Carob facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Carob |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Carob pods on the tree | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Ceratonia |
| Species: |
C. siliqua
|
| Binomial name | |
| Ceratonia siliqua |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The carob (KERR-əb; Ceratonia siliqua) is an evergreen flowering tree or shrub. It belongs to the legume family, Fabaceae. People grow carob trees for their tasty pods. They also plant them as pretty trees in gardens.
Carob trees originally come from the Mediterranean area and the Middle East. Today, Portugal grows the most carob. Italy and Morocco are also big producers.
In the past, especially in the Mediterranean, carob pods were mainly used to feed animals. During tough times, like when food was scarce, people also ate them. The ripe, dried pods are often ground into carob powder. In the 1970s, this powder was sometimes used instead of cocoa powder. Carob powder and chips can still be used as a chocolate alternative in many recipes.
Contents
What Does a Carob Tree Look Like?
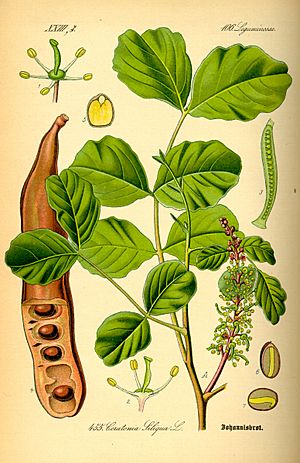
A carob tree can grow up to 50 feet (15 meters) tall. It has a wide, round top. The trunk is thick with rough brown bark. Its branches are strong.
The leaves are about 4 to 8 inches (10 to 20 cm) long. They grow in an alternating pattern. Each leaf has several smaller leaflets. Carob trees can handle cold weather down to about 19°F (–7°C).
Flowers and Fruit of the Carob Tree
Most carob trees have separate male and female plants. Some trees have both male and female parts (hermaphroditic). Only female or hermaphroditic trees produce fruit.
The flowers are small and grow in clusters in the autumn. They grow on older wood and even on the trunk. Both wind and insects help pollinate the flowers.
The fruit is a long, flat legume or pod. It can be straight or curved. The pods take a full year to grow and ripen. When the sweet, ripe pods fall, animals like pigs eat them. This helps spread the hard inner seeds.
Where Did the Name "Carob" Come From?
The word "carob" comes from an old French word, carobe. This word came from the Arabic word kharrūb, which means "locust bean pod." The scientific name for the carob tree, Ceratonia siliqua, comes from Greek and Latin. Kerátiοn means "fruit of the carob" (like a horn), and siliqua means "pod."
In English, carob is also called "St. John's bread." This is because some people believe the pods were the "locusts" that St. John the Baptist ate in the desert. It's also called "locust tree," but don't confuse it with the African locust bean tree.
The word "carat" also comes from the carob seed. A carat is a unit of mass used for gemstones. It also measures the purity of gold. The Greek word for a carob seed was keration.
Where Do Carob Trees Grow?
Carob trees are grown in many places. They can also be found growing wild in the eastern Mediterranean region. They have spread and become naturalized in the west.
You can find many carob trees in the southern Portuguese region of the Algarve. There, the tree is called alfarrobeira, and the fruit is alfarroba. They also grow in southern and eastern Spain, Malta, and the Italian islands of Sicily and Sardinia. Other places include Southern Croatia, eastern Bulgaria, Southern Greece, Cyprus, and Israel. In Turkey, it's known as "goat's horn."
Some trees in Latin America are also called algarrobo. These trees produce sweet pods like carob. However, they belong to a different plant family. Early Spanish settlers named them algarrobo because of their similar pods.
How Carob Trees Grow and Are Harvested
The carob tree grows well in warm and subtropical areas. It can handle hot and humid coastal regions. Carob is a drought-resistant plant. This means it is well-suited to the Mediterranean climate, which gets only about 10 to 20 inches (250 to 500 mm) of rain each year.
Carob trees can survive long dry periods. But to produce fruit, they need about 20 to 22 inches (500 to 550 mm) of rain per year. They prefer sandy soils that drain well. They don't like too much water. Their deep root systems can grow in many different soil types. They can also handle some salt in the soil.
Planting and Care
It's hard to grow new carob trees from cuttings. So, people usually grow them from seeds. Seeds are planted in pots in early spring. The young plants are then moved to the field after the last frost.
Carob trees take a while to start producing fruit. In good growing areas, they might start after 3–4 years. But in poorer soils, it can take up to 8 years. Trees produce the most fruit when they are 20–25 years old. Carob orchards usually have 25–45 trees per hectare. Male trees, which don't produce fruit, are planted in smaller numbers to help with pollination.
Farmers often grow other trees alongside carob trees. Carob trees don't need much care. They only need light trimming and occasional weeding. Adding nitrogen fertilizer can help them produce more fruit. Even though they are drought-tolerant, watering them two or three times in summer helps them grow faster and yield more fruit.
Harvesting Carob Pods
Harvesting carob pods takes a lot of work. Workers often use long sticks to knock the fruit down. Nets are spread on the ground to catch the falling pods. This job is tricky because the trees are also flowering for the next year's crop. Workers must be careful not to damage the new flowers.
