Neman facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Neman |
|
|---|---|

The Neman near Alytus
|
|
Map highlighting Neman
|
|
| Other name(s) | Nioman (in Belarusian); Nemunas (in Lithuanian); Niemen (in Polish) |
| Country | Belarus, Lithuania, Russia |
| Cities | Stowbtsy, Grodno, Druskininkai, Alytus, Birštonas, Prienai, Kaunas, Jurbarkas, Sovetsk |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source | Southwest of Minsk, Belarus 176 m (577 ft) 53°15′10″N 27°18′21″E / 53.25278°N 27.30583°E |
| River mouth | Curonian Lagoon West of Šilutė, Lithuania 0 m (0 ft) 55°20′12″N 21°14′50″E / 55.33667°N 21.24722°E |
| Length | 937 km (582 mi) |
| Basin features | |
| Basin size | 98,200 km2 (37,900 sq mi) |
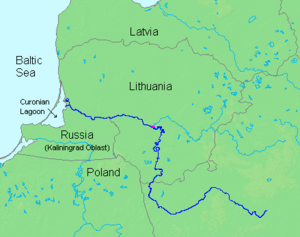
The Neman River is a major waterway in Eastern Europe. It is also known by other names like Niemen, Nioman, Nemunas, or Memel. The river starts in central Belarus and flows through Lithuania. It then forms part of the border between Lithuania and Russia's Kaliningrad Oblast.
The Neman eventually empties into the Curonian Lagoon, which is connected to the Baltic Sea. It flows for about 937 km (582 mi). This makes it one of the longest rivers in the region. It generally flows west towards Grodno, then north to Kaunas, and finally west again to the sea.
The Neman is the largest river in Lithuania and the third-largest in Belarus. Most of its length can be used by boats. It begins from two small streams that join together about 15 kilometers (9 mi) southwest of Uzda. This town is about 55 km (34 mi) southwest of Minsk, the capital city. Only a small part, about 17 kilometres (11 mi), forms a section of the Belarus–Lithuania border. The river also has interesting loops caused by natural shifts in the Earth's crust.
The river's basin was formed around 25,000 to 22,000 years ago. This was at the edge of the last glacial period. The Neman's depth changes from about 1 meter (3 ft 3 in) in its upper parts to 5 meters (16 ft) closer to the sea.
Amazing Facts About the Neman River
Here are some cool facts about the Neman River:
- The Neman is 937 km (582 mi) long. It is the 4th longest river that flows into the Baltic Sea.
- About 436 km (271 mi) of the river is in Belarus. Another 359 km (223 mi) flows through Lithuania.
- A 116 km (72 mi) section of the river forms the border between Lithuania and Russia's Kaliningrad oblast.
- The deepest part of the Neman is 5 m (16 ft). At its widest, it stretches about 500 m (1,600 ft) across.
- The Neman is a slow-moving river. It flows at about 1 to 2 m/s (3.3 to 6.6 ft/s).
- During heavy floods, the amount of water flowing can increase up to 11 times. It can reach over 6,800 m3/s (240,000 cu ft/s).
- Big floods happen in the lower parts of the river about every 12 to 15 years. Sometimes, these floods can even wash away bridges.

- The Neman is a very old river. It was formed during the last glacial period. Its valley is now up to 60 meters (200 ft) deep and 5 km (3 mi) wide.
- The river has about 105 smaller rivers and streams that flow into it. These are called tributaries.
- The largest tributaries are the Neris (Viliya) (510 km (320 mi)), Shchara (325 km (202 mi)), and Šešupė (298 km (185 mi)). Fifteen of these tributaries are longer than 100 km (62 mi).
- The Neman river basin in Lithuania includes more than 20,000 rivers and small streams. It covers 72% of Lithuania's land area.
- The total area of the Neman basin is 98,200 km2 (37,900 sq mi). About 34,610 km2 (13,360 sq mi) of this is in Belarus. The Lithuanian part of the basin is 46,695 km2 (18,029 sq mi).
