Sagittarius (constellation) facts for kids
| Constellation | |
List of stars in Sagittarius
|
|
| Abbreviation | Sgr |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Sagittarii |
| Pronunciation | genitive |
| Symbolism | the Archer |
| Right ascension | 19h |
| Declination | −25° |
| Quadrant | SQ4 |
| Area | 867 sq. deg. (15th) |
| Main stars | 12, 8 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars |
68 |
| Stars with planets | 32 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 7 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 3 |
| Brightest star | ε Sgr (Kaus Australis) (1.79m) |
| Messier objects | 15 |
| Bordering constellations |
|
| Visible at latitudes between +55° and −90°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of August. |
|
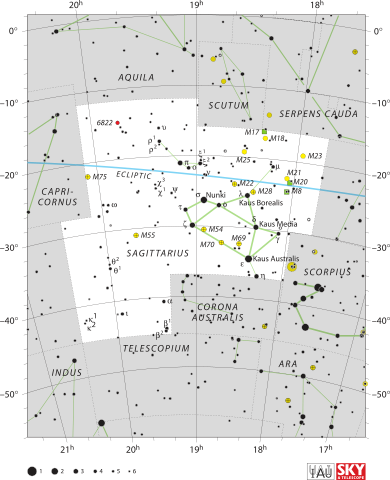
Sagittarius is a well-known group of stars, or constellation, that is part of the zodiac. You can find it in the southern part of the night sky. It was first listed by an ancient astronomer named Ptolemy almost 2,000 years ago. It's still one of the 88 modern constellations we recognize today. Its old symbol is ![]() (♐︎). The name "Sagittarius" comes from Latin and means "archer". People often imagine Sagittarius as a centaur, which is a creature that is half-human and half-horse, holding a bow and arrow. This constellation is located between Scorpius and Ophiuchus to the west, and Capricornus and Microscopium to the east.
(♐︎). The name "Sagittarius" comes from Latin and means "archer". People often imagine Sagittarius as a centaur, which is a creature that is half-human and half-horse, holding a bow and arrow. This constellation is located between Scorpius and Ophiuchus to the west, and Capricornus and Microscopium to the east.
The very center of our galaxy, the Milky Way, is found in the western part of Sagittarius. This area is home to something called Sagittarius A.
Contents
What Does Sagittarius Look Like?
The Teapot Asterism
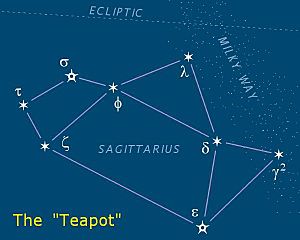
If you live in the northern half of the world, you can easily spot a famous star pattern in Sagittarius. It's called "the Teapot". The stars δ Sgr (Kaus Media), ε Sgr (Kaus Australis), ζ Sgr (Ascella), and φ Sgr make up the body of the teapot. λ Sgr (Kaus Borealis) is the lid's point. γ2 Sgr (Alnasl) forms the tip of the spout. Finally, σ Sgr (Nunki) and τ Sgr create the handle. These same stars were originally seen as the bow and arrow of the archer.
At the bottom of the teapot's handle, you'll find the bright star Zeta Sagittarii (ζ Sgr), also known as Ascella. It shines at magnitude 2.59. Nearby is the slightly fainter star Tau Sagittarii (τ Sgr).
If the sky is very clear, you might see a thick part of the Milky Way galaxy rising above the teapot's spout. It looks just like steam coming from a boiling kettle!
The Archer's Aim
The entire constellation is often drawn as a stick figure of an archer. Fainter stars help outline the horse's body. Sagittarius is famous for pointing its arrow directly at the heart of Scorpius. This "heart" is the reddish star Antares. It's like the two constellations are racing across the sky.
If you follow a straight line from Delta Sagittarii (δ Sgr) to Gamma2 Sagittarii (γ2 Sgr), you will point almost directly to Antares. It's fitting that Gamma2 Sagittarii is called Alnasl, which is an Arabic word for "arrowhead". Delta Sagittarii is named Kaus Media, meaning "center of the bow," where the arrow comes out. Kaus Media is between Lambda Sagittarii (λ Sgr) and Epsilon Sagittarii (ε Sgr). Their names, Kaus Borealis and Kaus Australis, refer to the northern and southern parts of the bow.
