Proposed 2019 amendment to the Constitution of Malaysia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Constitution (Amendment) Bill 2019 |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Parliament of Malaysia | |
| A Bill intituled an Act to amend the Federal Constitution. | |
| Territorial extent | Malaysia |
| Considered by | Dewan Rakyat |
| Legislative history | |
| Bill citation | D.R 7/2019 |
| Introduced by | Liew Vui Keong |
| First reading | 4 April 2019 |
| Second reading | 9 April 2019 (negatived) |
| Related legislation | |
| Constitution (Amendment) Act 1976 | |
| Summary | |
| To restore the constitutional status of Sabah and Sarawak according to the Malaysia Agreement. | |
| Status: Not passed | |
On 4 April 2019, a new bill (a proposed law) was presented in the Dewan Rakyat, which is part of the Parliament of Malaysia. This bill suggested a change, called an amendment, to the Constitution of Malaysia. The main goal was to change Article 1(2) of the Constitution.
This change aimed to give the states of Sabah and Sarawak in East Malaysia their original special status back. This status was agreed upon when Malaysia was formed in 1963, under the Malaysia Agreement.
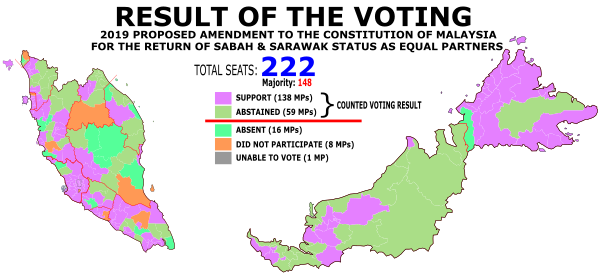
Even after six hours of discussion in Parliament on 9 April, the bill did not pass. Only 138 MPs voted for it. To change the Constitution, a bill needs a two-thirds majority, which means 148 votes in this case. The bill was 10 votes short. The remaining 59 MPs did not vote, and they were all from the political parties that were not in power.
Contents
Why the Change Was Needed
The 1976 Change to the Constitution
In 1976, when Hussein Onn was the Prime Minister, a change was made to Article 1(2) of the Constitution. This change made the states in Peninsular Malaysia and the states of Sabah and Sarawak seem the same.
The idea at the time was to make all parts of Malaysia more uniform. No MPs from Sabah or Sarawak spoke against this change back then.
Promises from the Malaysia Agreement
The Malaysia Agreement of 1963 was a very important document. It was signed when Sabah and Sarawak joined with Malaya to form Malaysia. This agreement included special rules to give Sabah and Sarawak a lot of control over their own affairs, known as autonomy. You can read more about these promises in the 18-point and 20-point agreement.
However, over time, some of these special rights for Sabah and Sarawak were reduced. For example, they received less money from oil revenue than agreed. Their control over their own waters also became smaller.
After winning the 2018 election, the Pakatan Harapan political group promised to fix these issues. They wanted to change Article 1(2) and give Sabah and Sarawak a bigger share of oil money. Other disagreements between East and West Malaysia included freedom of religion, how money from natural resources is shared, and changes in the number of people living there.
Before 2010, only Sabah and Sarawak celebrated Malaysia Day as a public holiday. Later, the government made it a national holiday for everyone. Some groups, like the Borneo Heritage Foundation, have pointed to these problems as reasons why Sabah and Sarawak should have more independence or even consider leaving Malaysia.
| What was agreed for |
What MA63 said (agreed by |
What is happening now under |
|---|---|---|
| Money for Development | Britain promised both states £1.5 million each year for five years. Malaya would give $200 million to North Borneo and $300 million to Sarawak for the first five years. Singapore would also give a $150 million loan, with $100 million being interest-free for five years. | Sabah: RM5 billion per year Sarawak: RM4.3 billion per year |
| Education | Right to have their own education system | Malaysia has a standard education system (Schools are often old, and history books sometimes have wrong information about Sabah and Sarawak history) |
| Immigration | Control who enters their states | Control who enters, but with a permit (Sabah: The Federal government gave special documents (IMM13) to refugees from the civil war in the Philippines. This meant the Sabah state government could not remove these documents, or the refugees would become stateless.) |
| Language | English as the official language | Sabah: Malay became the official language through a debated change in the 1973 State Constitution Sarawak: Both Malay and English are official languages since 2015 (Malay is also used in most courts, except the High Court and Native Court) |
| Laws | Power to agree or disagree with changing laws | Recognized as states under Malaysian laws, but some laws do not apply to them (e.g., National Land Code) (There are often disagreements with the federal government about land rights for native people) |
| Natural Resources | North Borneo: 40% of the state's income Sarawak: Up to RM21 million for the first four years (Both states kept import, excise (tax on goods), and export duties. North Borneo kept 30% from customs and excise as long as it paid for health and medical costs.) |
In 1966, the federal government made the Continental Shelf Act apply to both states, even though they already controlled the waters near their land. In 1974, the Petroleum Development Act was also put in place, giving them only 5% of the money from oil. |
| Religion | No official religion | Sabah: Islam was made the official religion through a debated change in the 1973 State Constitution Sarawak: No official religion (as of 2015). In 2018, Sarawak started allowing people to leave Islam if they wanted to, without being forced to stay. (There are often cases where non-Muslims in Sabah and Sarawak are mistakenly identified as Muslims. Also, Muslims who want to leave Islam are sometimes stopped. There are also issues with religious intolerance and non-Muslim students being converted in schools without their parents' permission.) |
| See also: 1962 Inter-Governmental Committee (IGC) Report and 1963 Malaysia Agreement | ||
Discussions Between Governments
In October 2009, Prime Minister Najib Razak announced that Malaysia Day would become a national holiday. This was done to help unite West and East Malaysia. After winning the 2018 election, Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad promised to make Sabah and Sarawak equal partners with Peninsular Malaysia. This would happen after reviewing the 1963 Malaysia Agreement.
On 5 March 2019, Prime Minister Mahathir met with leaders from Sabah and Sarawak. They discussed the 1963 agreement and found no major disagreements. Some smaller issues, like stamp duty, were sent to a special group for more detailed study.
Even though some issues were not fully solved, the Minister of Law, Liew Vui Keong, announced on 8 March that the cabinet had agreed to change Article 1(2) of the Federal Constitution. This change would be presented to Parliament soon. On 11 March, Parliament began its meeting with this amendment as a main topic.
On 2 April, Minister Liew confirmed that the government would present the amendment bill to Parliament the following week.
Parliament Debates the Bill
First Reading
(Right) The explanation for the bill.
On 4 April, before Minister Liew could present the bill for its first reading, some opposition MPs from Sabah and Sarawak raised concerns. They felt the amendment was being rushed without enough discussion with East Malaysian MPs.
Minister Liew explained that the amendment would change Sabah and Sarawak's status from "states" to "territories." This would happen after a special committee finished reviewing the 1963 agreement. He also said that this special committee was led by Prime Minister Mahathir and included important leaders from Sabah and Sarawak.
However, he did not explain why the bill needed to pass before other changes that would give more power to Sabah and Sarawak were made. After the reading, the bill was opposed. One opposition MP, Sim Kui Hian, said that the amendment still kept Sarawak as one of 13 states, not an equal partner. He also pointed out that there was no change to Article 160, which defines "Federation." It should be based on the 1963 Malaysia Agreement, not the 1957 Malaya Agreement. Other opposition MPs also asked for the bill to be put on hold.
Second Reading

On 8 April, Minister Liew said that the bill's wording would match the 1963 version of Article 1(2) of the Constitution. He also mentioned that the Prime Minister and the Attorney General had no objections. However, Fadillah Yusof, a leader from the Sarawak Parties Coalition, still asked for the bill to be temporarily withdrawn or sent to a special committee for more discussion.
During the second reading on 9 April, Prime Minister Mahathir said the amendment was a "starting point." He felt it was the right time for the Pakatan Harapan government to begin meeting the needs of people in Sabah and Sarawak, as agreed in the 1963 Malaysia Agreement. PKR President Anwar Ibrahim agreed. He said the issue had been widely discussed and that the government was addressing the concerns of Sabah and Sarawak. He also stated that giving the two states their original status back was a big step, especially after the previous government had done nothing for 50 years.
When asked by MP Tan Sri Annuar Musa about the need for a special committee, Sabah Chief Minister Shafie Apdal said it was not necessary. He believed it would only delay other changes that would restore parts of the 1963 agreement. He also disagreed with claims that passing the bill would weaken the sense of national identity among people in Sabah and Sarawak.