- The valley of the Neman in the Grodno Region is the lowest point above sea level in Belarus. It is about 80 to 90 m (260 to 300 ft) high.
The River's Journey
Nemunas Loops: A Natural Wonder
The "Nemunas loops" are famous for their unique shape. They are often called by the Lithuanian name for the river, Nemunas. In 1992, the Nemunas Loops Regional Park was created. Its main goal is to protect these amazing loops in the Punia forest.
Near Prienai, the Nemunas makes a 17-kilometer-long (11 mi) loop that looks like a teardrop. It comes very close to completing the loop, within just 1.2 km (3⁄4 mi). The river flows along a double bend between Balbieriškis and Birštonas for 48 km (30 mi). Then it turns north for only 4.5 km (2+3⁄4 mi).
These loops are not typical river bends. They follow natural cracks in the Earth's crust called faults. These faults are also the source of local mineral springs. This area is important for history and culture. Its old castles once protected against attacks from the Teutonic knights.

The Neman Delta
When the Neman reaches its delta, it splits into many river branches and canals. This area is a mix of polders (low-lying lands) and wetlands. It's a great place for eco-tourism, where people can enjoy nature.
The four main branches of the delta are Atmata, Pakalnė, Skirvytė, and Gilija. Skirvytė forms the international border to the south. The river's delta is very important for the Curonian Lagoon. It brings most of the water into the lagoon, keeping it almost fresh. This allows both freshwater and slightly salty water animals to live there. Since the delta is in Lithuania, it is often called the Nemunas Delta. The Nemunas Delta Regional Park was created in 1992 to protect this special area.
Rivers Joining the Neman
Many rivers flow into the Neman. Here are some of the main ones:
- From the Left: Servach, Mowchadz’, Shchara, Zelvyanka, Svislach, Lasosna, Czarna Hańcza, Zembrė, Peršėkė, Šešupė, Tylzha.
- From the Right: Western Berezina, Gauja, Kotra, Haradnichanka, Merkys, Verknė, Strėva, Neris, Nevėžis, Dubysa, Mituva, Jūra, Minija.
Major Cities Along the Neman
Several important cities are located along the Neman River. From west to east, these include Sovetsk/Tilsit, Neman, Kaunas, Alytus, Druskininkai, Grodno, and Masty.
The Neman in Culture and History
Ptolemy, an ancient Greek scholar, may have called the Neman "Chronos." However, some believe Chronos was actually the Pregolya River.
The Neman River gave its name to the Neman Culture. This was an ancient group of people from the Neolithic Age (New Stone Age).
In German, the part of the river flowing through historic Prussia was called Memel since about 1250. This was when the Teutonic Knights built Memelburg castle and the town of Memel at the mouth of the Curonian Lagoon. They named it after the local name for the river. The city of Memel is now known as Klaipėda in Lithuania.
The border between the State of the Teutonic Order and Lithuania was set in 1422 by the Treaty of Lake Melno. This border stayed the same for many centuries. The Treaty of Tilsit was signed on a raft in the river in 1807. This treaty was between Napoleon and Tsar Alexander I.
Napoleon's army crossed the Neman in 1812 at the start of the French invasion of Russia. This event is mentioned in famous books like War and Peace and Pan Tadeusz. In 1919, the Treaty of Versailles made the river the border. It separated the Memel Territory from German East Prussia starting in 1920.
At that time, Germany's Weimar Republic adopted the Deutschlandlied as its national anthem. The first verse of this song, written in 1841, mentions the Neman (Memel) as Germany's eastern border:
| German lyrics | Approximate English translation |
|---|---|
| Von der Maas bis an die Memel, Von der Etsch bis an den Belt |
From the Meuse to the Memel, From the Adige to the Belt |
Lithuanians often call the Nemunas "the father of rivers." Many companies and groups in Lithuania use "Nemunas" in their names. This includes a folklore group, an art magazine, a health resort, and many hotels. The Nemunas is also mentioned a lot in Lithuanian and Polish literature. One of the most famous poems by Maironis begins:
| Lithuanian lyrics | Approximate English translation |
|---|---|
| Kur bėga Šešupė, kur Nemunas teka | Where the Šešupė runs, where the Nemunas flows |
| Tai mūsų tėvynė, graži Lietuva | That's our fatherland, beautiful Lithuania |
Almost every Lithuanian knows these words by heart.