When to See Sagittarius
Sagittarius is a bright sight in the summer skies for people in the northern half of the world. However, in places like Scotland and Scandinavia, it's too low to the horizon to be seen clearly. In southern Brazil, South Africa, and central Australia, Sagittarius can be seen directly overhead.
The Sun passes through Sagittarius from mid-November to mid-January. This means you can't see the constellation then. The Sun is in Sagittarius during the December solstice. By March, Sagittarius rises around midnight. In June, it's opposite the Sun, so you can see it all night long. The full moon in June also appears in Sagittarius.
Long ago, during the time of the Roman Empire, the Sun was in Capricorn during the December solstice. But because of something called the precession of the equinoxes, it shifted to Sagittarius. Around the year 2700 AD, the Sun will be in Scorpius during the December solstice.
Interesting Features of Sagittarius
Stars in Sagittarius

Even though α Sgr is called "Alpha" (usually the brightest star), it's not the brightest in Sagittarius. It's named Rukbat, meaning "the archer's knee," and has a brightness of 3.96. The brightest star is actually Epsilon Sagittarii (ε Sgr), or "Kaus Australis" ("southern part of the bow"). It shines at magnitude 1.85, which is about seven times brighter than Alpha Sgr.
Sigma Sagittarii (σ Sgr), also known as "Nunki," is the second brightest star. It has a brightness of 2.08. Nunki is a B2V star about 260 light-years away. Its name, "Nunki," comes from ancient Babylonian times. It might be the oldest star name still used today!
Zeta Sagittarii (ζ Sgr), or "Ascella," looks like one star but is actually a double star. Its two parts have brightnesses of 3.3 and 3.5.
Delta Sagittarii (δ Sgr), or "Kaus Meridionalis," is a K2 type star. It has a brightness of 2.71 and is about 350 light-years from Earth.
Eta Sagittarii (η Sgr) is another double star with parts shining at magnitudes 3.18 and 10. Pi Sagittarii (π Sgr), called "Albaldah," is a triple star system with components of magnitudes 3.7, 3.8, and 6.0.
The name Beta Sagittarii (β Sgr) refers to two separate star systems: β¹ Sagittarii (magnitude 3.96) and β² Sagittarii (magnitude 7.4). These two stars are 378 light-years from Earth. Beta Sagittarii is in the area of the centaur's forelegs and is traditionally called "Arkab," meaning "Achilles tendon".
In 2015, a new bright star, Nova Sagittarii 2015 No. 2, was found near the center of the constellation. It became as bright as magnitude 4.3 before fading away.
Amazing Deep-Sky Objects
The Milky Way galaxy is most crowded near Sagittarius. This is because the center of our galaxy is located here. Because of this, Sagittarius is full of many star clusters and nebulae.
Star Clouds
Sagittarius has two famous star clouds that are great to see with binoculars.
- The Large Sagittarius Star Cloud is the brightest part of the Milky Way that we can see. It's a section of the galaxy's central bulge. It appears around the thick dust of the Great Rift. This is the deepest part of the galaxy we can see with our eyes. It has several star clusters and dark nebulae within it.
- The Small Sagittarius Star Cloud, also known as Messier 24, has a brightness of 2.5. This cloud is very large, stretching 10,000 to 16,000 light-years deep. Inside M24, you can find NGC 6603, a small but very dense star cluster. Also nearby are NGC 6567, a faint planetary nebula, and Barnard 92, a dark cloud of gas and dust called a Bok globule.
Nebulae
Sagittarius is home to several well-known nebulae:
- The Lagoon Nebula (M8) is a glowing cloud of gas located 5,000 light-years from Earth. It measures 140 by 60 light-years across. To our eyes through a telescope, it looks gray. But long-exposure photos show its beautiful pink color, which is common for glowing nebulae. It's quite bright, with a total brightness of 3.0. The Lagoon Nebula was discovered by several astronomers, including John Flamsteed in 1680. The middle part of the Lagoon Nebula is also called the Hourglass Nebula because of its unique shape. This shape is created by material pushed out by the star Herschel 36. The Lagoon Nebula also has three dark nebulae listed in the Barnard Catalogue. This nebula was important in finding Bok globules. These are small, dark clouds where new stars are thought to form.
- The Omega Nebula (M17) is a bright nebula, sometimes called the Horseshoe Nebula or Swan Nebula. It has a total brightness of 6.0 and is 4890 light-years from Earth. It was discovered in 1746 by Philippe Loys de Chésaux. People have described it in many ways, which is why it has so many names. Most often, it looks like a checkmark.
- The Trifid Nebula (M20, NGC 6514) is another glowing nebula in Sagittarius. It's less than two degrees away from the Lagoon Nebula. Discovered by French comet-hunter Charles Messier, it's located between 2,000 and 9,000 light-years from Earth. It is about 50 light-years wide. The outside of the Trifid Nebula is a bluish reflection nebula. The inside is pink with two dark bands that divide it into three parts, or "lobes." Hydrogen gas in the nebula glows because it's lit up by a central triple star. This star formed where the two dark bands meet. M20 is connected to a star cluster that has a brightness of 6.3.
- The Red Spider Nebula (NGC 6537) is a planetary nebula about 4000 light-years from Earth.
- NGC 6559 is a place where new stars are forming. It's about 5000 light-years from Earth in Sagittarius. It shows both red glowing areas and blue reflecting areas.
Other Interesting Objects
In 1999, a huge burst of energy from V4641 Sgr made scientists think they had found the closest black hole to Earth. However, later studies showed it was much farther away. The complex radio source Sagittarius A is also in Sagittarius, near its western edge. Astronomers believe that one part of it, called Sagittarius A*, is a supermassive black hole at the very center of our galaxy. It has a mass equal to 2.6 million Suns! You can't see Sagittarius A* with your eyes, but it's located just above the spout of the Teapot asterism. The Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy is a small galaxy located just outside the Milky Way.
Baade's Window is a special area in Sagittarius. It has very little dust blocking the view. This allows us to see objects closer to the Milky Way's center than we normally could. NGC 6522 (magnitude 8.6) and NGC 6528 (magnitude 9.5) are both globular clusters visible through Baade's Window. They are 20,000 and 24,000 light-years from Earth.
2MASS-GC02, also known as Hurt 2, is a globular cluster about 16,000 light-years from Earth. It was discovered in 2000.
Space Exploration and Sagittarius
The space probe New Horizons is currently traveling out of our Solar System. As of 2016, it is moving in front of Sagittarius as seen from Earth. New Horizons will run out of power long before it reaches any other stars.
The Wow! signal was a very strong radio signal that seemed to come from the direction of Sagittarius. Scientists are still not sure what caused it.
Mythology of Sagittarius
Ancient Babylonians saw Sagittarius as the god Nergal. This god was a centaur-like creature shooting an arrow from a bow. It was often shown with wings, two heads (one panther, one human), and a scorpion's stinger. The Sumerian name Pabilsag means 'Forefather' or 'Chief Ancestor'. This figure looks a lot like how Sagittarius is shown today.
Greek Legends
In Greek mythology, Sagittarius is usually thought to be a centaur: half human, half horse. There's some confusion about which centaur it is. Some say it's Chiron, a wise centaur who taught heroes like Jason. Chiron was said to have changed into a horse to escape his jealous wife. Since there are two centaur constellations in the sky, some people think Chiron is the other one, Centaurus. Another story says that Chiron created both Sagittarius and Centaurus to help guide the Argonauts on their journey to find the Golden Fleece.
Another old story, told by Eratosthenes, says the Archer is not a centaur but a satyr named Crotus. Crotus was the son of Pan. Greeks believed he invented archery. The myth says Crotus loved to hunt on horseback and lived with the Muses. The Muses asked Zeus to place him in the sky, where he is seen showing off his archery skills.
The arrow of Sagittarius points towards the star Antares, which is called the "heart of the scorpion." Sagittarius stands ready to attack if Scorpius ever tries to harm the nearby Hercules, or to get revenge for Scorpius killing Orion.
The Terebellum Asterism
On the western side of Sagittarius, Ptolemy also described a small star pattern called Terebellum. It's made of four stars that are not very bright. One of these stars, Omega Sagittarii, is the closest and fastest-moving member of this group.
Sagittarius in Astrology
In tropical astrology, the Sun is considered to be in the sign of Sagittarius from November 22 to December 21. In sidereal astrology, it's from December 16 to January 14. However, in reality, the Sun appears in the constellation Sagittarius from December 18 to January 18.
|
See also
 In Spanish: Sagitario (constelación) para niños
In Spanish: Sagitario (constelación) para niños
 | Jewel Prestage |
 | Ella Baker |
 | Fannie Lou Hamer |