Voting Result
At 10:20 pm local time, the Parliament voted. Out of 197 MPs present, 138 voted for the amendment. However, 59 MPs, mostly from the Barisan Nasional group, did not cast a vote. The bill was put to a vote by the Speaker, Mohamad Ariff Md Yusof, after a day of debate. No MPs openly opposed the idea of restoring the states' status.
| No. | Name | Party (coalition) | Constituency | State |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supported (138) | ||||
| 1 | Abdul Latiff Ahmad | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Mersing | |
| 2 | Abdul Rahim Bakri | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kudat | |
| 3 | Abdullah Sani Abdul Hamid | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kapar | |
| 4 | Ahmad Faizal Azumu | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Tambun | |
| 5 | Ahmad Hassan | Sabah Heritage Party | Papar | |
| 6 | Akmal Nasrullah Nasir | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Johor Bahru | |
| 7 | Ali Biju | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Saratok | |
| 8 | Alice Lau Kiong Yieng | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Lanang | |
| 9 | Amiruddin Hamzah | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kubang Pasu | |
| 10 | Anifah Aman | Independent | Kimanis | |
| 11 | Anthony Loke Siew Fook | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Seremban | |
| 12 | Anuar Tahir | National Trust Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Temerloh | |
| 13 | Anwar Ibrahim | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Port Dickson | |
| 14 | Arthur Joseph Kurup | United Sabah People's Party (Gabungan Bersatu Sabah) | Pensiangan | |
| 15 | Awang Husaini Sahari | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Putatan | |
| 16 | Azis Jamman | Sabah Heritage Party | Sepanggar | |
| 17 | Azizah Dun | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Beaufort | |
| 18 | Azman Ismail | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kuala Kedah | |
| 19 | Baru Bian | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Selangau | |
| 20 | Cha Kee Chin | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Rasah | |
| 21 | Chan Foong Hin | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kota Kinabalu | |
| 22 | Chan Ming Kai | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Alor Setar | |
| 23 | Chang Lih Kang | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Tanjong Malim | |
| 24 | Charles Santiago | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Klang | |
| 25 | Chong Chieng Jen | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Stampin | |
| 26 | Chow Kon Yeow | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Tanjong | |
| 27 | Christina Liew Chin Jin | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Tawau | |
| 28 | Darell Leiking | Sabah Heritage Party | Penampang | |
| 29 | Dzulkefly Ahmad | National Trust Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kuala Selangor | |
| 30 | Eddin Syazlee Shith | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kuala Pilah | |
| 31 | Edmund Santhara | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Segamat | |
| 32 | Fahmi Fadzil | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Lembah Pantai | |
| 33 | Farid Rafik | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Tanjung Piai | |
| 34 | Fasiah Fakeh | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Sabak Bernam | |
| 35 | Fong Kui Lun | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Bukit Bintang | |
| 36 | Fuziah Salleh | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kuantan | |
| 37 | Gobind Singh Deo | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Puchong | |
| 38 | Hamzah Zainudin | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Larut | |
| 39 | Hannah Yeoh Tseow Suan | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Segambut | |
| 40 | Hasan Bahrom | National Trust Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Tampin | |
| 41 | Hasanuddin Yunus | National Trust Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Hulu Langat | |
| 42 | Hassan Abdul Karim | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Pasir Gudang | |
| 43 | Hatta Ramli | National Trust Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Lumut | |
| 44 | Ikmal Hisham Abdul Aziz | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Tanah Merah | |
| 45 | Isnaraissah Munirah Majilis | Sabah Heritage Party | Kota Belud | |
| 46 | Jeffrey Kitingan | Homeland Solidarity Party (Gabungan Bersatu Sabah) | Keningau | |
| 47 | Johari Abdul | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Sungai Petani | |
| 48 | Jonathan Yasin | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Ranau | |
| 49 | Jugah Muyang | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Lubok Antu | |
| 50 | June Leow Hsiad Hui | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Hulu Selangor | |
| 51 | Kamarudin Jaffar | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Bandar Tun Razak | |
| 52 | Karuppaiya Muthusamy | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Padang Serai | |
| 53 | Kasthuriraani Patto | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Batu Kawan | |
| 54 | Kelvin Yii Lee Wuen | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Bandar Kuching | |
| 55 | Kesavan Subramaniam | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Sungai Siput | |
| 56 | Khalid Abdul Samad | National Trust Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Shah Alam | |
| 57 | Khoo Poay Tiong | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kota Melaka | |
| 58 | Larry Sng Wei Shien | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Julau | |
