Geography of New York City facts for kids

The geography of New York City is all about its special location. It sits right where the Hudson River meets the Atlantic Ocean, forming a naturally protected harbor. Because there isn't much land available, New York is the most crowded major city in the United States. This high population density also means New York is very energy-efficient and relies less on cars than many other U.S. cities. The city has a mild climate.
Contents
New York City's Location and Land
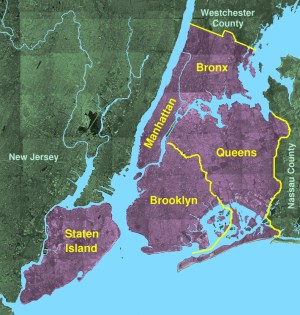
New York City is on the coast of the Northeastern United States. It's at the mouth of the Hudson River in southeastern New York state. The city is part of the New York–New Jersey Harbor Estuary. The New York Harbor is key to this area. Its deep waters and safe bays helped New York become a major trading city.
Most of New York City is built on three islands: Manhattan, Staten Island, and western Long Island. This makes land scarce and leads to a very high population. The Hudson River flows into New York Bay. It becomes a tidal estuary, which is like a river where ocean tides can flow in and out. This estuary separates the Bronx and Manhattan from Northern New Jersey. The Harlem River is another tidal waterway. It flows between the East and Hudson Rivers, separating Manhattan from the Bronx.
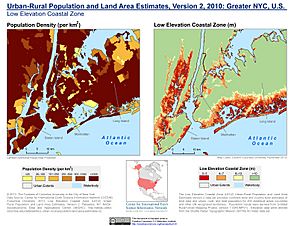
People have changed the city's land a lot over time. They have created new land along the waterfronts, especially since Dutch colonial times. This is called land reclamation. A good example is Battery Park City in Lower Manhattan. Many natural hills and valleys have also been flattened, especially in Manhattan. The West Side of Manhattan still has some hills, especially in Upper Manhattan. The East Side is much flatter, though Duffy's Hill in East Harlem is a notable exception.
The city's land area is about 304.8 square miles (789.4 km2). Sometimes, people compare the size of Icebergs to the area of Manhattan.
The highest natural point in New York City is Todt Hill on Staten Island. It is 409.8 ft (124.9 m) above sea level. This makes it the highest hill on the Eastern Seaboard south of Maine. The top of the hill is mostly covered with trees. It is part of the Staten Island Greenbelt. Many spots are called the geographic center of the city. One is a plaque in the middle of Queens Boulevard and 58th Street in Woodside, Queens.
How New York City's Land Was Formed
The different parts of New York City sit on the edge of two major geologic regions of eastern North America. Brooklyn and Queens, which are on Long Island, are part of the eastern coastal plain. Long Island itself is a huge pile of rocks and dirt called a moraine. This moraine formed at the southern edge of the Laurentide Ice Sheet during the last ice age.
The Bronx and Manhattan are on the eastern edge of the Newark Basin. This is a part of the Earth's crust that sank down. This happened when the supercontinent Pangaea broke apart during the Triassic period. The Palisades Sill on the New Jersey side of the Hudson River shows ancient, melted rock that filled this basin.
The solid rock layer under much of Manhattan is called Manhattan schist. This is a very strong metamorphic rock. It formed when Pangaea came together. This strong rock is perfect for building the foundations of tall buildings. You can see outcrops of Manhattan schist in Central Park. Rat Rock is a large example.
The bedrock under Manhattan is closer to the surface near Midtown Manhattan. It then dips lower between 29th Street and Canal Street. After that, it rises closer to the surface again in Lower Manhattan. People used to think that the depth of this bedrock was the main reason why skyscrapers are clustered in Midtown and the Financial District. However, studies have shown that economic reasons played a bigger role in where these tall buildings were built.
Scientists have also looked at the risk of earthquakes. In 2014, the United States Geological Survey found a "slightly lower hazard for tall buildings" than they thought before. This means there's a lower chance of slow shaking near New York City. This type of shaking would be more likely to damage very tall buildings during an earthquake.
Neighboring Counties
New York City shares borders with counties in two states:
New York:
New Jersey:
New York City's Five Boroughs
New York City is made up of five boroughs. This is a special way the city organizes its five counties. Inside these boroughs, there are hundreds of unique neighborhoods. Many of them have their own history and character. If each borough were its own city, four of them (Brooklyn, Queens, Manhattan, and the Bronx) would be among the ten largest cities in the United States by population!
- The Bronx (Bronx County, pop. 1,364,566) is the northernmost borough of New York City. It is famous as the birthplace of rap and hip hop culture. It's also home to Yankee Stadium. The Bronx is the only part of the city that is on the North American mainland, except for a small piece of Manhattan called Marble Hill.
- Brooklyn (Kings County, pop. 2,511,408) is the city's most populated borough. It used to be its own city until 1898. Brooklyn is known for its many different cultures, a lively independent art scene, and distinct neighborhoods. It also has a long beach and Coney Island, which is famous as one of the country's first amusement parks.
- Manhattan (New York County, pop. 1,606,275) is the most densely populated borough. It has most of the city's skyscrapers. This borough holds the city's main business areas and many cultural attractions. Manhattan is generally divided into downtown, midtown, and uptown areas.
- Queens (Queens County, pop. 2,256,576) is the largest borough by land area. It is also the most ethnically diverse county in the United States. Queens was once a group of small towns founded by the Dutch. Today, it is mostly residential and middle class. It is the only large county in the U.S. where the average income for African-American families is higher than for Caucasian families. Queens is home to Citi Field, where the New York Mets play. It also hosts the annual US Tennis Open.
- Staten Island (Richmond County, pop. 475,014) feels the most like a suburb among the five boroughs. It is connected to Brooklyn by the Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge. You can get to Manhattan by taking the free Staten Island Ferry. Until 2001, the borough was home to the Fresh Kills Landfill, which was once the world's largest landfill. Now, it is being turned into Freshkills Park, one of the biggest urban parks in the United States.
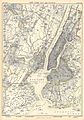
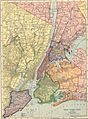
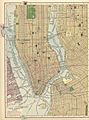
Maps and Satellite Images
-
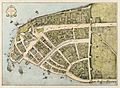
New Amsterdam in 1660
See also
- Climate change in New York City
- Geography of New York–New Jersey Harbor Estuary
- New York metropolitan area
- Northeast megalopolis
- New York City Audubon
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |