Asia facts for kids
 |
|
| Area | 44,579,000 km2 (17,212,000 sq mi) (1st) |
|---|---|
| Population | 4,560,667,108 (2018; 1st) |
| Population density | 100/km2 (260/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | $41.02 trillion (2025 est; 1st) |
| GDP (PPP) | $94.66 trillion (2025 est; 1st) |
| GDP per capita | $9,180 (2025 est; 4th) |
| Religions |
|
| Demonym | Asian |
| Countries |
|
| Dependencies | |
| Non-UN states | |
| Languages | List of languages |
| Time zones | UTC+02:00 to UTC+12:00 |
| Internet TLD | .asia |
| Largest cities |
|
| UN M49 code | 142 – Asia001 – World |
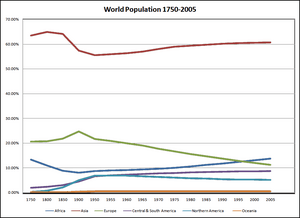
Asia is the largest continent on Earth, both in land area and population. It covers over 44 million square kilometers, which is about 30% of Earth's total land. Asia has been home to most of the human population for a long time. Many of the first civilisations started here. Today, about 4.7 billion people live in Asia, making up roughly 60% of the world's population.
Asia shares a large landmass called Eurasia with Europe. It also shares Afro-Eurasia with Europe and Africa. Asia is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Indian Ocean to the south, and the Arctic Ocean to the north. The boundary between Asia and Europe is not a clear physical line. It is more of a historical and cultural idea.
People usually say Asia is east of the Suez Canal (which separates it from Africa). It is also east of the Turkish straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River. To the south, the Caucasus Mountains, Caspian Sea, and Black Sea separate it from Europe.
The idea of "Asia" came from a European viewpoint, meaning the eastern region. Because of this, Asia is a huge area with many different cultures, not just one. Its border with Europe has changed over time. This division shows cultural differences between East and West.
For much of history, China and India were the world's biggest economies. China was a major economic power until about 1500 CE. The Silk Road was a key trade route across Asia. The Straits of Malacca was an important sea route. In the 20th century, Asia saw strong economic growth and population increases. Asia is also where most major religions began, like Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, Jainism, Judaism, Sikhism, and Taoism.
Asia is very diverse in its different regions. It has many different ethnic groups, cultures, environments, and government systems. Its climate also varies a lot. You can find tropical areas in the south, hot deserts in West Asia, Central Asia, and South Asia. There are also temperate areas in the east and center, and very cold subarctic and polar areas in North Asia.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The name "Asia" might come from an old word, Assuwa, from the Bronze Age. This word was used for a part of northwestern Anatolia (modern-day Turkey). Ancient texts from the Hittites mention Assuwa around 1400 BCE.
The Greek historian Herodotus used "Asia" for Anatolia and the Persian Empire. He said Greeks thought it was named after Prometheus's wife. But people from Lydia said it was named after Asies, a local leader. In Greek stories, "Asia" was also a goddess from Lydia.
The Romans later used the term for their province of Asia in western Anatolia. Pliny was one of the first writers to use "Asia" for the entire continent.
Asia's Borders
The idea of dividing the world into Africa, Asia, and Europe has been around since the 6th century BCE. Greek geographers like Anaximander first used this idea.
Asia and Europe's Border
The border between Asia and Europe has changed throughout history. Early Greek geographers placed it along the Phasis River in Georgia. Later, during the Hellenistic period, the Don River was seen as the border.
In the 18th century, a Swedish mapmaker suggested the Ural Mountains as the border. Over time, the Ural River became accepted as part of the boundary. The border between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea is usually along the Caucasus Mountains.
Asia and Africa's Border
The border between Asia and Africa is the Suez Canal, the Gulf of Suez, the Red Sea, and the Bab-el-Mandeb. This means Egypt is a transcontinental country. Its Sinai Peninsula is in Asia, while the rest of the country is in Africa.
Asia and Oceania's Border
The border between Asia and Oceania is usually in the Indonesian Archipelago. The Wallace Line is an important natural boundary. It separates animals from Asia and those from Australia. Culturally, this region shows a mix of Austronesian and Melanesian people influences.
Asia and North America's Border
The Bering Strait and Bering Sea separate Asia and North America. This is also the border between Russia and the United States. The Diomede Islands are in the Bering Strait. Big Diomede is in Russia, and Little Diomede is in the United States. At their closest, Alaska and Russia are only about 2.5 miles apart.