After harvest, carob pods have some moisture. They need to be dried to about 8% moisture. This stops them from rotting. Next, the seeds are separated from the pulp. This process is called kibbling. It creates seeds and pieces of carob pods (kibbles). The pulp can be ground for animal feed or roasted and milled for human food. The seeds are peeled, then the inner parts are separated for different uses.
Pests and Diseases
Carob orchards usually don't have many serious pest problems. So, farmers don't often use pesticides. Some common pests, like leopard moth larvae or dried fruit moths, can sometimes cause damage. Small rodents like rats can also be a problem.
One pest that specifically targets carob is the carob moth. Its larvae can cause a lot of damage after the pods are harvested. Scientists are studying this moth to find ways to control it, like using temperature control or special traps.
| Carob production – 2017 | |
|---|---|
| Country | (tonnes) |
| 41,909 | |
| 28,910 | |
| 21,983 | |
| 15,016 | |
| 12,528 | |
| World | 136,540 |
| – FAO estimate Source: UN Food and Agriculture Organization |
|
In 2017, the world produced 136,540 tonnes of carob. Portugal was the top producer, making 30% of the world's total. Italy, Morocco, Turkey, Greece, Spain, and Cyprus were also major producers.
What Are Carob Pods Used For?
Carob pods are used in many ways, especially in food. The dried pods have two main parts: the pulp (90%) and the seeds (10%). Carob pulp is sold as flour or in "chunks." The flour from the carob seed can also be used for food.
Carob pods are naturally sweet, with about one-third to half their dry weight being sugar. They are used in powdered, chip, or syrup form in cakes and cookies. They are often used as a chocolate substitute because of their similar color, texture, and taste. In Malta, a traditional sweet called karamelli tal-harrub is made from carob pods. It's eaten during Christian holidays like Lent and Good Friday. Dried carob fruit is also eaten on the Jewish holiday of Tu Bishvat.
Carob Powder
Carob powder is made by roasting and then finely grinding the carob pod pulp. It's a popular ingredient in many recipes.
Locust Bean Gum (LBG)
One of the most important uses of carob seeds is to make locust bean gum (LBG). This is a thickening agent used in the food industry. LBG helps make foods thicker and more stable. It can also replace fat in low-calorie products or be used instead of gluten.
To make 1 kilogram (2.2 pounds) of LBG, you need about 3 kilograms (6.6 pounds) of carob seeds. These seeds come from about 30 kilograms (66 pounds) of carob pods. LBG comes from the endosperm of the seed, which is rich in substances called galactomannans. These substances absorb water and swell. When mixed with other gelling agents, LBG can thicken the liquid part of food. This is why it's used in canned food for animals to create a "jellied" texture.
Carob for Animals
Unlike chocolate, carob does not contain theobromine, a chemical that can be harmful to some mammals. It also has no caffeine. Because of this, carob is sometimes used to make chocolate-like treats for dogs. Carob pod meal is also used as an energy-rich feed for livestock, especially for ruminants like cows.
Historically, carob pods were mainly used as animal feed in the Maltese Islands. During times of famine or war, they became part of the diet for many Maltese people. In Spain and Portugal, carob pods were traditionally fed to donkeys.
Carob Syrup and Drinks
Carob pods are very sweet. Their sugar can be extracted to make a syrup. In Malta, a carob syrup called ġulepp tal-ħarrub is made from the pods. Carob syrup is also used in Crete and exported from Cyprus.
In Palestine, crushed carob pods are heated to caramelize their sugar. Then water is added and boiled. The result is a cold drink called kharrub, sold by juice shops and street vendors, especially in summer.
Carob is also used to make compote, liqueur, and syrup in Turkey, Malta, Portugal, Spain, and Sicily. In Libya, carob syrup (called rub) is used with a dish called asida. In Yemen, people use carob pods as a juice to help lower blood sugar levels, following traditional medicine.
Carob as an Ornamental Plant

The carob tree is very popular in the plant nursery industry. It's grown as an ornamental plant for Mediterranean climates and other temperate regions around the world. It's especially liked in California and Hawaii. As it grows, the carob tree develops a unique, sculpted trunk. It can be shaped into a beautiful ornamental tree or used as a thick, large screening hedge.
The plant is very drought tolerant. This means it doesn't need much water, especially if you don't care about getting a big fruit harvest. So, it's great for xeriscape landscape design in gardens, parks, and public areas.
Carob Wood
In some parts of Greece, like Crete, carob wood is often used as firewood. It burns so well that it's sometimes preferred over oak or olive wood.
Carob wood is rarely used for building because its stem often has internal rot. However, it is sometimes used for decorative items, especially furniture. The natural shape of the trunk works well for this. Also, the wood's very wavy grain makes it super strong and resistant to splitting. Because of this, sections of carob bole are good for chopping blocks.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Algarrobo para niños
In Spanish: Algarrobo para niños
 | William Lucy |
 | Charles Hayes |
 | Cleveland Robinson |