Limpopo facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
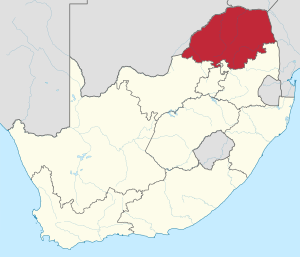
Limpopo
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Motto(s):
Peace, Unity and Prosperity
|
||
Location of Limpopo in South Africa
|
||
| Country | South Africa | |
| Established | 27 April 1994 | |
| Capital | Polokwane Lebowakgomo (legislative) |
|
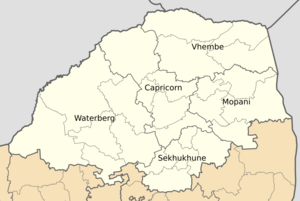
| Districts |
List
Mopani
Vhembe Capricorn Waterberg Sekhukhune |
|
| Government | ||
| • Type | Parliamentary system | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 125,754 km2 (48,554 sq mi) | |
| Area rank | 5th in South Africa | |
| Highest elevation | 2,126 m (6,975 ft) | |
| Population | ||
| • Total | 5,404,868 | |
| • Rank | 5th in South Africa | |
| • Density | 42.97969/km2 (111.3169/sq mi) | |
| • Density rank | 5th in South Africa | |
| Population groups | ||
| • Black | 96.5% | |
| • White | 2.5% | |
| • Indian or Asian | 0.5% | |
| • Coloured | 0.3% | |
| • Other | 0.1% | |
| Languages | ||
| • Pedi | 52.9% | |
| • Tsonga | 24.0% | |
| • Venda | 16.7% | |
| • Afrikaans | 2.6% | |
| • Tswana | 2.0% | |
| • Southern Ndebele | 2.0% | |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (SAST) | |
| ISO 3166 code | ZA-LP | |
| HDI (2019) | 0.710 high · 3rd of 9 |
|
| GDP | US$31.3 billion | |
| Website | www.limpopo.gov.za | |
| Zulu | iLimpopo |
|---|---|
| Xhosa | iLimpopo |
| Afrikaans | Limpopo |
| Sepedi | Limpopo |
| Setswana | Limpopo |
| Xitsonga | Limpopo |
| Venda | Limpopo |
Limpopo is the northernmost province of South Africa. It is named after the Limpopo River. This river forms the province's western and northern borders. The capital city is Polokwane, which is also the largest city. The provincial government's law-making body is in Lebowakgomo.
Limpopo was formed from parts of three former homelands: Lebowa, Gazankulu, and Venda. It also included a part of the old Transvaal province. Limpopo became one of South Africa's nine new provinces. This happened after the country's first democratic election on 27 April 1994. The province was first called "Northern Transvaal". Then, on 28 June 1995, its name changed to "Northern Province". In 2002, it was renamed "Limpopo Province". The main ethnic groups living here are the Pedi, the Tsonga, and the Venda.
Traditional leaders and chiefs play an important role in the province. The Limpopo House of Traditional Leaders was set up in 2005. Its main job is to advise the government on local customs and traditions. They also help with development plans for rural communities.
Contents
Exploring Limpopo's Geography and Borders
Limpopo Province shares borders with three other countries. To the west and northwest, it borders Botswana. To the north and northeast, it borders Zimbabwe. To the east, it borders Mozambique. Limpopo is a key link between South Africa and other countries in sub-Saharan Africa.
On its southern side, Limpopo borders three other South African provinces. These are Mpumalanga, Gauteng, and North West. The border with Gauteng includes the busy Johannesburg-Pretoria area. This is the most industrialised part of Africa. Limpopo is important for trade within the region and internationally.
A large part of Limpopo is covered by the Waterberg Biosphere. This is a mountain area of about 15,000 square kilometres. It was the first place in northern South Africa to be named a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve.
Understanding Limpopo's Municipalities
Limpopo Province is divided into five main areas called district municipalities. Each district municipality is then divided into smaller areas called local municipalities. There are 25 local municipalities in total.
Limpopo's District Municipalities
- Capricorn District
- Blouberg
- Lepele-Nkumpi
- Molemole
- Polokwane
- Mopani District
- Ba-Phalaborwa
- Greater Giyani
- Greater Letaba
- Greater Tzaneen
- Maruleng
- Sekhukhune District
- Elias Motsoaledi
- Ephraim Mogale
- Fetakgomo Tubatse
- Makhuduthamaga
- Vhembe District
- Makhado
- Musina
- Collins Chabane
- Thulamela
- Waterberg District
- Bela-Bela
- Lephalale
- Modimolle–Mookgophong
- Mogalakwena
- Thabazimbi
Limpopo's Economy and Resources
Limpopo has a population of over 6 million people. The province has a good Human Development Index (HDI) score. This score measures things like health, education, and living standards. Limpopo ranks third highest in South Africa for HDI.
Farming and Agriculture in Limpopo
The bushveld areas of Limpopo are great for raising beef cattle. Many large farms focus on cattle ranching. About 80% of South Africa's game hunting industry is found in Limpopo. This means many places offer hunting experiences.
Farmers in areas like Bela-Bela and Modimolle grow crops. These include sunflowers, cotton, maize, and peanuts. Modimolle is also famous for its table grapes. A small but growing wine industry is also found here. Tropical fruits like bananas, litchis, pineapples, mangoes, and pawpaws are grown. Various nuts are also produced in the Tzaneen and Louis Trichardt areas. Tzaneen is a hub for citrus fruits, tea, and coffee farms. It also has a large forestry industry. Many farmers and homes in Limpopo drill their own boreholes for water.
Housing and Homes in Limpopo
Most people in Limpopo live in rural areas. This has led to a new trend in rural development. Residents are building beautiful, large homes on their tribal land. These homes have been featured on TV and social media. About 96.2% of Limpopo residents live in formal housing. This is higher than the national average of 84.0%. This makes Limpopo the province with the most people living in formal housing in South Africa.
Mining Limpopo's Rich Minerals

Limpopo has many valuable minerals. These include platinum, iron ore, chromium, and high-quality coking coal. Diamonds, antimony, phosphate, and copper are also found. Other minerals include gold, emeralds, scheelite, magnetite, vermiculite, silicon, and mica. The province also has black granite, corundum, and feldspar. Mining makes up more than one-fifth of Limpopo's economy.
Limpopo holds the largest platinum deposits in South Africa. The Waterberg Coalfield is also here. It is thought to contain 40% of South Africa's coal reserves.
Tourism and Wildlife in Limpopo
The Limpopo government wants the province to be a top eco-tourism spot. Eco-tourism focuses on visiting natural areas responsibly. This includes tourism, protected areas, and community development. The goal is to help the economy grow in a way that protects nature.
Limpopo is one of South Africa's poorer provinces. However, it is rich in wildlife, which attracts many tourists. Both private companies and the government are investing in tourism. Near Modjadjiskloof, there is a huge Baobab tree. It has been turned into a pub, which is a unique attraction.
Transportation and Communication Networks
Limpopo has good ways to travel and communicate. It has excellent roads, railways, and airports. The N1 route from Johannesburg runs through the whole province. This is Africa's busiest land route for trade. Goods like raw materials and finished products are transported here. The province is directly connected to major ports like Durban, Richards Bay, and Maputo. Polokwane International Airport is located just north of Polokwane. Limpopo province has about 56 airports and airstrips in total.
Education and Learning in Limpopo
The Department of Education in Limpopo works to provide good education and training for everyone. They help with professional development for teachers. They also create policies and procedures for schools.
Higher Education Institutions in Limpopo
As of December 2020, about 12.9% of Limpopo's population had completed some form of education after high school. Here are some of the higher education institutions in Limpopo:
- University of Limpopo (Polokwane, Mankweng)
- University of Venda (Thohoyandou)
- Tshwane University of Technology (Polokwane Campus)
- Capricorn College for TVET (Seshego)
- Capricorn College for TVET (Polokwane)
- Lephalale TVET College (Lephalale)
- Letaba TVET College (Tzaneen)
- Mopani South East TVET College (Phalaborwa)
- Sekhukhune TVET College (Motetema)
- Vhembe TVET College (Venda)
- Waterberg TVET College (Mokopane)
- Giyani Campus Of Nursing College
- Limpopo Province College of Nursing (Giyani Campus)
Sports and Recreation in Limpopo
Limpopo is home to various sports activities and teams.
Football (Soccer) in Limpopo
Polokwane was one of the host cities for the 2010 FIFA World Cup. Matches were played at the Peter Mokaba Stadium. Football clubs in the province include Real Rovers, Silver Stars, Black Leopards, Polokwane City, Baroka, Ria Stars, and Dynamos.
Rugby Union in Limpopo
Limpopo does not have its own provincial rugby team. It is represented in the Currie Cup by the Pretoria-based Blue Bulls. The Blue Bulls also have a Super Rugby team called the Bulls. Limpopo has produced some top rugby players. Two of the most famous are John Smit and Victor Matfield. They are both from Polokwane and played for the national team.
Basketball in Limpopo
The province has a professional basketball team called Limpopo Pride. They play in South Africa's top basketball league, the Basketball National League.
Understanding Limpopo's Diverse Population
Limpopo's population is made up of different groups. These groups are known for their unique cultures, languages, and backgrounds. About 97.3% of the people are Black. Around 2.4% are White, 0.2% are Coloured, and 0.1% are Indian or Asian. Limpopo has the smallest percentage of White South Africans in the country. However, some areas like Hoedspruit and Modimolle have a majority White population. Limpopo also has the highest percentage of Black people among all provinces.
The Northern Sotho people make up the largest group, about 52% of the population. The Tsonga people are about 24.0% of the province. The Venda make up about 16.7%. Most of Limpopo's White population speaks Afrikaans. This is about 95,000 people. English-speaking White people number just over 20,000. The Vhembe district has the fewest White people in Limpopo, about 5,000 in total. The Waterberg district has the most, with over 60,000 White residents. Coloureds and Asians/Indians make up a very small part of the province's total population.
See also
 In Spanish: Provincia de Limpopo para niños
In Spanish: Provincia de Limpopo para niños
- List of cities and towns in Limpopo
- Limpopo River
 | Lonnie Johnson |
 | Granville Woods |
 | Lewis Howard Latimer |
 | James West |