ready for action in 2006.
In 2009, France rejoined the NATO Military Command Structure. France played a big role in the no-fly zone over Libya in 2011. In 2014, the last Dassault Mirage F1 planes were retired and replaced by Rafales.
On July 13, 2019, President Emmanuel Macron announced a new space command. This command would be part of the French Air Force. This led to the Air Force changing its name to the French Air and Space Force. This change shows its new focus on space defense. The new name became official on July 24, 2020.
How the Air and Space Force is Organized
The Chief of Staff of the French Air and Space Force (CEMAAE) leads the service. This person decides how the Air and Space Force operates. They also advise the Chief of the Defence Staff on how to use the Air and Space Force.
The Air and Space Force is divided into several main parts. These include the headquarters, different forces, air bases, and human resources. The main headquarters are in Paris, at the Balard armed forces complex.
Main Commands
The French Air and Space Force has several important commands:
- The Commandement de la Défense Aérienne et des Opérations Aériennes (CDAOA) handles air defense and operations. It watches French airspace and manages all ongoing air missions.
- The Strategic Air Forces Command (CFAS) is in charge of France's nuclear strike units. It also manages tanker and strategic transport aircraft.
- The Air Forces Command (CFA) prepares units for their missions. It includes brigades for fighters, transport, airspace control, and special forces.
- The French Space Command (CDE) focuses on space operations. It manages space surveillance and control. This command was added in 2019, leading to the name change of the Air Force.
Wings, Squadrons, and Flights
A Wing (called Escadre in French) is a large group of units. It usually has different types of aircraft or units that do similar missions. Wings were brought back in 2014 to improve how aircraft maintenance and flying units work together.
A Squadron (Escadron) is a basic operational unit. It usually has about twenty aircraft for fighter squadrons. Transport squadrons might have fewer, especially for larger planes.
A Flight (Escadrille) is a smaller unit within a squadron. Pilots are assigned to flights, but equipment is managed at the squadron level. Many flights keep the traditions and names of famous units from World War I.
Special Forces
The Fusiliers Commandos de l'Air are the special forces of the French Air and Space Force. They include:
- Protection squadrons: These units guard air bases both in France and abroad.
- Air Parachute Commandos (CPA 10, CPA 20, CPA 30): These are special operations units. They can intervene quickly and strengthen security at important air locations.
Air Bases
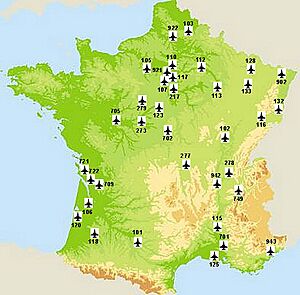
The French Air and Space Force uses a network of air bases. These bases are where planes take off, land, and are maintained. They also house staff, control centers, and training schools.
Some important air bases in France include:
- BA 105 Évreux-Fauville Air Base: Focuses on command, support, and air transport.
- BA 113 Saint-Dizier – Robinson Air Base: Home to Rafale fighter jets.
- BA 123 Orléans – Bricy Air Base: A major air transport hub with Airbus A400M Atlas and Lockheed C-130 Hercules planes.
- BA 702 Avord Air Base: Important for nuclear strike support and AWACS planes.
- BA 118 Mont-de-Marsan Air Base: Another home for Rafale jets and a test center.
- BA 125 Istres-Le Tubé Air Base: Used for inflight refueling and as a test center.

The French Air and Space Force also has bases overseas. These include locations in Senegal, Djibouti, French Guiana, and Abu Dhabi. Many air bases have closed since 2009 as the force has become more efficient. An air base commander is in charge of all units at their base.