Asia's Long History
Early Times
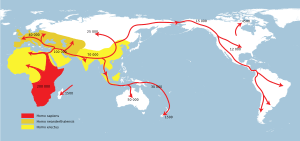
About 1.8 million years ago, early humans called Homo erectus left Africa. They lived in East and Southeast Asia. Modern humans, Homo sapiens, arrived in South Asia about 60,000 years ago. They mixed with other ancient human groups.
Ancestors of East Asians separated from other groups about 46,000 years ago. The first people in the Americas came from ancient East Asians. They moved north into Siberia and then into North America.
Ancient Civilizations

Asia's history includes many different regions. The coastal areas were home to some of the world's first civilizations. These grew around fertile river valleys like Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley, and the Yellow River. These early civilizations shared ideas and technologies. Cities and empires grew in these areas.
The central steppe region was home to horse-riding nomads. They could travel across Asia. Mountains and deserts often separated the city dwellers from the nomads. While cities were more advanced, they sometimes struggled to defend against the powerful nomadic armies.
Medieval Period

In the 7th century, the Islamic Caliphate expanded into West Asia and parts of Central and South Asia. Islam also spread through trade to southern India and Southeast Asia. The Mongol Empire conquered a huge part of Asia in the 13th century. This empire stretched from China to Europe.
The Black Death, a terrible disease, is thought to have started in Central Asia. It then spread along the Silk Road.
Modern Times
European countries became more involved in Asia from the 15th century onwards. Explorers like Vasco da Gama found new sea routes to Asia. The Russian Empire also expanded into Siberia and Central Asia.
Among non-European empires, the Ottoman Empire controlled a large area from the 16th century. In the 17th century, the Manchu people took over China, starting the Qing dynasty. The Islamic Mughal Empire and the Hindu Maratha Empire ruled much of India.

From the 18th to 20th centuries, Western powers gained more influence in Asia. The British Empire became very powerful in South Asia. The completion of the Suez Canal in 1869 made it easier for Britain to reach India. Western powers also began to dominate China. This period is sometimes called the "century of humiliation" for China.
The Japanese colonial empire also grew, controlling parts of East and Southeast Asia. Japan became powerful by adopting industrial knowledge from the West. After the Ottoman Empire broke up in the early 20th century, the Middle East was divided by Britain and France.
Recent History
After World War II ended in 1945, many Asian countries gained independence from colonial rule. The independence of India led to the creation of Pakistan and later Bangladesh. The Cold War in Asia affected many countries. When the Soviet Union ended in 1991, five new Central Asian countries became independent.
Some Arab countries became very rich due to large oil deposits. East Asian nations like Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan became economically strong. China also grew rapidly after making economic changes. India has also seen significant economic growth since the 1990s.
Asia's Geography

Asia is the largest continent. It covers 9% of Earth's surface and has the longest coastline. It is generally the eastern part of Eurasia. Asia is east of the Suez Canal and Ural Mountains. It is south of the Caucasus Mountains, Caspian Sea, and Black Sea. The Pacific Ocean is to its east, the Indian Ocean to its south, and the Arctic Ocean to its north. Asia has 49 countries. Five of them (Georgia, Azerbaijan, Russia, Kazakhstan, and Turkey) are partly in Europe.
The Gobi Desert is in Mongolia, and the Arabian Desert covers much of the Middle East. The Yangtze in China is the longest river in Asia. The Himalayas, between Nepal and China, are the world's tallest mountain range. Southern Asia has tropical rainforests, while northern areas have coniferous and deciduous forests.
Main Regions
Asia is divided into several regions for easier study. The United Nations uses these regions for statistics:
- North Asia (Siberia)
- Central Asia
- West Asia (also called the Middle East)
- South Asia (the Indian subcontinent)
- East Asia (the Far East)
- Southeast Asia (East Indies and Indochina)
Climate
Asia has many different climates. It ranges from very cold Arctic and subarctic areas in Siberia to tropical areas in southern India and Southeast Asia. Some parts are very wet, while the interior is mostly dry. The monsoon season brings a lot of rain to southern and eastern Asia in the summer. Southwestern Asia is hot. Siberia is one of the coldest places in the Northern Hemisphere.
Politics in Asia
Some of the most democratic countries in Asia include Japan, Taiwan, and Israel. These countries have strong systems where people can vote and have a say in their government.
Countries and Territories
Asia is home to many independent countries and some territories. Here is a list of the main countries:
| Symbol | Flag | Name | Population (2018) |
Area (km2) |
Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | 37,171,921 | 652,864 | Kabul | ||
| Armenia | 2,951,745 | 29,743 | Yerevan | ||
| Azerbaijan | 9,949,537 | 86,600 | Baku | ||
| Bahrain | 1,569,446 | 760 | Manama | ||
| Bangladesh | 161,376,708 | 147,570 | Dhaka | ||
| Bhutan | 754,388 | 38,394 | Thimphu | ||
| Brunei | 428,963 | 5,765 | Bandar Seri Begawan | ||
| Cambodia | 16,249,792 | 181,035 | Phnom Penh | ||
| China (PRC) | 1,427,647,786 | 9,596,961 | Beijing | ||
| Cyprus | 1,189,265 | 9,251 | Nicosia | ||
| Egypt | 98,423,598 | 1,001,449 | Cairo | ||
| Georgia | 4,002,942 | 69,700 | Tbilisi | ||
| India | 1,352,642,280 | 3,287,263 | New Delhi | ||
| Indonesia | 267,670,543 | 1,904,569 | Jakarta | ||
| Iran | 81,800,188 | 1,648,195 | Tehran | ||
| Iraq | 38,433,600 | 438,317 | Baghdad | ||
| Israel | 8,381,516 | 20,770 | Jerusalem (limited recognition) | ||
| Japan | 127,202,192 | 377,915 | Tokyo | ||
| Jordan | 9,965,318 | 89,342 | Amman | ||
| Kazakhstan | 18,319,618 | 2,724,900 | Astana | ||
| Kuwait | 4,137,312 | 17,818 | Kuwait City | ||
| Kyrgyzstan | 6,304,030 | 199,951 | Bishkek | ||
| Laos | 7,061,507 | 236,800 | Vientiane | ||
| Lebanon | 6,859,408 | 10,400 | Beirut | ||
| Malaysia | 31,528,033 | 329,847 | Kuala Lumpur | ||
| Maldives | 515,696 | 298 | Malé | ||
| Mongolia | 3,170,216 | 1,564,116 | Ulaanbaatar | ||
| Myanmar | 53,708,320 | 676,578 | Naypyidaw | ||
| Nepal | 28,095,714 | 147,181 | Kathmandu | ||
| North Korea | 25,549,604 | 120,538 | Pyongyang | ||
| Oman | 4,829,473 | 309,500 | Muscat | ||
| Pakistan | 211,103,000 | 881,913 | Islamabad | ||
| Philippines | 106,651,394 | 343,448 | Manila | ||
| Qatar | 2,781,682 | 11,586 | Doha | ||
| Russia | 145,734,038 | 17,098,242 | Moscow | ||
| Saudi Arabia | 33,702,756 | 2,149,690 | Riyadh | ||
| Singapore | 5,757,499 | 697 | Singapore | ||
| South Korea | 51,171,706 | 100,210 | Seoul | ||
| Sri Lanka | 21,228,763 | 65,610 | Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte | ||
| Syria | 16,945,057 | 185,180 | Damascus | ||
| Tajikistan | 9,100,835 | 143,100 | Dushanbe | ||
| Thailand | 69,428,453 | 513,120 | Bangkok | ||
| Timor-Leste | 1,267,974 | 14,874 | Dili | ||
| Turkey | 82,340,088 | 783,562 | Ankara | ||
| Turkmenistan | 5,850,901 | 488,100 | Ashgabat | ||
| United Arab Emirates | 9,630,959 | 83,600 | Abu Dhabi | ||
| Uzbekistan | 32,476,244 | 447,400 | Tashkent | ||
| Vietnam | 95,545,962 | 331,212 | Hanoi | ||
| Yemen | 28,498,683 | 527,968 |
Some areas in Asia are not fully recognized as independent countries. These include:
| Symbol | Flag | Name | Population |
Area (km2) |
Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abkhazia | 242,862 | 8,660 | Sukhumi | ||
| Northern Cyprus | 326,000 | 3,355 | North Nicosia | ||
| Palestine | 6,025 | Jerusalem (limited recognition) | |||
| South Ossetia | 51,547 | 3,900 | Tskhinvali | ||
| Taiwan (ROC) | 36,193 | Taipei |
Asia's Economy
Asia has the largest economy in the world. It is also the fastest growing economic region. As of 2025, China is the largest economy on the continent. Other big economies include India, Japan, South Korea, Turkey, Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, and Taiwan. Many of these are among the top 20 largest economies globally.
For a long time, China and India were the world's biggest economies. Japan was the largest economy in Asia for several decades in the late 20th century. In 2010, China became the world's second-largest economy, passing Japan. By 2025, India is expected to become Asia's second-largest economy.
Asia is rich in natural resources like petroleum, forests, fish, and water. Manufacturing is strong in East and Southeast Asia. Many companies from other parts of the world have operations in Asia. They use the large supply of skilled workers and good infrastructure.
Asia has three main financial centers: Hong Kong, Tokyo, and Singapore. India and the Philippines are becoming major places for Call centers and business services. This is because they have many skilled, English-speaking workers.
Trade between Asian countries and other continents mostly happens by sea. Important routes go from China, through the Strait of Malacca, to the Indian Ocean and beyond. The melting Arctic ice is also opening new shipping routes. Trade within Asia is also growing quickly.
In 2011, Asia had more millionaires than Europe. By the end of 2011, the total wealth of very rich people in Asia was more than in North America. This shows that the world's economic power is shifting towards Asia.
People and Cultures
Population and Development
East Asia has seen a huge improvement in its Human Development Index (HDI). This index measures health, education, and income. China has made great progress in HDI since 1970, mainly due to its income growth. Hundreds of millions of people have moved out of poverty there.
Nepal, a country in South Asia, has also improved a lot. Its people live much longer now than in the 1970s. More children attend primary school. Hong Kong, Singapore, Japan, and South Korea have very high HDI scores.
Languages of Asia
Asia is home to many language families. Most Asian countries have more than one language spoken by their people. For example, Indonesia has over 700 languages. India has over 400, and the Philippines has over 100. China also has many different languages and dialects.
Religions in Asia
Many of the world's major religions started in Asia. These include Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, Chinese folk religions, and Buddhism. Asian stories and beliefs are very diverse. For example, the story of a great flood appears in many ancient myths.
Abrahamic Religions
Judaism, Christianity, and Islam all began in West Asia.
- Judaism is the oldest of these faiths. It is mainly practiced in Israel, the historical homeland of the Jewish people. Small Jewish communities also exist in other Asian countries.
- Christianity is widespread in Asia, with over 286 million followers. In the Philippines and Timor-Leste, Catholicism is the main religion. In Armenia and Georgia, Eastern Orthodoxy is common. There are also Christian communities in other parts of Asia.
- Islam is the second largest religion in Asia, with over 1 billion Muslims. Indonesia has the largest Muslim population in the world. Other countries with many Muslims include Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, Iran, and Turkey. Mecca, Medina, and Jerusalem are the three holiest cities in Islam.
Indian and East Asian Religions

Many Asian religions have deep philosophical ideas. Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism all started in India. In East Asia, Confucianism, Taoism, and Zen Buddhism developed.
- Hinduism has about 1.1 billion followers. It is the largest religion in Asia, mostly found in South Asia. Over 80% of people in India and Nepal are Hindu.
- Buddhism is very popular in Southeast Asia and East Asia. It is the main religion in Cambodia, Thailand, Burma, Japan, Bhutan, Sri Lanka, Laos, and Mongolia.
- Jainism is mainly found in India. Sikhism is found in Northern India and among Indian communities elsewhere in Asia.
- Confucianism and Taoism are mostly practiced in China, South Korea, Taiwan, and among Chinese communities.
Culture and Achievements
The culture of Asia is a rich mix of customs and traditions. These have been practiced by many different groups for centuries. West Asia has cultural roots in ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia. These civilizations gave rise to the Persian, Arab, and Ottoman empires. They also saw the birth of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Despite the continent's large size, trade has helped create a shared culture across Asia.
Nobel Prize Winners

Rabindranath Tagore, a writer from India, won the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1913. He was the first Asian to receive a Nobel Prize. His writings had a big impact worldwide.
Other Asian writers who won the Nobel Prize for literature include Yasunari Kawabata (Japan), Kenzaburō Ōe (Japan), Gao Xingjian (China), Orhan Pamuk (Turkey), and Mo Yan (China).
Mother Teresa of India and Shirin Ebadi of Iran won the Nobel Peace Prize. They were recognized for their work for human rights, especially for women and children. Ebadi was the first Iranian and first Muslim woman to win this prize. Aung San Suu Kyi from Burma also won the Nobel Peace Prize for her peaceful fight for democracy. Chinese activist Liu Xiaobo received the Nobel Peace Prize for his efforts for human rights in China. In 2014, Kailash Satyarthi from India and Malala Yousafzai from Pakistan won the Nobel Peace Prize for their work against child labor and for children's right to education.
C.V. Raman was the first Asian to win a Nobel Prize in Sciences. He won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on light. Japan has won the most Nobel Prizes among Asian nations.
Amartya Sen from India won the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1998. He was recognized for his work on welfare economics and helping the poorest people.
Other Asian Nobel Prize winners include scientists and leaders from various countries. In 2006, Muhammad Yunus from Bangladesh won the Nobel Peace Prize. He created Grameen Bank, which gives small loans to poor people.
Images for kids
-
Rainforest in Borneo
-
Mongolian steppe
-
Taman Negara, Peninsular Malaysia
-
Wadi Rum in Jordan
See also
 In Spanish: Asia para niños
In Spanish: Asia para niños
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |