Sierras Pampeanas facts for kids
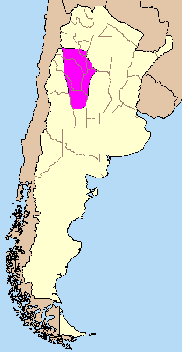
The Sierras Pampeanas (also known as Central Sierras or Pampas Sierras) are a group of mountains in Argentina. They are like a chain of mountains that rise sharply from the flat pampa region in Northwest Argentina.
These mountains run next to the Andes Mountains, but they are about 540 km (336 mi) east of the Andes. They stretch across seven provinces in Argentina: San Luis, San Juan, Córdoba, La Rioja, Catamarca, Santiago del Estero, and Tucumán.
Contents
Exploring the Geography of the Sierras Pampeanas
The highest point in the Sierras Pampeanas is Cerro General Belgrano. This peak is 6,250 meters (20,505 feet) above sea level and is located in La Rioja, within the Sierra de Famatina.
Between these mountain ranges, you can find several areas filled with salt. The Salinas Grandes is a large salt flat that spreads across Cordoba, La Rioja, Catamarca, and Santiago del Estero. A cool fact about these mountains is that their western sides are usually much steeper than their eastern sides. The narrow valleys are often called "broken" or "open," and small gaps between valleys are known as "doors."
The land here looks very different in various places. This is because of things like erosion (when wind and water wear away the land) and other natural forces. You might see cliffs, narrow river channels, and many caves. Some mountains are separated by large open areas called "barreales" (mud-flats) or "pampas" (grassy plains).
Main Mountain Ranges in the Sierras Pampeanas
The Sierras Pampeanas are made up of many smaller mountain ranges. Here are some of them:
- Tucumán and Catamarca: Cumbres Calcahaquíes, Sierra del Aconquija.
- Catamarca: Sierra de Belén, Sierra de Ambato, Sierra de Ancasti, Sierra de Fiambalá, Sierra de Hualfín.
- La Rioja: Sierra de Famatina, Sierra de Sañogasta, Sierra de Velasco, Sierra de los Llanos, Sierra de los Colorados, Sierra de las Minas, Sierra de Chepes, Sierra de Paganzo.
- San Juan: Sierra de Valle Fértil, Sierra de la Huerta, Sierra Guayaguas, Sierra de Pie de Palo.
- Santiago del Estero: Sierra de Ambargasta, Sierra de Guasayán, Sierra de Sumampa.
- San Luis: Sierra de las Quijadas, Sierra de Varela, Sierra del Portezuelo, Sierra del Alto Pencoso, Sierra del Yulto, Sierras de San Luis, Sierra de Guayaguas, Sierra de Cantantal, Sierra del Tala.
- Córdoba: Sierras de Córdoba, which includes Sierras de Comechingones (bordering San Luis).
The name "Pampean Ranges" can be a bit confusing. This is because the Argentine Pampas cover most of the northern and eastern parts of the country. However, other mountains in these flat areas are considered different types of landforms.
Understanding the Climate and Water in the Sierras Pampeanas
This region has a mild and somewhat dry climate. Summers are warm, and winters are cool. The northern eastern slopes get a lot of rain and are covered by rainforests. This is because of the high humidity in this subtropical area.
The parts of the region in Córdoba and San Luis have a climate similar to the Mediterranean. They get strong rainstorms in summer and snow in winter. Here, you can find conifer trees. More rain falls on the eastern slopes because they face the moist winds coming from the Atlantic Ocean.
There isn't a lot of groundwater in most of this area. However, the eastern slopes have more people living there because they have more runoff water available. There are short, fast-flowing rivers and many small streams. These rivers usually have low water levels, but they can have sudden, strong floods during summer rains. People use these rivers to make hydropower (electricity from water).
Discovering the Flora and Fauna of the Sierras Pampeanas
The plants (flora) and animals (fauna) in the Sierras Pampeanas change depending on how high up you go and which way the slopes face. The Dry Chaco, an area with dry forests and grasslands, is found in the lower parts to the east.
The eastern slopes of the mountains catch the winds that carry moisture. This makes them more humid than the flatlands nearby. These slopes, which get more rain, are home to the Southern Andean Yungas humid forests. The western slopes are much drier because they are in the rain shadow of the mountains. The High Monte shrublands grow on these western slopes and in the valleys between the mountains. High up on the Sierra de Aconquija, you can find Central Andean Puna grasslands.
Plant Life in the Sierras Pampeanas
Some of the plants you can find here include:
- White carob (algarrobo blanco)
- Black carob (algarrobo negro)
- Chañar
- Jarilla
- Mistol
- Piquillin
- Tala
- Alpataco
- Tabaquillo
- Espinillo
In the drier western areas, you will see large or medium-sized cactus plants and various shrubs like chilca and tola.
The Southern Andean Yungas are humid forests on the eastern slopes that get more rain. Trees in the Yungas include Andean alder, the conifer Podocarpus parlatorei, and deciduous trees like walnut, jacaranda, Pisonia, Schinus molle, quebracho, and acacia. You can also find beautiful flowering plants such as orchids, jasmine, and bromeliads.
The Sierras de Córdoba in Córdoba and San Luis provinces have many plants on their eastern slopes. These include carob, "coconuts" (a local name for palm trees), garabato blanco (acacia), and willow.
Sadly, much of this area has lost its forests. This is due to desertification (when land becomes like a desert), logging (cutting down trees), mining without replanting, animals eating too much grass, and burning land to create grazing areas.
Animal Life and Reproduction in the Sierras Pampeanas
The area has many different animals, but some species are becoming rare. These include the puma, brocket deer (in the north), wildcat, fox, armadillo, and mule deer. You can also find rodents like the viscacha and guinea pig.
The animals you see depend on the mountains, how high up you are, and the climate. The Pampas Sierras have different types of natural areas, like dry areas, rainforests, and fertile areas with natural forests (especially in Córdoba and San Luis). In the dry parts of La Rioja and Catamarca, you might find vicuña and some alpaca. Long ago, jaguars lived in the rainforests, and spectacled bears were seen in the 1700s.
Birds are common in the higher, mostly dry areas. These include Andean condors and vultures. In the fertile plains of Tucumán Province, you used to find rhea, turkey, parrot, hummingbird, woodpecker, and pigeons.
People who settled in the region brought their own animals, such as horses, donkeys, goats, pigs, cattle, and sheep.
Economy and What People Do in the Sierras Pampeanas
Farming is the main way people make a living in this area. Some places are famous for making wine and olive oil. They also produce cheeses, homemade breads, pies, and sweets. The most famous sweets are made from sweet potato and quince. Most of these products are for people living in the area. Only where there is more rainfall is the farm output sold outside the region.
Tree crops are grown in the foothills of the Sierras de Córdoba. These include olives, peach, pear, apricot, fig trees, quince, and lemon trees. People also grow plantations of cypress, cedar, ponderosa pine, eucalyptus, poplar, oak, and willow for timber and wood products. Shrubs and medicinal herbs grown in the Sierras de Córdoba include peperina, pennyroyal, dandelion, plantain, canchalagua, wild grapes, chamomile, malva, lime, and passion fruit.
In dry areas like central and western La Rioja and Catamarca, people grow grapes for wine using irrigation. They also have large farms of olive trees, jujube (brought by immigrants in the early 1900s), grains, aloe, and jojoba.
Most of these products are sold within the region, often to tourists. Because of its nice climate and amazing scenery, the Sierras Pampeanas is a very popular place for tourists in Argentina.
Mining salt is also an important business here. The salt beds are the largest in the country, covering about 8,400 square kilometers (3,243 square miles).
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Sierras Pampeanas para niños
In Spanish: Sierras Pampeanas para niños