Aircraft and Equipment
Aircraft


| Aircraft | Origin | Type | Introduced | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combat Aircraft | |||||
| Dassault Rafale B/C | France | Multirole fighter | 2006 | 100 | This fighter jet can do many different jobs. More Rafale jets are on order. |
| Dassault Mirage 2000D | France | Fighter-bomber | 1995 | 66 | These planes are being updated to a newer version. |
| Dassault Mirage 2000-5F | France | Multirole fighter | 1993 | 26 | |
| AWACS | |||||
| Boeing E-3F Sentry | United States | AEW&C | 1990 | 4 | These planes act as flying radar stations. They help control air battles. |
| Reconnaissance | |||||
| Dassault Falcon Archange | France | SIGINT / ELINT / EW | TBD | 0 | This new plane will collect electronic information. It is still being developed. |
| ASLR VADOR | United States | ISTAR / SIGINT | 2022 | 2 | These planes gather intelligence using various sensors. |
| Tanker | |||||
| Airbus A330 MRTT Phénix | Europe | Aerial refueling / Airborne command and control node / Transport | 2018 | 12 | These planes refuel other aircraft in the air. They can also carry troops and cargo. |
| Lockheed KC-130J | United States | Aerial refueling / Transport | 2019 | 2 | |
| Boeing C135FR/KC135 | United States | Aerial refueling | 1964 | 11 | These older tankers are being replaced by the A330 MRTT. |
| Transport | |||||
| Airbus A400M Atlas | Europe | Tactical airlifter with strategic capabilities | 2013 | 22 | These large planes carry heavy equipment and troops. |
| Lockheed C-130J Super Hercules | United States | Tactical airlifter | 2018 | 2 | |
| Lockheed C-130 Hercules | United States | Tactical airlifter | 1987 | 14 | These planes are used for carrying cargo and troops. |
| CASA CN235 | Spain | Tactical airlifter | 1993 | 27 | |
| Airbus A330-200 | Europe | VIP transport | 2010
2020 |
4 | One is the main plane for the French President. |
| Dassault Falcon 7X | France | VIP transport | 2009 | 2 | Part of the presidential fleet. |
| Dassault Falcon 2000EX/LX | France | VIP transport | 2011 | 2 | Part of the presidential fleet. |
| Dassault Falcon 900 | France | VIP transport | 1991 | 2 | Part of the presidential fleet. |
| Socata TBM 700 | France | Liaison aircraft | 1990 | 15 | |
| DHC-6 Twin Otter | Canada | Liaison aircraft | 1978 | 5 | |
| Helicopter | |||||
| Airbus Helicopters H225M Caracal | Europe | Transport / CSAR helicopter | 2006 | 10 | These helicopters are used for transport and rescuing people in combat. |
| Airbus Helicopters H225 | Europe | Transport / SAR helicopter | 2016 | 2 | Used for transport and search and rescue missions. |
| Airbus Helicopters H215 Super Puma | France | VIP transport helicopter | 1984 | 3 | Used for transporting important people like the President. |
| Aérospatiale SA330 Puma | France | Medium utility helicopter | 1974 | 18 | These are being replaced by newer helicopters. |
| Eurocopter AS555 Fennec | Europe | Light utility helicopter | 1990 | 40 | These will be replaced by the Airbus Helicopters H160M Guépard. |
| Airbus Helicopters H160M Guépard | Europe | Medium multirole helicopter | TBD | 0 | A new helicopter planned for the Air and Space Force. |
| Trainer aircraft | |||||
| Dassault Mirage 2000B-S5 | France | Conversion trainer | 1993 | 7 | Used to train pilots for the Mirage 2000. |
| Pilatus PC-21 | Switzerland | Advanced trainer | 2018 | 17 | These planes replaced the Alpha Jet for advanced pilot training. |
| Embraer EMB 121 Xingu | Brazil | Multi-engine trainer | 1982 | 22 | |
| Beechcraft Super King Air 350 Extended Range | United States | Multi-engine trainer / Navigation trainer | 2020 | 1 | Used for training pilots. |
| Grob 120A-F | Germany | Basic trainer | 2007 | 18 | Used for basic flight training. |
| Cirrus SR20 | United States | Ab initio trainer | 2013 | 16 | Used for initial flight training. |
| Cirrus SR22 | United States | Ab initio trainer | 2013 | 9 | Used for initial flight training. |
| Diamond HK36 Super Dimona | Austria | Motor glider | 2010 | 5 | |
| Airbus Helicopters H225M Caracal | Europe | Rotorcraft trainer | 2006 | 1 | Used to train helicopter pilots. |
| Dassault/Dornier Alpha Jet | France Germany |
Aerobatic display | 1978 | 18 | These jets are used by the Patrouille de France for air shows. |
| Extra EA-300 | Germany | Aerobatic display | 2005 | 3 | |
| UAVs | |||||
| General Atomics MQ-9 Reaper | United States | ISTAR / UCAV | 2013 | 12 | These are drones used for intelligence and combat. |
Satellites
| Name | Origin | Type | Introduced | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airbus Defence and Space / Thales Alenia Space
CSO |
France | Earth observation constellation | 2018 | 2 satellites | These satellites take pictures of Earth for intelligence. |
| Airbus Defence and Space
Pléiades Neo |
France | Earth observation constellation | 2021 | 2 satellites | These are newer satellites for observing Earth. |
| Airbus Defence and Space
Pléaides |
France | Earth observation constellation | 2011 | 2 satellites | These satellites are still working and observing Earth. |
| Airbus Defence and Space
Helios 2 |
France | Earth observation constellation | 2004 | 2 satellites | These satellites are also used for Earth observation. |
| Airbus Defence and Space / Thales Alenia Space
CERES |
France | Electromagnetic intelligence constellation | 2021 | 3 satellites | These satellites collect electronic signals for intelligence. |
| Thales Alenia Space / Airbus Defence and Space
Syracuse IV |
France | Telecommunication satellite constellation | 2021 | 2 satellites | These satellites provide secure communication for the military. |
| Thales Alenia Space
Syracuse III |
France | Telecommunication satellite constellation | 2005 | 2 satellites | Older communication satellites that are still in use. |
| Thales Alenia Space
Sicral 2 |
France Italy |
Telecommunication satellite | 2015 | 1 satellite | This satellite helps with military communications. |
| Thales Alenia Space
Athena-Fidus |
France Italy |
Telecommunication satellite | 2014 | 1 satellite | Another satellite for military communications. |
| Galileo | Europe | Global navigation satellite system | 2011 | 24 satellites | This system provides navigation services, like GPS. |
Air Defense Systems
| Name | Origin | Type | Introduced | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eurosam SAMP/T Mamba | France Italy |
High to Medium Air Defense system | 2011 | 8 batteries | This system protects against aircraft and missiles from medium to high altitudes. |
| Thales Crotale NG | France | Short Range Air Defense system | 1990 | 8-10 units | This system protects against threats at shorter distances. |
| Thales/CS Group PARADE | France | Modular counter-drone platform | 2023 | Unknown | This system is designed to detect and stop enemy drones. |
| MC2 Technologies NEROD F5 | France | Man-portable anti-drone jamming system | 2020 | Unknown | This device can block signals used by drones, making them unable to fly. |
Personnel
The French Air and Space Force has about 40,500 military members. They include officers, non-commissioned officers, and air military technicians. There are also civilians who work for the force.
People in the Air and Space Force have many different jobs. Some are pilots, flying the aircraft. Others are mechanics who keep the planes working. There are also air traffic controllers, meteorologists, and special forces members.
Training for Personnel

Officers in the French Air and Space Force get their training at special schools. These include the Air School (École de l'air) and the Military Air School. There are also specific schools for piloting, transport aviation, and fighter pilot training.
Non-commissioned officers (like sergeants) train at the EFSOAA school in Rochefort. Air military technicians also receive special training. Air traffic controllers learn their skills at the Instruction Control and Air Defense Center.
Ranks
Officers
| NATO code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) | Student officer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
  |
  |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Général d´armée aérienne | Général de corps aérien | Général de division aérienne | Général de brigade aérienne | Colonel | Lieutenant-colonel | Commandant | Capitaine | Lieutenant | Sous-lieutenant | Aspirant | Élève-officier | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Student Ranks
Enlisted Personnel
| NATO code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Major | Adjudant-chef | Adjudant | Sergent-chef | Sergent | Caporal-chef | Caporal | Aviateur 1e classe | Aviateur 2e classe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
 In Spanish: Ejército del Aire y del Espacio (Francia) para niños
In Spanish: Ejército del Aire y del Espacio (Francia) para niños
- List of Escadres of the French Air Force
- List of French Air and Space Force aircraft squadrons
- French Naval Aviation
- List of military aircraft of France