| 59 | Lee Boon Chye | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Gopeng | |
| 60 | Liew Vui Keong | Sabah Heritage Party | Batu Sapi | |
| 61 | Lim Guan Eng | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Bagan | |
| 62 | Lim Kit Siang | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Iskandar Puteri | |
| 63 | Lim Lip Eng | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kepong | |
| 64 | M. Kulasegaran | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Ipoh Barat | |
| 65 | Ma'mun Sulaiman | Sabah Heritage Party | Kalabakan | |
| 66 | Mahathir Mohamad | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Langkawi | |
| 67 | Mahfuz Omar | National Trust Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Pokok Sena | |
| 68 | Mansor Othman | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Nibong Tebal | |
| 69 | Maria Chin Abdullah | Independent | Petaling Jaya | |
| 70 | Mas Ermieyati Samsudin | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Masjid Tanah | |
| 71 | Maximus Ongkili | United Sabah Party (Gabungan Bersatu Sabah) | Kota Marudu | |
| 72 | Michael Teo Yu Keng | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Miri | |
| 73 | Mohamad Sabu | National Trust Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kota Raja | |
| 74 | Mohamed Azmin Ali | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Gombak | |
| 75 | Mohamed Hanipa Maidin | National Trust Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Sepang | |
| 76 | Mohammadin Ketapi | Sabah Heritage Party | Silam | |
| 77 | Mordi Bimol | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Mas Gading | |
| 78 | Muhammad Bakhtiar Wan Chik | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Balik Pulau | |
| 79 | Muhyiddin Yassin | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Pagoh | |
| 80 | Mujahid Yusof Rawa | National Trust Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Parit Buntar | |
| 81 | Mukhriz Mahathir | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Jerlun | |
| 82 | Mustapa Mohamed | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Jeli | |
| 83 | Natrah Ismail | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Sekijang | |
| 84 | Nga Kor Ming | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Teluk Intan | |
| 85 | Ngeh Koo Ham | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Beruas | |
| 86 | Nik Nazmi Nik Ahmad | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Setiawangsa | |
| 87 | Noor Azmi Ghazali | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Bagan Serai | |
| 88 | Noorita Sual | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Tenom | |
| 89 | Nor Azrina Surip | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Merbok | |
| 90 | Nurul Izzah Anwar | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Permatang Pauh | |
| 91 | Ong Kian Ming | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Bangi | |
| 92 | Oscar Ling Chai Yew | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Sibu | |
| 93 | Pang Hok Liong | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Labis | |
| 94 | P. Prabakaran | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Batu | |
| 95 | R. Sivarasa | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Sungai Buloh | |
| 96 | Ramkarpal Singh | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Bukit Gelugor | |
| 97 | Rashid Hasnon | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Batu Pahat | |
| 98 | Redzuan Yusof | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Alor Gajah | |
| 99 | Rina Harun | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Titiwangsa | |
| 100 | Ronald Kiandee | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Beluran | |
| 101 | Rosol Wahid | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Hulu Terengganu | |
| 102 | Rozman Isli | Sabah Heritage Party | Labuan | |
| 103 | Rusnah Aluai | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Tangga Batu | |
| 104 | Sanisvara Nethaji | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Jelutong | |
| 105 | Saifuddin Abdullah | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Indera Mahkota | |
| 106 | Saifuddin Nasution Ismail | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kulim-Bandar Baharu | |
| 107 | Salahuddin Ayub | National Trust Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Pulai | |
| 108 | Shabudin Yahaya | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Tasek Gelugor | |
| 109 | Shafie Apdal | Sabah Heritage Party | Semporna | |
| 110 | Shahruddin Salleh | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Sri Gading | |
| 111 | Sim Tze Tzin | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Bayan Baru | |
| 112 | Steven Choong Shiau Yoon | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Tebrau | |
| 113 | Steven Sim Chee Keong | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Bukit Mertajam | |
| 114 | Su Keong Siong | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kampar | |
| 115 | Syed Ibrahim Syed Noh | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Ledang | |
| 116 | Syed Saddiq Syed Abdul Rahman | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Muar | |
| 117 | Tan Kok Wai | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Cheras | |
| 118 | Tan Yee Kew | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Wangsa Maju | |
| 119 | Teh Kok Lim | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Taiping | |
| 120 | Tengku Zulpuri Shah Raja Puji | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Raub | |
| 121 | Teo Nie Ching | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kulai | |
| 122 | Teresa Kok Suh Sim | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Seputeh | |
| 123 | Tony Pua Kiam Wee | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Damansara | |
| 124 | V. Sivakumar | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Batu Gajah | |
| 125 | Wan Azizah Wan Ismail | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Pandan | |
| 126 | Wilfred Madius Tangau | United Pasokmomogun Kadazandusun Murut Organisation | Tuaran | |
| 127 | William Leong Jee Keen | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Selayang | |
| 128 | Willie Mongin | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Puncak Borneo | |
| 129 | Wong Chen | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Subang | |
| 130 | Wong Hon Wai | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Bukit Bendera | |
| 131 | Wong Kah Woh | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Ipoh Timor | |
| 132 | Wong Ling Biu | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Sarikei | |
| 133 | Wong Shu Qi | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kluang | |
| 134 | Wong Tack | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Bentong | |
| 135 | Xavier Jayakumar Arulanandam | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kuala Langat | |
| 136 | Yeo Bee Yin | Democratic Action Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Bakri | |
| 137 | Zakaria Edris | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Libaran | |
| 138 | Zuraida Kamaruddin | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Ampang | |
| Did Not Vote (59) | ||||
| 1 | Aaron Ago Dagang | Sarawak Peoples' Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Kanowit | |
| 2 | Abdul Azeez Abdul Rahim | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Baling | |
| 3 | Abdul Latiff Abdul Rahman | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Kuala Krai | |
| 4 | Adham Baba | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Tenggara | |
| 5 | Ahmad Amzad Hashim | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Kuala Terengganu | |
| 6 | Ahmad Fadhli Shaari | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Pasir Mas | |
| 7 | Ahmad Johnie Zawawi | United Bumiputera Heritage Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Igan | |
| 8 | Ahmad Maslan | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Pontian | |
| 9 | Ahmad Marzuk Shaary | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Pengkalan Chepa | |
| 10 | Ahmad Tarmizi Sulaiman | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Sik | |
| 11 | Alexander Nanta Linggi | United Bumiputera Heritage Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Kapit | |
| 12 | Annuar Musa | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Ketereh | |
| 13 | Anyi Ngau | Progressive Democratic Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Baram | |
| 14 | Awang Hashim | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Pendang | |
| 15 | Bung Moktar Radin | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Kinabatangan | |
| 16 | Che Abdullah Mat Nawi | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Tumpat | |
| 17 | Che Alias Hamid | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Kemaman | |
| 18 | Fadillah Yusof | United Bumiputera Heritage Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Petra Jaya | |
| 19 | Halimah Mohamed Sadique | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Kota Tinggi | |
| 20 | Hanifah Hajar Taib | United Bumiputera Heritage Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Mukah | |
| 21 | Hasbi Habibollah | United Bumiputera Heritage Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Limbang | |
| 22 | Hasbullah Osman | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Gerik | |
| 23 | Henry Sum Agong | United Bumiputera Heritage Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Lawas | |
| 24 | Ismail Muttalib | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Maran | |
| 25 | Ismail Sabri Yaakob | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Bera | |
| 26 | Jalaluddin Alias | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Jelebu | |
| 27 | Ahmad Jazlan Yaakub | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Machang | |
| 28 | Khairuddin Aman Razali | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Kuala Nerus | |
| 29 | Lukanisman Awang Sauni | United Bumiputera Heritage Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Sibuti | |
| 30 | M. Saravanan | Malaysian Indian Congress (Barisan Nasional) | Tapah | |
| 31 | Mahdzir Khalid | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Padang Terap | |
| 32 | Masir Kujat | Sarawak United Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Sri Aman | |
| 33 | Mastura Yazid | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Kuala Kangsar | |
| 34 | Nancy Shukri | United Bumiputera Heritage Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Batang Sadong | |
| 35 | Nik Abduh Nik Abdul Aziz | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Bachok | |
| 36 | Nik Muhammad Zawawi Salleh | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Pasir Puteh | |
| 37 | Nizar Zakaria | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Parit | |
| 38 | Noh Omar | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Tanjong Karang | |
| 39 | Noraini Ahmad | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Parit Sulong | |
| 40 | Ramli Nor | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Cameron Highlands | |
| 41 | Richard Riot Jaem | Sarawak United Peoples' Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Serian | |
| 42 | Robert Lawson Chuat | United Bumiputera Heritage Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Betong | |
| 43 | Rohani Abdul Karim | United Bumiputera Heritage Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Batang Lupar | |
| 44 | Rubiah Wang | United Bumiputera Heritage Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Kota Samarahan | |
| 45 | Sabri Azit | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Jerai | |
| 46 | Salim Sharif | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Jempol | |
| 47 | Mohd Shahar Abdullah | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Paya Besar | |
| 48 | Shaharizukirnain Abdul Kadir | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Setiu | |
| 49 | Shahidan Kassim | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Arau | |
| 50 | Shamsul Anuar Nasarah | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Lenggong | |
| 51 | Takiyuddin Hassan | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Kota Bharu | |
| 52 | Tiong King Sing | Progressive Democratic Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Bintulu | |
| 53 | Tuan Ibrahim | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Kubang Kerian | |
| 54 | Wan Hassan Ramli | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Dungun | |
| 55 | Wan Junaidi | United Bumiputera Heritage Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Santubong | |
| 56 | Wee Ka Siong | Malaysian Chinese Association (Barisan Nasional) | Ayer Hitam | |
| 57 | Wilson Ugak Kumbong | Sarawak People's Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Hulu Rajang | |
| 58 | Yusuf Abdul Wahab | United Bumiputera Heritage Party (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) | Tanjong Manis | |
| 59 | Siti Zailah Yusoff | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Rantau Panjang | |
| Did Not Participate (8) | ||||
| 1 | Ahmad Hamzah | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Jasin | |
| 2 | Hasan Arifin | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Rompin | |
| 3 | Hishammuddin Hussein | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Sembrong | |
| 4 | Reezal Merican Naina Merican | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Kepala Batas | |
| 5 | Tajuddin Abdul Rahman | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Pasir Salak | |
| 6 | Tengku Adnan | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Putrajaya | |
| 7 | Tengku Razaleigh Hamzah | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Gua Musang | |
| 8 | Zahidi Zainul Abidin | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Padang Besar | |
| Absent (16) | ||||
| 1 | Abdul Hadi Awang | Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Gagasan Sejahtera) | Marang | |
| 2 | Abdul Rahman Mohamad | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Lipis | |
| 3 | Syed Abu Hussin Hafiz | Independent | Bukit Gantang | |
| 4 | Ahmad Nazlan Idris | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Jerantut | |
| 5 | Ahmad Zahid Hamidi | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Bagan Datok | |
| 6 | Azalina Othman Said | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Pengerang | |
| 7 | Idris Jusoh | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Besut | |
| 8 | Ismail Mohamed Said | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Kuala Krau | |
| 9 | Khairy Jamaluddin | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Rembau | |
| 10 | Maszlee Malik | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Simpang Renggam | |
| 11 | Muslimin Yahaya | Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Sungai Besar | |
| 12 | Najib Razak | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Pekan | |
| 13 | Nazri Aziz | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Padang Rengas | |
| 14 | Noor Amin Ahmad | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Kangar | |
| 15 | Shamsul Iskandar | People's Justice Party (Pakatan Harapan) | Hang Tuah Jaya | |
| 16 | Yamani Hafez Musa | United Malays National Organisation (Barisan Nasional) | Sipitang | |
| Vacant (1) | ||||
| 1 | Vacant | Sandakan | ||
| Source: Division result from an unspecified article on Malaysiakini via Reddit | ||||
A separate proposal by MP Wan Junaidi Tuanku Jaafar to send the bill to a special committee for review was supported by only 60 MPs and opposed by 136. One MP, Wong Tien Fatt, had passed away a week before the vote, so there was one less MP present. Since the bill did not get the needed two-thirds majority, it could not move forward to a third reading in Parliament.
Despite this, PKR President Anwar Ibrahim said he was happy with the support shown by government MPs. Prime Minister Mahathir also said that even though this bill failed, he believed future attempts to change the constitution would succeed. He also stated that there was no need to ask the Conference of Rulers to review the amendment, as it was not their job. However, the government would not object if MPs wanted to form a special committee to review the 1963 agreement.
Later Changes to the Constitution in 2021
Two years after the bill failed, on 16 September 2021, Prime Minister Ismail Sabri Yaakob promised to look into issues for Sabah and Sarawak. He did this through a special group called the Special Council on Malaysia Agreement 1963.
New changes were presented on 3 November 2021. These changes included four main points:
- Making Sabah and Sarawak "territories" again.
- Defining Malaysia Day as the day Sabah and Sarawak joined.
- Changing the definition of the Federation.
- Defining who are considered native people of Sabah and Sarawak.
On 14 December 2021, the proposed amendment was passed in the Parliament. It received 199 votes in favor, with no votes against. 21 MPs were not present during the six-hour debate. This new law officially started on 11 February 2022.
See also
- List of amendments to the Constitution of Malaysia
- Groups wanting to separate from Malaysia
- When Singapore left Malaysia
 | Leon Lynch |
 | Milton P. Webster |
 | Ferdinand Smith |