Smaller rivers and streams in Lithuania have names similar to Nemunas. These include Nemunykštis, Nemuniukas, Nemunynas, Nemunėlis, and Nemunaitis.
The origin of the name "Nemunas" is debated. Some say it means "a damp place." Others believe it means "mute, soundless river" from words like nemti or nėmti ("to become silent"). It might also come from the Finnic word niemi meaning "cape."
Artists like Michał Kulesza have painted beautiful pictures of the Neman.
How the Neman River is Used
The Neman River is used for many important things. People use it for fishing, making electricity, and getting water for homes and industries. It's also used for farming, fun activities, tourism, and transporting goods by boat.
Lithuania has plans to dig deeper parts of the river below Kaunas. This would make it easier for boats to use the river more often.
The biggest cities on the river are Grodno in Belarus, Alytus and Kaunas in Lithuania, and Sovetsk in Russia. About 5.4 million people live in the river's basin.
In Belarus, industries near the river include metal processing, chemical factories, paper production, and making building materials. There are also food processing plants. In Lithuania, the city of Kaunas, with about 400,000 people, is the main user of the river. Industries there include making electricity, machinery, chemicals, wood products, paper, furniture, textiles, and food. In Kaliningrad, cities like Sovetsk and Neman have large paper factories near the river.
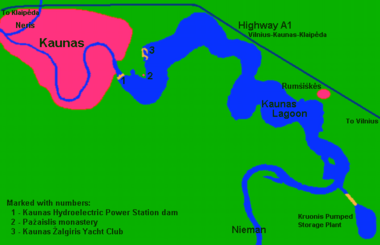
Above Kaunas, a dam was built in 1959. This dam helps power the Kaunas Hydroelectric Power Plant. The dam created the Kaunas Reservoir, which is the largest lake of its kind in Lithuania. It covers 63.5 km2 (24+1⁄2 sq mi). It is 93 km (58 mi) long and its deepest point is 22 m (72 ft). The reservoir is a popular spot for yachting in Lithuania.
The Augustów Canal, built in the 1800s, connects the Neman to the Vistula River.
Animals Living in the Neman
The Neman River is home to many kinds of fish. These include perch, pike, zander, roach, tench, bream, rudd, ruffe, and bleak.
In the smaller streams that flow into the Neman, you can find fish like stone loach, three-spined stickleback, minnows, trout, sculpins, gudgeon, dace, and chub.
Atlantic salmon used to swim upstream in the Neman to lay their eggs. However, dams built on the river, mostly in the 20th century, have made it hard for them. The dam at Kaunas does not have special paths for fish to swim around it. Before the dams, people used to fish for salmon at night using torches and harpoons during the fall spawning season.
Protecting the Neman River
A report by the Swedish EPA (Environmental Protection Administration) says that the Neman River's water quality in Lithuania is from moderately polluted to polluted. Some parts of the river have high levels of organic pollutants, nitrates, and phosphates.
The main environmental problems include water pollution (like too many nutrients and pollutants from old sewage treatment plants), changes in how the river flows, and managing floods. Each country in the river basin has slightly different problems. In Belarus, the main issues are oil products and certain chemicals. In the Kaliningrad section, there are high levels of chemicals from paper factories. In Lithuania, the Kaunas Hydroelectric Power Plant dam affects the natural river environment.
Working together to improve water quality is difficult because the river flows through three different countries. However, there are projects underway to make the water cleaner.
See also
 In Spanish: Río Neman para niños
In Spanish: Río Neman para niños
- List of rivers of Europe
- Normandie-Niemen (a famous French Air Force squadron)
- Memelland
- East Prussia
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |